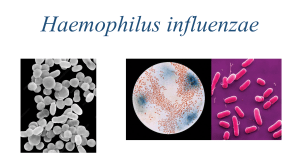
Streptococcus sp.
advertisement

Scientific classification Domain:Bacteria Kingdom:Eubacteria Phylum:Proteobacteria Class:Gammaproteobacteria Order:Pasteurellales Family:Pasteurellaceae Genus:Haemophilus Species:H. influenzae Medical important species Haemophilus influenzae Haemophilus aegyptius Haemophilus ducreyi Normal habitat H.influenzae (mostly non-capsulated strains), H. parainfluenzae and H.aegyptius is normal flora of the upper respiratory tract Infections causing: 1. Pyogenic meningitis 2. Acute epiglottitis 3. Cellulitis, middle ear infection,etc conjuctivitis Microscopy Small, non-motile, Gram negative rods or coccobacili Long thread-like form in old csf culture Microscopic observation Culture of H.influenzae H.influenzae grows better in aerobically compare to anaerobically The optimum temperature for growth 35 – 37oC The are X and V factor Both represent in blood agar and permit the culture to grow H.influenzae and H.aegyptius need X and V factor, H. parainfluenzae need V factor and H.ducreyi need X factor Biochemical tests Not usually used to identify hemophilus 6 biovars of H.influenzae are recognized based on the indole, urease and ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) reactions of the diff strains Serology Consist of 1 – f serotypes Mostly causing meningitis belong to serogroup b Most strains that cause chronic bronchial disease are non-capsulated Antimicrobial sensitivity Resistant towards chloramphenicol, ampicilin, tetracycline, erythromycin and cotrimoxazole H. ducreyi is sensitive to sulphonamides Ampicillin resistant are common Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epidermidis Staphylococcus saprophyticus Scientific classification Kingdom:Bacteria Phylum:Firmicutes Class:Bacilli Order:Bacillales Family:Staphylococcaceae Genus:Staphylococcus Introduction Are microbial flora of the skin, upper respiratory tract and intestinal tract S.aureus usually cause abscesses, boils, conjuctivitis, pneumonia, septicemia, food poisoning and scalded skin syndrome S. epidermidis causing bactericaemia S. saprophyticus causing cystitis and acute urethritis Laboratory diagnosis Microscopy Non-motile Non capsulate Gram positive cocci Arrangement single or in pair Size 1 µm diameter Culture Grow well in aerobically and also in present of carbon dioxide Temperature between 10 – 420C, optimum temperature are between 35 370C S.aureus Produce yellow to cream in blood and chocolate agar (heated agar) Occationally produce white 1-2 mm in diameter colonies Some strain produce beta-hemolytic when grown aerobically Colonies are slightly raised and easily emulsified on a slide Non- lactose fermenter in MacConkey agar Mannitol salt agar is a useful differential and selective agar to identify S.aureus On blood agar S.epidermidis Colony is white Non hemolytic in blood agar S. saprophyticus Maybe white or yellow There are non-hemolytic in BA Not grow anaerobically No growth in MacConkey agar Biochemical reactions S.aureus DNAse test will be positive for S.aureus but negative in other species Catalase test will be positive in all staphylococcus but negative in all streptococcus S. epidermidis and S. saprophyticus Coagulase negative DNAse negative Catalase positive Antimicrobial sensitivity Erythromycin Clindamysin Fucidin Vancomycin Many strains of S.aureus are penicillinresistant S.epidermidis are more resistant than S.aureus to antibiotics S. saprophyticus less resistant to antibiotics than S.aureus and S.epidermidis Streptococcus pyogenes Streptococcus agalactiae Enterococci Lecture content Basic characteristics Classification Grouping of species Pathogenesis Lab diagnosis Scientific classification Kingdom – Bacteria Phylum - Firmicutes Class – Bacili Order – Lactobacillales Family – Streptococcaceae Genus - Streptococcus Species – 22 sp. Basic characteristics Gram-positive Lactic acid bacteria group Spherical Grow in chain (twisted) or pairs Mostly are facultative anaerobes Habitat Available in food such as Emmentaler (Swiss) cheese Normal flora of the mouth, skin, intestine and upper respiratory tract of humans Classification Beta hemolysis Alpha hemolysis • Lancerfield serotyping • Based on carbohydrates in the bacterial cell wall • Viridans groups • S.pneumoniae separated group Alpha hemolysis Surrounded by an area of partial haemolysis Green-brown colour (reduced haemoglobin) Consist of pneumococci and viridans group( alpha hemolytic and no Lancerfield antigens Pathogenicity S.pyogenes (Group A) Acute sore throat Scarlet fever Ear infections Peurperal sepsis Septicemia and occasionally endocarditis Skin infection such as celulitis and impetigo Post-streptococcal disease From the implication of pathogenesis, it will leads to a serious stage of diseases: Acute glomerulonephritis Rheumatic fever Enzymes & toxin production By S. pyogenes Streptolysin O Streptolysin S Streptokinase (cause fibrinolysis) Hyarulonidase DNAses DPNAse Erythrogenic toxin Other species S.Agalactiae (Group B) Neonatal septicaemia, pneumoniae, meningitis Septic abortion and peurperal sepsis Enterococci (Group D) Urinary tract infection Infections of ulcer and wounds Endocarditis and meningitis Viridans Endocarditis Dental caries Brain abscess Microscopy Gram positive (purple) Non-motile Long chains Sometimes in pair Culture Aerobically and anaerobically Temperature between (22 – 42o C) And enterococci are between (15 – 45o C) On BA, colony usually less than 1 mm in diameter Grey – white or colourless Dry / shiny, irregular outline Most of the pathogenic streptococcus producing hemolysins S. pyogenes Produce beta hemolysis Sensitive to bacitracin (can’t rely 100% to it, coz not only group A sensitive to it) but for viridans it is resistance towards bacitracin A selective BA containing crystal violet was suggested Does not grow in MacConkey agar S.agalactiae Optochin resistant but S.pneumoniae is sensitive Beta hemolysis in BA In serum starch agar, it produces orange pigment Biochemical test Species Catalase Bacitracin Optochin Litmus Milk CAMP S.pyogenes - + - - - S. agalactiae - - - - + Enterococci - - - + - Viridans streptococci - - - - - Pneumococci - - + - -