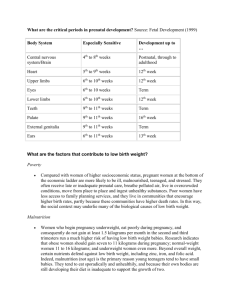
Social and Behavioral Teratogens
advertisement

Biology of Toxins Final Presentation Spring ‘08 Teratogens - substances that may cause structural and/or functional fetal abnormalities (dose dependent) Biology of Toxins Final Presentation Spring ‘08 Teratogens Introduction Social and Behavioral Teratogens Alvena Largo Psychoactive Drugs and Diseases Candice Lovato Environmental Toxins and Fetal Development Jennifer Rice Teratogens: Medications Katie Weeks Introduction • Critical periods during Fetal Development www.cerebralpalsychildren.com/CP1.jpg Introduction • Teratogens vary from recreational and medicinal drugs to behavior and environmental factors. The devastating effects of many teratogens depends on gestational timing and duration of exposure. • The following presentation reveals some of the most common and hazardous teratogens. Social and Behavioral Teratogens • Alvena Largo news.bbc.co.uk Social and Behavioral Teratogens • Stress • Diet • Caffeine news.bbc.co.uk wpclipart.com Stress • Leads to many problems for mother and fetus. • Pre-term births and low birth rate are some dangers for the fetus (March of Dimes). posetech.com/training/images/treadmillrunning.jpg Reducing Stress • Follow good healthy habits such as a good diet and getting plenty of rest (Organization of Teratology). • Excess of stress can also lead to bed rest as well as taking other medications. • Exercise is a Taboo when pregnant, however it can increase blood flow to the baby which is good. • Do not proceed with exercise if pain occurs and sustain from exercising baby area. Foods to stay away from!!! Its important to watch what you eat when pregnant because some food may contain Listeria Bacteria • Seafood- Source of Omega 3fatty acids, but contains Mercury and other bacteria • Deli Meats- may cause food-borne illnesses • Dairy Products- potentially causes illness if not using pasteurized products (Harms, Roger W. M.D., et al) fishfloridakeys.com/stonecrab.htm Other things to prevent sickness while pregnant: • Wash hands, clothes as necessary • Cook all food well!! • Avoid ALL raw foods!! www.nbutexas.com/Images/washing_machine.png Caffeine • Caffeine is a stimulant found in many foods, beverages and plants (naturally). • Increases alertness within 1 hour and lasts up to 6 hours. • Although increased consumption doesn’t cause birth defects, its important to remember that caffeine will cross the placenta and can affect the fetus (Cnattingius S, et al) • Some studies have shown than in combination with alcohol or smoking may cause miscarriages. • Women should also be aware that caffeine can also be passed through breast milk (Organization of Teratology). Psychoactive Drugs • Candice Lovato www.azag.gov Psychoactive Drugs • Among women of reproductive age (15-44) – 90% have used alcohol – 44% have used marijuana – 14% have used cocaine (Rayburn, 2007) Psychoactive Drugs Most women abstain or decrease substance use once their pregnancy is medically diagnosed. However, diagnosis may take as long as one to several months post conception. The first three months of pregnancy are crucial for fetal development. Therefore, substance use during this time may be detrimental to the fetus. www.fshtest.com/fhc-114.jpg Psychoactive Drugs • Alcohol is one of the most common causes of birth defects in the U.S. and therefore one of the most researched. (Gundogan et al., 2007) www.cap.org.uk/.../0/bottles2_300_afoncn.jpg Psychoactive Drugs • Some of the clinical features of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome are: – Growth deficiency (pre and postnatal) – Abnormal facial features (small eyes, sunken nasal bridge, smooth skin surface between nose and upper lip, etc) – Central Nervous System dysfunction (Fryer et al., 2007) – Defects in brain morphology (attributed to abnormal cell growth, differentiation and migration) (Cuzon et al., 2008) Psychoactive Drugs files.turbosquid.com Fetal nicotine exposure increased risk for : spontaneous abortion, limb malformation, defects in lung and urinary tract development. (Berger, 2006) Fetal marijuana exposure increased risk for: defects in Central Nervous System, delayed fetal growth. (Berger, 2006) byrumjason.files.wordpress.com Psychoactive Drugs • Fetal cocaine exposure increased risk for: premature labor, delayed