addendum lecture notes 3 cell reproduction
advertisement

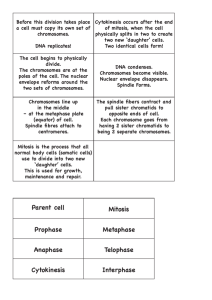
CELL REPRODUCTION BEGINS WITH REPLICATION (DUPLICATION) OF DNA THESE REPLICAS BECOME THE DNA IN THE TWO NEW DAUGHTER CELLS DNA NUCLEOTIDES ARE “PROOF-READ”; WHEN A MISTAKE IS MADE—MUTATION Chromosomes & their Replication Human cell contains 46 chromosomes, arranged in 23 pairs Protein HISTONES packages DNA tightly Newly formed chromosomes attached at a point called centromeres The duplicated but still attached chromosomes are called chromatids CELL MITOSIS PROCESS BY WHICH THE CELL SPLITS INTO TWO STEPS: SHORTLY BEFORE MITOSIS, TWO PAIRS OF CENTRIOLES BEGIN TO MOVE APART FROM EACH OTHER FORMING SPINY STAR-SHAPE (ASTER). SOME SPINES PENETRATE THE NUCLEAR MEMBRANE. TOGETHER WITH THE SPINDLE, THEY FORM THE MITOTIC APPARATUS INTERPHASE Before a dividing cell enters mitosis, it undergoes a period of growth called interphase. Some 90 percent of a cell's time in the normal cellular cycle may be spent in interphase. G1 phase: The period prior to the synthesis of DNA. Cell increases in mass in preparation for cell division. S phase: G2 phase: Period during which DNA is synthesized. Period after DNA synthesis has occurred but prior to the start of prophase. Cell synthesizes proteins and continues to increase in size. In the latter part of interphase, the cell still has nucleoli present. MITOSIS Prophase Spindle is forming Chromosomes become condensed into well-defined chromosomes Kinetochores, which are specialized regions in the centromeres of chromosomes, attach to a type of microtubule called kinetochore fibers. Pro-metaphase Fragmentation of the nuclear membrane Microtubules from aster attach to chromatids at center Tubules pull one chromatid toward cellular pole and partner to opposite pole Metaphase Actin slides the spines in a reverse direction along each other Chromatids pulled to form the equatorial plate Remember this stage by thinking of M as in middle Anaphase Once the paired sister chromatids separate from one another, each is considered a "full" chromosome. They are referred to as daughter chromosomes Two chromatids of each chromosome are pulled apart at the centromere The 46 pairs of chromatids are separated forming two separate sets of 46 daughter chromosomes Remember this stage by remembering A representing AWAY Telophase Two sets of daughter chromosomes are pushed completely apart Mitotic apparatus dissolves New nuclear membrane develops around each set of chromosomes Cell pinches in two caused by formation of a contractile ring (composed of actin and myosin) Remember this stage by remembering T representing TWO Cytokinesis The division of the original cell's cytoplasm Begins prior to the end of mitosis Completes shortly after telophase/mitosis. At the end of cytokinesis, two genetically identical daughter cells are produced