Methods of Transport Across Membranes
advertisement
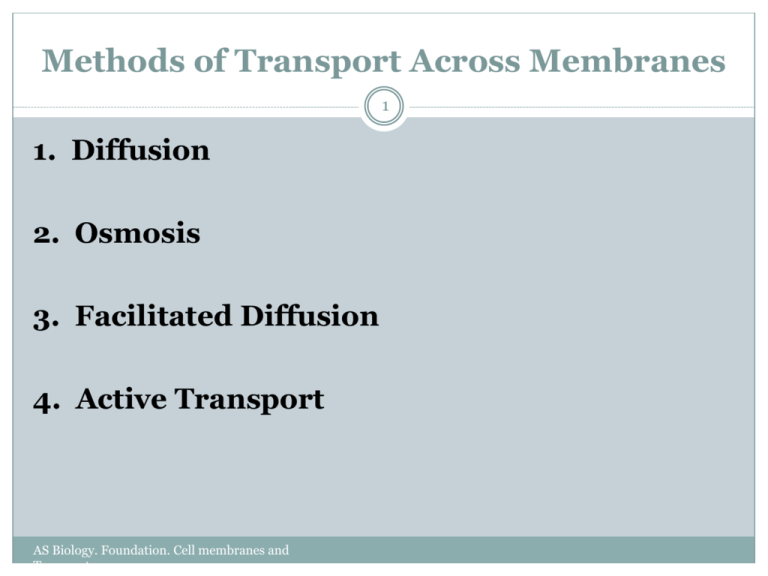
Methods of Transport Across Membranes 1 1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis 3. Facilitated Diffusion 4. Active Transport AS Biology. Foundation. Cell membranes and Transport Solution Review 2 Solutions are made of solute and a solvent Solvent - the liquid into which the solute is poured and dissolved. We will use water as our solvent today. Solute - substance that is dissolved or put into the solvent. Salt and sucrose are solutes. AS Biology. Foundation. Cell membranes and Transport Diffusion-movement of molecules down a concentration gradient 1.Passive transport = no energy used 3 2. Molecules move from high concentration to low concentration http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VY0 mZUDvbH4 AS Biology. Foundation. Cell membranes and Transport Osmosis- movement of water down a concentration gradient 1.Passive transport =no energy used 4 2. Water moves from high concentration to low concentration due to solute concentration http://leukophobia.files.wordpress.com /2008/01/gummi-bear.jpg http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w3_ 8FSrqc-I AS Biology. Foundation. Cell membranes and Transport 5 Hypotonic Solution - solution has a lower concentration of solute outside of cell than inside cell. Hypertonic Solution - solution has a higher concentration of solute outside the cell than inside cell. Isotonic Solution - both solutions have same concentrations of solute. *Predict what will happen to an animal and plant cell when put into each solution. AS Biology. Foundation. Cell membranes and Transport Examples of Osmosis isotonic hypotonic http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/beakers_solutions_ABC.p ng hypertonic Plant and Animal Cells put into various solutions AS Biology. Foundation. Cell membranes and Transport 7 Facilitated Diffusion No use of energy It requires protein molecules to transport molecules across the membrane Proteins are specific to the molecules they transport The molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. -SUGAR and charged molecules pass across the cell membrane by this method of transport http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__ how_facilitated_diffusion_works.html Carrier Proteins Carry Molecules Across the Membrane Good Example - transport of Glucose into the cell Affects on the Rate of Diffusion Temperature Medium in which diffusion takes place Size of solute concentration http://www.austincc.edu/biocr/1406/labm/ex5/images/Diffusion_animated.gif “Yellow food coloring diffusing through water. The glass on the left contains hot water, while the glass on the right contains cold water. The food coloring was added to the cold water slightly before the coloring was added to the hot water, yet after a few seconds it has diffused more thoroughly through the hot water. The frames are roughly 1 second apart (so the animation is roughly 2x real-time).” Active Transport 11 Active transport -requires energy – ATP is used directly or indirectly to fuel active transport -moves substances from low to high concentration -requires the use of carrier proteins Active Transport 12 1. Protein pump -an active transport mechanism -ATP energy is used to change the conformation of the carrier protein - large ions (Na+ or K+) are carried across the membrane that are traveling from low to high concentration http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/an imation__how_the_sodium_potassium_pump_works.h tml 13 Bulk Transport- Active 14 2. Endocytosis occurs when the plasma membrane envelops food particles and liquids. Phagocytosis (particles) Pinocytosis (liquids) 3. Exocytosis occurs when material is discharged from the cell. -vesicles in the cytoplasm fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents to the exterior of the cell 15 Endocytosis (white blood cell takes in bacteria to destroy it https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0TvTyj5FAaQ Exocytosis- let big bulk 16 items out of the cell http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/sit es/dl/free/0072437316/120068/bio02.swf::Endocytosis %20and%20Exocytosis