fetal growth, fetal death, symmetric growth restrictions and childhood learning disabilities. www.brake.org.uk/resources/images/Cocaine.jpg Diseases •Candice Lovato www.lurican-pictures.co.uk/.../rubella.PNG Diseases • If a woman has certain diseases while pregnant, it may harm the fetus during the gestational period or during delivery. • It is therefore very important to maintain good health during pregnancy as well as attend regular medical appointments. Diseases • Rubella: An acute, contagious viral infection. In the three trimesters of pregnancy, the embryo is more vulnerable to the virus. It may cause blindness and deafness. It may also cause brain damage. (Berger, 2006 and http://www.healthscout.com) Diseases • Toxoplasmosis: An infection caused by a parasite, remains in the host for life. If a pregnant women is infected, her baby will be born with the disease. It may cause blindness, deafness, cerebral palsy, brain damage and mental retardation. (Berger, 2006 and http://www.medicinenet.com) Diseases • Syphilis: a sexually transmitted bacterial infection. A child may contract the infection during birth or during pregnancy. May cause damage to the brain, bone and may even lead to death. (Berger, 2006 and http://www.pregnancy-info.net) Diseases • Infections of the gums, teeth and urinary tract: non-specific infection Minor infections may lead to premature birth, which may have several adverse effects on the child. (Berger, 2006) Links to Information on Fetal Development • http://channel.nationalgeographic.com/episode/in-the-womb-2228/#tabVideos/01586_05 • http://health.discovery.com/centers/pregnancy/americanbaby/fetaldevelopm ent.html • www.babycenter.com Work Cited • CuzonV., Yeh,P. Yanagawa,Y., Obata,K., and Yeh,H. 2008. Ethanol consumption during Early Pregnancy Alters the Disposition of Tangentially Migrating GABAergic Interneurons in the Fetal Cortex. Journal of Neuroscience 28: 1854-1864. • Fryer,S., McGee,C., Matt,G., Riley,E. and N,S. 2007. Evaluation of Psychopathological Conditions in Children With Heavy Prenatal Alcohol Exposure. Pediatrics 119: 733-741. • Gundogan,F., Elwood,G., Longato,L., Tong,M., Feijoo,A., Carlson,R., Wands,J. and de la Monte,S. 2007. Impaired Placentation in Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. Plancenta 29: 148-157. • Rayburn,W. 2007. Maternal and Fetal Effects from Substance Use. Clinics in Perinatology 34: 559-571. • Berger,K.S. 2006. The Developing Person. NY: Worth Publishers • http://www.medicinenet.com Work Cited • http://www.healthscout.com Environmental Toxins and Fetal Development Jennifer Rice Environmental Toxins Environmental toxins can enter the body of a pregnant woman in several ways: Drinking Water Contamination from Food Packaging Air Pollutants www.allposters.com Methods of Investigation We have increasing knowledge about the effects of environmental toxins, from research using: Animal Models Human longitudinal and epidemiological studies Toxins in our water: TCE & TCA TCE is an industrial chemical In its manufacture, use, and disposal, groundwater can become contaminated TCA is a TCE metabolite Water treatment with chlorine produces TCA Toxins in our water: TCE & TCA Gestational exposure to TCE and TCA has been linked with increased risk of congenial heart defects in humans The EPA recommended safe limit for human exposure is 5ppb (parts per billion) pubs.rsc.org Toxins in our water: TCE & TCA Chicken embryos Chicken embryos were given TCE and TCA levels near the EPA limit for humans Exposure during late cardiac development lead to heart malformation and dysfunction Toxins in our Food Bisphenol A is an estrogenic compound used as monomer to manufacture: Polycarbonate plastic The resin used to line most food and drink cans Polycarbonate and Bisphenol A www.dwell.com www.backcountrygear.com Ester bonds in polycarbonate are easily hydrolyzed by high temperatures or high/low pH Human fetuses, at birth, have 2-3 ng/ml biologically active bisphenol A in their bodies Polycarbonate and Bisphenol A Mice Exposed during pregnancy to levels of bisphenol A lower than average human levels Male offspring have malformation and enlargement of prostate In humans a similar effect is likely to increase rates of prostate cancer later in life Toxins in our Air There is a wide variety of air pollutants