Diffusion and Osmosis
advertisement

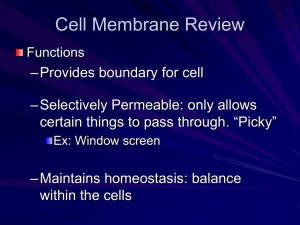
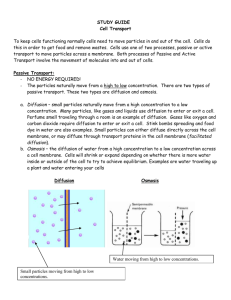
INSANE IN THE MEMBRANE! INSANE IN THE BRAIN… CELL MEMBRANES *Surrounds cell *Plants and animals have them *Bouncer of the cell – decides what goes in or out *Looks smooth….actually made of gaps that particles can move through!! MORE ON MEMBRANES *PERMEABILITY – ability of particles to move through a membrane ***Let’s draw some lines!! *Non-permeable – nothing through – tough bouncer *Semi-permeable – certain things get through (in and out) – bouncer takes bribes… *Permeable – everything through (in and out) – bouncer is on break LOOK AT YOUR LINES Which is non-permeable? How do you know? Which is semi-permeable? How do you know? Which is permeable? How do you know? ----So what are cell membranes??----- CELL MEMBRANES *Are SEMI-PERMEABLE – only certain things getting through *How do they get through??? QUESTION…. Which is easier – going uphill or downhill? QUESTION… Which is harder – walking through a crowded or empty hallway? QUESTION… Which do you choose – the automatic or the one requiring effort? TRANSPORT! *Particles moving ALL THE TIME!! -Bumping, hitting, bouncing, CONSTANT *TRANSPORT required for movement through cell membranes -2 types – Active and Passive *Active Transport – requires energy -Crowded hall, push door, uphill *Passive Transport – does not require energy! -Empty hall, automatic door, down hill LET’S REVIEW THIS… *Cell membranes are semipermeable *Particles move in and out – TRANSPORT *Active Transport – requires ENERGY! *Passive Transport – lazy version – NO ENERGY! SO IN OR OUT? WHERE DO THE PARTICLES GO?? *Particles are CONSTANTLY moving *Want EQUILIBRIUM = even numbers on both sides; a state of rest or balance -Once reached, particles still partying! *Smell this… *DIFFUSION – movement of particles from areas of high concentration to low concentration *Concert ends *Hallway when bell rings *Smell of cookies baking! *Let’s try it!! EXIT TICKET Look at the demonstration. On a sheet of paper, describe what is happening. 1.22.13 REVIEW 1. What is the difference between active and passive transport? 2. Transport describes particle movement. What are the particles (proteins, lipids, water molecules) moving through? LETS SEE HOW OSMOSIS WORKS!!! http://highered.mcgraw hill.com/sites/0072495 855/student_view0/cha pter2/animation__how_ osmosis_works.html LET’S TAKE THIS ONE MORE STEP… *Diffusion moves particles high to low concentration…ALL PARTICLES *OSMOSIS – diffusion of WATER through cell membranes (semi-permeable) -So important – has it’s own name!! -FOCUS is WATER!! *Wants equilibrium, moves to achieve it! HOW DO WE KNOW THE DIRECTION OF MOVEMENT? *Osmosis and Diffusion move from HIGH concentrations to LOW concentrations *Concentration is the proportion (ratio) of a molecule or particle in a certain solution – high or low *Let’s make a visual of PURE water, a solution with LOW CONCENTRATION, and a solution with HIGH CONCENTRATION of water. REWIND… *How do active and passive transport fit into all of this? *Transport is the movement of particles – including water!! *Active and passive transport refer to SMALL PARTICLES (sugar, water) -Passive requires no energy and moves from a HIGH concentration to a LOW concentration -Active requires energy and moves from a LOW concentration to a HIGH concentration *So which type of transport is OSMOSIS???? LET’S REVIEW… -Membranes are SEMI-PERMEABLE – stuff goes in and out...if allowed -This TRANSPORT is either passive (no energy) or active (requires energy) for SMALL particles *Passive – HIGH to LOW *Active – LOW to HIGH -Particles want EQUILIBRIUM, and find it through DIFFUSION *HIGH concentration to LOW concentration -OSMOSIS is diffusion of water through cell membranes *HIGH concentration to LOW concentration ONE MORE ITEM… *Active and Passive Transport refer to SMALL PARTICLES *Large particles (proteins) move in and out in a different way *Endocytosis(entrance): process by which a cell membrane surrounds a large particle, encloses it in a vesicle, and brings it into the cell *Exocytosis(exit): process by which a cell releases a large particle by enclosing it in a vesicle, moving it to the surface, then fusing with the membrane *****Both refer to movement of LARGE particles and are forms of active transport!!******* YOUR JOB *Illustrate endocytosis and exocytosis! -Do this in your notes *Use textbook pages 80 and 81 -Copy diagrams provided -Add your own style if you like!! ROUND 1 1. What is the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration? 2. Which type of transport requires energy? 3. What is the diffusion of water through cell membranes? 4. Define passive transport. 5. Define equilibrium. 6. What does it mean to be semi-permeable? ROUND 2 1. Which type of transport is osmosis? 2. Give a real world example of diffusion. 3. How are osmosis and diffusion connected? 4. What is the difference between active and passive transport (energy and concentration)? 5. What do all particles crave and work to achieve? 6. There are 36 water molecules and 48 sugar molecules in a solution. Write the ratio of sugar to water in simplest form. EXIT TICKET Look at the gummy bear in the water. In your ENB, write your prediction about what you think will happen with the gummy bear.