ESTERS
advertisement

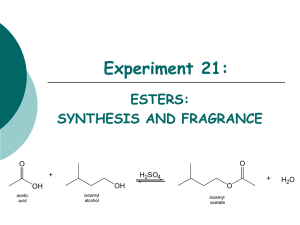
Experiment 21: ESTERS: SYNTHESIS AND FRAGRANCE O RCOH + H + R'OH O RCOR' + H2O Objectives: To synthesize an ester from acetic acid with isoamyl alcohol under reflux. To purify your product through acid-base extraction and simple distillation. To identify and analyze the purity of your compound using GC analysis. To identify your product by analyzing the NMR and IR spectra. Before coming to lab… Review these techniques: Reflux Acid-Base Extraction Simple distillation Drying over MgSO4 GC Analysis FISCHER ESTERIFICATION Fischer esterification is an acid catalyzed nucleophilic acyl substitution. Net effect is the replacement of an –OH of a carboxylic acid with the –OR of an alcohol to produce an ester. O R O H + H O C O R' H + R O C R' + H O It is an equilibrium reaction with an unfavorable Keq, thus we can improve product yield in several ways: Use an excess of the alcohol reactant. Use an excess of the carboxylic acid reactant. Remove water as it forms. H MECHANISM H O C H3C CH3 O + H OSO3H + C OH H3C acids are not reactive enough to undergo nucleophilic addition directly. H OH C OH CH3 • Carboxylic • By using sulfuric acid as a catalyst, the carbonyl group oxygen is protonated to give the carboxylic acid a positive charge. This makes it more reactive. • The carboxylic ester is formed after loss of water from the tetrahedral intermediate. H3C OH C H 3C HO H C O CH3 H H H3C O H C O H3C H O H C O H CH3 H O H3C C H 3C H C O CH3 H2O H2SO4 EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (SYNTHESIS) • Combine acetic acid, isoamyl alcohol and sulfuric acid in a 25 mL round bottom flask. water out • Clamp flask to ringstand and add boiling chips. • Place water cooled condenser on top of flask, with a CaSO4 drying tube in the top. water in • Heat to reflux. Reflux 30 minutes. • Cool to room temp. • Add 10% NaHCO3 slowly to flask. heating mantle to voltage regulator iron ring EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (PURIFICATION) • Transfer liquid to separatory funnel. • Rinse reaction flask with ether and transfer to separatory funnel. • Wash the organic layer with 10% NaHCO3. • Transfer the organic layer to a clean flask. • Dry over MgSO4. • Transfer liquid to a preweighed 50 mL round bottom flask. • Clamp flask to ringstand. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (PRODUCT ISOLATION) • Set up a simple distillation apparatus, using a 25 mL round bottom as the receiving flask. •Collect all distillate that boils under 40oC. water out water in • Record distillation range, Ti-Tf. Heating Mantle • Allow reaction flask to cool to room temperature. • Reweigh flask to determine final product mass and calculate % yield. • Prepare GC sample. iron ring to voltage regulator Table 21.1 Determine limiting reagent 1st, before calculating theoretical yield! Theoretical yield (g) Actual yield (g) % yield Record physical state and color of product! Product Appearance Table 21.2 GC Retention Times (min) Compound methanol isoamyl alcohol isoamyl acetate Standard Adjusted Area % Sample GC SOLVENT! REACTANT! PRODUCT! EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (IR ANALYSIS) CH3 5 CH3CHCH2CH2OH 4 3 CH3 2 1 O 5 CH3CHCH2CH2OCCH3 4 3 2 1 6 7 Table 21.3 Functional Group sp3 CH stretch Base Values Acetic acid Isoamyl alcohol Isoamyl acetate Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) 2800-3000 C-O stretch 1000-1300 OH stretch 3100-3350 C=O stretch 1680-1740 EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (NMR ANALYSIS) CH3 5 CH3CHCH2CH2OH 4 3 2 CH3 1 O 5 CH3CHCH2CH2OCCH3 4 3 2 1 6 O C H3C 1 2 OH 3 7 SAFETY CONCERNS CAUTION: H2SO4 is a STRONG ACID! WASTE MANAGEMENT • All aqueous washes from the extraction can be flushed down the drain with plenty of water! • Ester product and distilled ether should be placed in the bottle labeled, “ORGANIC WASTE (Esters)”. CLEANING Clean round bottom flasks and distillation glassware with wash acetone only! Separatory funnel and all other glassware should be cleaned with soap, water, and a brush if necessary, followed by a wash acetone rinse before returning to lab drawer. DO NOT return any glassware to lab drawer dirty or wet!