distributed throughout the world Sources of toxins: Vehicles burning diesel and gasoline Power plants burning coal Burning of wood for heat and cooking Industrial incineration of waste www.abc.net.au Toxins in our Air Some of the most dangerous air pollutants are Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) They are known carcinogens and mutagens in humans TCDD (Dioxin) is one of the most harmful www.spitzer.caltech.edu Toxins in our Air In Great Brittan Children born near “hot spots” of toxin emissions showed at much higher risk of childhood cancers Most of the 22,458 cases of childhood cancer and leukemia studied could be traced back to atmospheric contaminants. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons In Krakow, Poland and New York City Increased exposure to PAH, even at low levels, leads to reduction in birth weight Low birth weight and early delivery have been associated with developmental and health problems as the child grows. www.uwm.edu Focus on a dangerous toxin: TCDD 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin Known as Dioxin, or TCDD Persists in the environment a long time, and has a long half-life in humans www.chm.bris.ac.uk TCDD in human tissues Most people have ~2-5 ppt (parts per trillion) in their bodies, even without an obvious exposure source Dioxin compounds tend to accumulate in adipose tissue Women have more adipose tissue, so higher concentrations of TCDD than men Fetal exposure to TCDD www.dgfett.de Toxins that are lipid-soluble tend to cross through the placenta by simple diffusion Dioxin is also transferred through breast milk, which can carry lipid-soluble compounds These lead to higher concentrations of TCDD in the fetus and newborn than in the mother TCDD and Thyroid Function TCDD has a similar structure to thyroid hormones Dioxin www.ktf-split.hr Thyroid www.answers.com TCDD competes with normal thyroid hormones, leading to symptoms of hypo-thyroidism Exposure from placental transfer and breast milk may lead to thyroid dysfunction in infants TCDD and Immune Function Fetal exposure to TCDD has been linked to impaired function in: Cytotoxic T-cell response Delayed-type hypersensitivity Graft vs. host response Thymus and bone-marrow function Resistance to bacteria and bacterial toxins www.karlloren.com TCDD and Immune Function Mice were exposed to prenatal doses of TCDD similar to normal human exposure Adult offspring were exposed to Influenza A Immune impairment was dose- and sexdependent Higher exposure lead to greater immune system impairment In male offspring, only the innate response was impaired, while in females, both innate and adaptive responses were affected www.molvray.com TCDD Mechanism of Action The Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor TCDD acts as a ligand for AhR in the cytosol When it binds AhR, an inhibitor protein leaves AhR moves to the nucleus and binds Dioxinresponse elements (DREs) in 5’ region of target genes TCDD Mechanism of Action Exposure to TCDD leads to upregulation of www.cbp.pitt.edu CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 Other drug-metabolizing enzymes Genes that regulate the cell cycle Inflammatory mediators Environmental Toxins We have looked at the effects of: TCE and TCA in drinking water congenital heart defects Bisphenol A prostate malformation and enlargement Air pollutants childhood cancers and leukemia PAH low birth weight and early delivery www.thetripflare.org Environmental Toxins TCDD/Dioxin concentration in fetus through placenta and breast milk thyroid dysfunction Impaired immune response Disruption of gene expression www.measurement.gov.au Multiple Exposures Each of these toxins individually can cause problems in fetal development Typically, humans are exposed to multiple toxins which can interact with each other, compounding the effects Many of the toxins cause primary health effects, as well as secondary, lesser effects Secondary effects can multiply with one another into dangerous problems How to protect yourself and others Personally avoiding dangerous toxins Education of at-risk populations Reducing your personal impact Burning fewer fossil fuels Encouraging companies to implement practices that reduce our exposure to toxins in our water, food supply, and air Resources Choi, H., et al. International Studies of Prenatal Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Fetal Growth. