Cells and Their Environment Chapter 4 p 74-84
advertisement
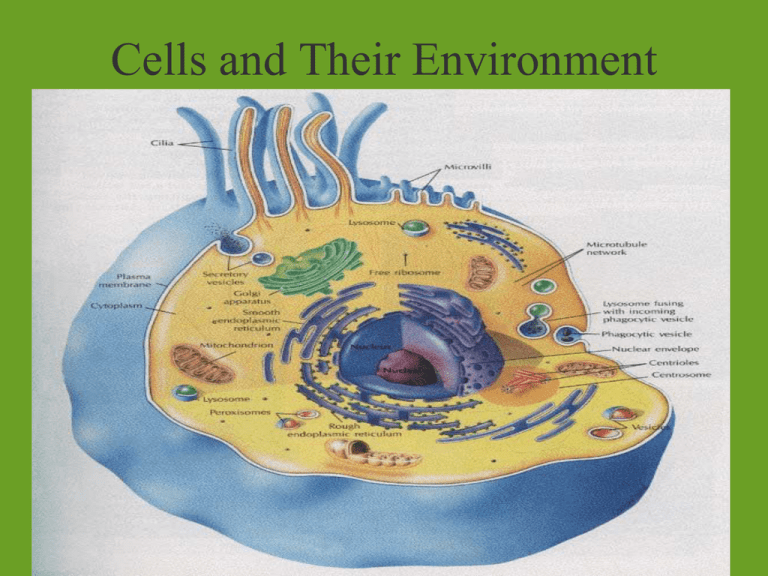
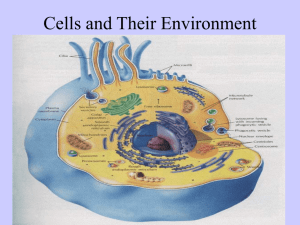
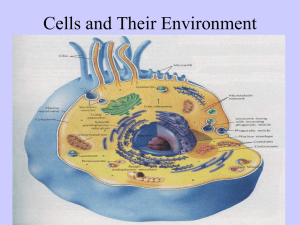
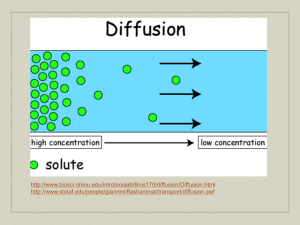
Cells and Their Environment Chapter 4 p 74-84 Homeostasis • A biological balance • Cells, tissues, organs, and organisms must maintain a balance. • Cells do so by controlling and regulating what gets into and out of the cell. Membrane Structure & Function Transport • Passive • Active • Transport that does not require chemical energy to occur • ie: diffusion and osmosis • The movement of any substance across a cell membrane with the use of chemical energy – ie: Na+/K+ pump DIFFUSION • Process by which molecules spread from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration • Concentration gradient: a difference in the concentration of a substance ***Molecules are in constant motion Osmosis • Diffusion of water through a membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_vie w0/chapter2/animation__how_osmosis _works.html HYPOTONIC • Concentration of solute molecules in the environment outside of the cell is lower than that in the cell. • Water moves in Red blood cell Hypertonic • Concentration of solute molecules outside the cell is greater than that in the cell • Water moves out Isotonic Concentration of solute molecules outside cell and inside are equal. **equilibrium Think about it… What happened if you eat salty foods? Why do you gargle warm salt water if you have a sore throat? Why do athletes need to have electrolytes in their drinks? Grass wilts if you add too much fertilizer…WHY? http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter14/animation__the_nerve_impulse.html Requires Energy: ex.: thyroid gland concentrates Iodine glucose is completely absorbed by digestive tract http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/a nimation__phagocytosis.html Exocytosis • Ex. LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol) http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olc/dl/120068/bio02.swf