PLACE - aishscbusinessstudies
advertisement

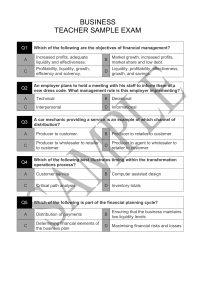
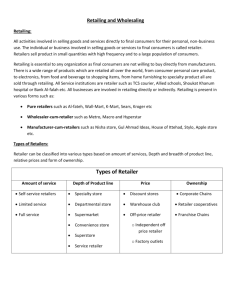
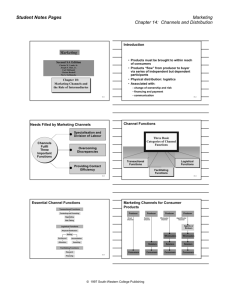
PLACE Place/Distribution • Crucial to getting the product to the customer • Efficient distribution system needed • Most products are distributed by different companies who are selling them • For example the textbook we use is passes though, authors, publishers, printers, wholesalers and retailers before it gets to us, the customers Traditional Distribution Channels • Product to customer no intermediaries • Producer to retailer to customer Retailer is an intermediary who sells to the customer, used for perishable items e.g. fruits or furniture • Producer to wholesaler to retailer most common method, used for distribution or consumer goods, wholesaler buys in bulk, from a producer, then resells in smaller quantities to retailers • Product to agent to wholesaler to retailer to customer agents distribute products but never own them, paid a commission by the producer, used for inexpensive, frequently used products, a business that doesn’t have sale representation will often use an agent Non-Store Retailing • A retailing activity conducted away from the traditional store • Methods • • • • • • Door to door selling Mail-order catalogues Party-plan merchandising Vending machines Telemarketing Internet marketing Internet marketing has become popular as customers can order products that can be delivered directly Examples • 'But wait, if you ring this line in the next 15 minutes, we'll throw in a set of steak knives absolutely free‘ (Telemarketing) • ’Would you like to do a 30 day trial on our skincare product?’ (Telemarketing) (Internet Marketing Channel Choice • How a business chooses the channel of distribution best suited to its product depends largely on the location of the business's market or market coverage • Market coverage refers to the number of outlets a firm chooses for its product • business can decide to cover the market in one of the three ways as follows, the difference being the intensity of coverage • Intensive Distribution occurs when the business wishes to saturate the market with its product • Selective Distribution involves using only a moderate proportion of all possible outlets • Exclusive Distribution only used for one retail outlet for a product in a large geographic area Physical Distribution Issues • Is all those activities concerned with the efficient movement of the products from the producer to the customer • It is therefore the movement of the products themselves through their channels of distribution • Includes the functions of transportation, warehousing and inventory control • Electronic post and parcel delivery channels will be used more extensively to meet the increasing demand Transport • An intricate network of transportation is required to deliver the vast array of products on supermarket shelves • The method of transportation a business uses will largely depend on the type of product and the degree of service the business wishes to provide. The most common methods include: rail, road, sea, and air Warehouse/Inventory • A warehouse is a central meeting point for products • They are used for receiving, storing and dispatching goods • Inventory is the amount of stock they have in storage and in their retail shop • If a business carries too much stock it an cause for the business to have to pay high storage fees • If the business doesn’t have enough stock and is always ‘out of stock’ it causes in having ‘stock-out costs’ or loss of sales • The goal of inventory is to have a good inventory control system which balances their stock to not have too much stock and not too have too little stock Short Answer Questions • Define the term ‘Place’ • Create 3 examples of telemarketing