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2006. 114,11: 1744-1750. De Rosa, C.T., et al. A Regional Approach to Assess the Impact of Living in a chemical World. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2006. 1076: 829-838. Drake, V.J., et al. Cardiogenic Effects of Trichloroethylene and Trichloroacetic Acid Following Exposure during Heart Specification of Avian Development. Toxicological Sciences, 2006. 94,1: 153-162. Giacomini, S.M., et al. Dioxin Effects on neonatal and infant thyroid function: routes of perinatal exposure, mechanisms of action and evidence from epidemiology studies. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 2006. 79: 396-404. Knox, E.G., et al. Childhood cancers and atmospheric carcinogens. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 2005. 59: 101-105. Timms, B.G., et al. Estrogenic chemicals in plastic and oral contraceptives disrupt development of the fetal mouse prostate and urethra. PNAS, May 10, 2005. 102,19: 7014-7019. Williamson, M.A., et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Expression and Activity in Cerebellar Granule Neuroblasts: Implications for Development and Dioxin Neurotoxicity. Toxicological Sciences, 2005. 83,2: 340-348. Vorderstrasse, B.A., et al. A dose-response study of the effects of prenatal and lactational exposure to TCDD on the immune response to influenza virus. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, 2006. 69: 445-463. Teratogens: Medications Katie Weeks Introduction: In addition to recreational drugs, alcohol, the environment, and diseases, prescribed and over the counter medications can disrupt the development of the fetus. Introduction: A study showed that 45% of women take at least one prescription drug and many more take over the counter drugs. A British study also suggested that only 10% of women take medications during early pregnancy. Introduction: Approximately 1 to 3% of the general population has major congenital defects at birth. Of these, only 2 to 3% are thought to be due to drug treatment. Currently, few drugs are proven teratogens, but they are important to study, for they are preventable. Drug Metabolism During Pregnancy: Due to physiological changes during pregnancy, it is important to give extra precaution to the drugs used and the doses taken. The metabolism and elimination of drugs varies greatly during pregnancy. “Clearance rates of many drugs increase during late pregnancy due to increases in both hepatic and renal elimination processes (e.g., digoxin, phenytoin), while in some cases clearance rates decrease (e.g., theophylline).” Sensitive Periods for Teratogens: The effect of a teratogen depends on the time of development in which the fetus is exposed to that teratogen. Pre-implantation exposure: – “All or none” Period= Insults to the embryo may result in death. – However, the embryo still contains totipotent cells which may allow for repair from damage. – Teratogens during this time will most likely not result in congenital malformations. Sensitive Periods for Teratogens: Embryonic Period of Development: – 18 to 54-60 days after conception. – Organogenesis occurs during this time. – Maximum sensitivity to teratogenic effects. • Tissues are differentiating rapidly and they will no longer be able to repair damaged cells. – Teratogenic exposure during this time has the greatest chance of causing a structural defect. – The organ that is effected depends on the specific organ system that is developing during the specific time of exposure to the teratogen. Sensitive Periods for Teratogens: Fetal Stage of Development: – The end of the embryonic stage until birth. – Growth and maturation of already formed organs occurs. – Teratogenic exposure during this time will effect the growth of the fetus: • The size of an organ/fetus • The function of an organ • Termed “Fetal toxicity” Sensitive Periods for Teratogens: If a teratogen is going to effect the closing of the neural tube, for example, it must be consumed in the first 3.5 to 4.5 weeks of pregnancy. There are some organs that are sensitive to teratogens for the entirety of the pregnancy, including the central nervous system. Links to learn about Fetal Development Month by Month: http://channel.nationalgeographic.com/episode/in-the-womb-2228/#tabVideos/01586_05 