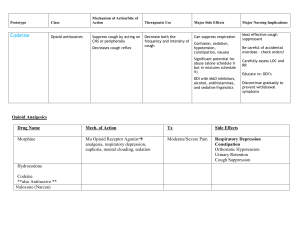
Pain Type Cause Characteristics Acute Results from effects of direct
advertisement
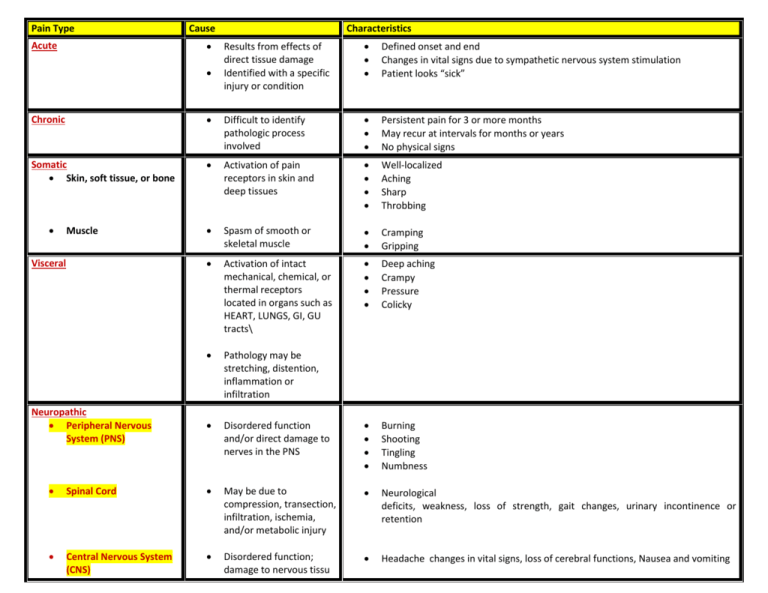
Pain Type Cause Acute Characteristics Results from effects of direct tissue damage Identified with a specific injury or condition Defined onset and end Changes in vital signs due to sympathetic nervous system stimulation Patient looks “sick” Chronic Difficult to identify pathologic process involved Persistent pain for 3 or more months May recur at intervals for months or years No physical signs Somatic Skin, soft tissue, or bone Activation of pain receptors in skin and deep tissues Well-localized Aching Sharp Throbbing Spasm of smooth or skeletal muscle Cramping Gripping Activation of intact mechanical, chemical, or thermal receptors located in organs such as HEART, LUNGS, GI, GU tracts\ Deep aching Crampy Pressure Colicky Pathology may be stretching, distention, inflammation or infiltration Disordered function and/or direct damage to nerves in the PNS Burning Shooting Tingling Numbness Muscle Visceral Neuropathic Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Spinal Cord May be due to compression, transection, infiltration, ischemia, and/or metabolic injury Neurological deficits, weakness, loss of strength, gait changes, urinary incontinence or retention Central Nervous System (CNS) Disordered function; damage to nervous tissu Headache changes in vital signs, loss of cerebral functions, Nausea and vomiting STEP (WHO ladder)* PAIN INTENSITY ANALGESIC OF CHOICE Step 1 Mild Pain: 1 – 3 on a 10 numerical analogue scale Aspirin (ASA) Acetaminophen (Acet) NSAID’s Coanalgesics Step 2 Moderate Pain: 4 - 6 on a 10 numerical analogue scale Codeine Hydrocodone (Vicodin) Oxycodone (Percocet) Dihydrocodeine Nonopioid analgesic Coanalgesics Step 3 Severe Pain: 7 – 10 on a 10 numerical analogue scale Morphine (Roxanol) Oxycodone Hydromorphone (dilaudid) Fentanyl (duragesic) Methadone MS Contin Nonopioid analgesics Coanalgesics *World Health Organization – 3 STEP Ladder for Management of Pain* Focuses on proper selection, dosing, titration and administration of analgesics in relation to persons’ self-described pain intensity and type of physical pain responsive to opioid therapy. Pain Source Somatic: Bone of soft tissue pain Pain Character Tenderness over bone or joint Muscle Somatic – Visceral Pain Examples of Medications Ibuprofen (motrin) Trilisate Prednisone Myofascial Cyclobenzaprine (flexeril) Cramping, Colic Dicyclomine HCI (Bentyl); Levsin or Levsinex Atropine tabs/drops Neuropathic Pain Burning, Tingling Amitriptyline (Elavil) Shooting, stabbing, lancinating PNS Carbamazepine Spinal Cord (Tegretol) CNS Gabapentin (Neurotin) Suggested List of Coanalgesic Drug Therapies Commonly Prescribed (Medication therapy may vary based on physician preference) Symptom Cause Suggested Treatment Uticaria, pruritus Mast cell destabilization and release of histamine Constipation Common to all opioids Nausea, Vomiting Starts with onset of opioids; tolerance develops within days. May also be due to constipation Phenergan (PO, PR) Ativan (PO, SL) Reglan (stimulates motility) Haldol Scopolamine patch Diarrhea Nurse to check for impaction prior to medication administration Imodium Lomotil Anxiety Depresses the CNS, most likely potentiating GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, causing sedation, decreased anxiety, decreased seizure activity Lorazepam (Ativan) Xanax (Alprazolam) Oral Thrush Generally from Abx therapy Mycostatin (antifungal) Magic Mouthwash (equal parts of Benadryl, Nystatin, Maalox, lidocaine) – Sleeplessness Acts at many levels in the CNS, producing generalized depression Restoril Respiratory secretions Small doses decrease salivary and bronchial secretions and decrease diaphoresis; Levsin Albuterol (dilator, bronchioles) Scopolamine patch Atropine gtts Sedation effects Defined as inability to wake up fully; need to evaluate with patient and family the amount of “natural” sedation patient desires. Could also be due to electrolyte imbalance such as high calcium levels May need to alter pain control plan to balance with desired level of sedation Ritalin may be ordered (depends of prescribing physician preference) Muscle jerking, twitching accompanied by insomnia, delirium, muscle spasms Opioid excess in tolerant patient; no decrease in RR or LOC, however CNS is excited Reduce opioid dose or consider rotating to another opioid Give Ativan for twitching as ordered Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) Atarax Follow bowel protocol for appropriate titration of bowel stimulant and stool softener Docusate (stool softener) Milk of Magnesia Magnesium Citrate Glycerin or Dulcolax Supp Lactulose Enema (fleets) 2% lidocaine jelly for disimpaction Possible adverse effect of Opioids, Cause and Suggested Treatments