Water - School District of La Crosse
advertisement

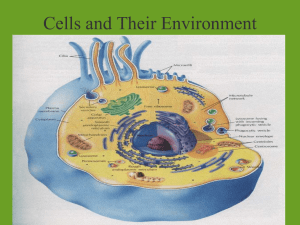
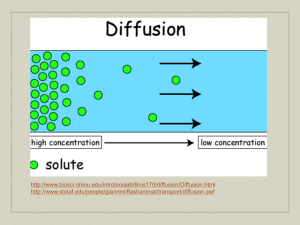
Water Water Facts ● There is the same amount of water on Earth as there was when the Earth was formed. The water from your faucet could contain molecules that dinosaurs drank. ● Nearly 97% of the world’s water is salty or otherwise undrinkable. Another 2% is locked in ice caps and glaciers. That leaves just 1% for all of humanity’s needs — all its agricultural, residential, manufacturing, community, and personal needs.http://water.epa.gov/learn/kids/drinkingwater/waterfactsoflife.cfm ● Water regulates the Earth’s temperature. It also regulates the temperature of the human body, carries nutrients and oxygen to cells, cushions joints, protects organs and tissues, and removes wastes. ● 75% of the human brain is water and 75% of a living tree is water. ● A person can live about a month without food, but only about a week without water. ● Water expands by 9% when it freezes. Frozen water (ice) is lighter than water, which is why http://water.epa.gov/learn/kids/drinkingwater/waterfactsoflife.cfm Water • Water is a compound • Formula – H2O (2 Hydrogen and 1 Oxygen) Why is water unique? • Hydrogen Bonds-Polarity, High Specific heat, cohesion, adhesion Polarity • Polarity allows water to be the perfect solvent – Water can dissolve many things – No other liquid can come close to being able to dissolve as many thing as water can – Because of this, water is nearly always carrying something else along with it Hydrogen bonds • High specific heat- resists changes in temperature • Cohesion- water sticks to itself causing surface tension • Adhesion- water sticks to other things, meniscus, capillary action • Capillarity- water travels upward through small tubes due to adhesion and cohesion Other Special Qualities • Water is the only naturally occurring compound on Earth that can be found in all three physical states • When water freezes it floats – Extremely unique property – Contracts as it cools until it hits 4° C when it expands again Why does Water Expand into Ice? Diffusion • Diffusion-The movement of particles from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration • Examples – Perfume bottle – Cookies in the oven – Kool-Aid What diffusion looks like •http://highered.mcgraw- hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/c hapter2/http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/c hapter2/animation__how_diffusion_works.ht ml Solutions • Mixture- a blend of substances that is not equal throughout (heterogeneous) • Solvent + Solute = Solution • Solvent- Liquid capable of dissolving other substances • Solute- substance being dissolved • Solution- a mixture of substances that is equal throughout (homogeneous) Mixtures Solutions + Solvent = Solute Solution Osmosis • Osmosis-Diffusion of water molecules, usually • • • involving a semi-permeable membrane Concentration Gradient- difference in concentration from one side of membrane to the other Equilibrium-the same everywhere Remember water always moves from areas of high water concentration to areas of low water concentration Osmosis http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view 0/chapter2/animation__how_osmosis_w The tonics of life • Isotonic-Concentration of solutes is the same in solution and cell. • Hypertonic-Concentration of solutes is higher in the solution. • Hypotonic-Concentration of solutes is lower in the solution.