http://health.discovery.com/centers/pregnancy/americanbaby/fetaldevelopment.html www.babycenter.com Common Concerns… Tylenol It is shown that taking the recommended doses of acetaminophen (Tylenol) during pregnancy cannot cause a miscarriage. A thorough study showed that acetaminophen cannot effect the developing brain of the baby (Studied IQ to age 4) Taking too much acetaminophen can cause kidney and liver damage and anemia in the mother, and can have similar effects in the baby. – Safe dose is less that 4000mg/day of acetaminophen. Only a small amount of acetaminophen gets into the breast milk and is considered safe to take while breast feeding as well. Ibuprofen… Ibuprofen used in early pregnancy has been shown by some studies to increase the risk of miscarriage, but other studies contradict this. There are concerns that drugs such as ibuprofen may cause problems with the implantation of the embryo. There is no definite risk, but women who wish to become pregnant, may want to stay away from ibuprofen. Not Shown to cause birth defects if used during the first two trimesters. The Concern: – Ibuprofen use during the third trimester is suggested to cause the ductus arteriosus (a part of the fetal heart) to close prematurely. • May cause high blood pressure in the fetal lungs. • Use late in pregnancy may inhibit labor or reduce the amount of amniotic fluid Tetracycline… Antibiotic used to treat acne and some respiratory conditions. No birth defects shown in children who were exposed during the first trimester. If taken after the fourth month, there is a risk of causing discoloration of the baby’s teeth. Suggested to affect the calcification of the bones and teeth and the growth of some bones. Echinacea… Only one study done suggests there is not an increased risk of birth defects or miscarriage with echinacea use. Taking an excessive amount of this alcohol containing product may cause birth defects. Chemotherapy: Risk for birth defects if chemotherapy is undergone during the first trimester of pregnancy. May increase the risk of miscarriage. Chemotherapy during the second and third trimesters pose a less severe risk. – Most of the organs (except the brain and reproductive system) are fully developed by this time. Antidepressants: Prozac. – No sign of it causing major birth defects. – There is suggestion that minor birth defects (not medically significant) may occur if taken during the first trimester of pregnancy. Zoloft – Not shown to increase the chance of birth defects more than 3 to 5 % more than the general public. – Much more research needed. Paxil – One study by the manufacturers suggested that use during the first trimester may increase the risk of having a baby with a heart defect. Depo Provera (Birth Control Shot): Suggested that the use of the shot may cause some malformations in the genitalia of the baby. One study suggested that use during the first trimester may lead to an increased risk of polysyndactyly and chromosomal abnormalities. Possibly causes lower birth weight. More research needed. Vaccines: Varicella (Chicken Pox) – No major malformations suggested – Wait one month after vaccine to become pregnant. Influenza Vaccine – Considered safe for use during pregnancy. MMR Vaccine – No increased risk of birth defects suggested – Wait 28 days after vaccine to become pregnant. Proven Human Teratogens: Proven to cause major birth defects… Alcohol Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) (captopril, enalapril, lisinopril) Carbamazepine Cocaine Coumarin anticoagulants Diethylstilbestrol Folic acid antagonists: Aminopterin and methotrexate Hydantoins (phenytoin and trimethadione) Isotretinoin (13-cis-retinoic acid) Lithium Misoprostol Tetracyclines Thalidomide Valproate For details on each of these drugs, go to http://www.nvpvolumes.org/p2_4.htm Possible Teratogenic Drugs: D-penicillamine– Methimazole– High doses are associated with connective tissue disorders. Thought to be associated with scalp defects. Diazepam– During first trimester exposure, there seems to be a slight increase in the incidence of cleft palate and lip. References: http://otispregnancy.org/otis_fact_sheets.asp http://www.nvp-volumes.org/p2_4.htm http://www.chw.org/display/PPF/DocID/22924/ router.asp http://msds.chem.ox.ac.uk/teratogens.html