Financial Statement Analysis by Tamondong, Cecille
advertisement
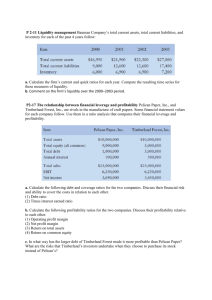
Financial Statement Analysis is defined as the process of identifying financial strengths and weaknesses of the firm by properly establishing relationship between the items of the balance sheet and the profit and loss account. Types of Analysis 1. 2. 3. Vertical Analysis Horizontal Analysis Ratio Analysis Horizontal Analysis Horizontal analysis of financial statements involves comparison of a financial ratio, a benchmark, or a line item over a number of accounting periods. This method of analysis is also known as trend analysis. Horizontal analysis allows the assessment of relative changes in different items over time. It also indicates the behavior of revenues, expenses, and other line items of financial statements over the course of time. Vertical Analysis Vertical analysis of financial statements is a technique in which the relationship between items in the same financial statement is identified by expressing all amounts as a percentage a total amount. This method compares different items to a single item in the same accounting period. Ratio Analysis Ratio analysis is the calculation and comparison of ratios which are derived from the information in a company's financial statements. The level and historical trends of these ratios can be used to make inferences about a company's financial condition, its operations and attractiveness as an investment. Types of Ratios 1. 2. 3. Profitability Liquidity Solvency Profitability Ratio - Ratios show a company's overall efficiency and performance. - Two Types: margins and returns. Ratios that show margins represent the firm's ability to translate sales dollars into profits at various stages of measurement. Ratios that show returns represent the firm's ability to measure the overall efficiency of the firm in generating returns for its shareholders. Liquidity Ratio Liquidity ratios are the ratios that measure the ability of a company to meet its short term debt obligations. These ratios measure the ability of a company to pay off its short-term liabilities when they fall due. The liquidity ratios are a result of dividing cash and other liquid assets by the short term borrowings and current liabilities. They show the number of times the short term debt obligations are covered by the cash and liquid assets. If the value is greater than 1, it means the short term obligations are fully covered. Solvency Ratio Solvency ratio are to measure a company's ability to meet long-term obligations. The solvency ratio measures the size of a company's after-tax income, excluding non-cash depreciation expenses, as compared to the firm's total debt obligations. It provides a measurement of how likely a company will be to continue meeting its debt obligations. Generally speaking, the lower a company's solvency ratio, the greater the probability that the company will default on its debt obligations. Profitability Ratios (margins) GROSS PROFIT MARGIN =gross profit / net sales Gross profit margin looks at cost of goods sold as a percentage of sales. This ratio looks at how well a company controls the cost of its inventory and the manufacturing of its products and subsequently pass on the costs to its customers. The larger the gross profit margin, the better for the company. OPERATING PROFIT MARGIN =expense before income tax / net sales Operating profit is also known as EBIT and is found on the company's income statement. EBIT is earnings before interest and taxes. The operating profit margin looks at EBIT as a percentage of sales. The operating profit margin ratio is a measure of overall operating efficiency, incorporating all of the expenses of ordinary, daily business activity. Profitability Ratios (margins) NET PROFIT MARGIN =net income / net sales Net profit margin shows how much of each sales dollar shows up as net income after all expenses are paid. The net profit margin measures profitability after consideration of all expenses including taxes, interest, and depreciation. CASH FLOW MARGIN =cash flow from operating cash flow / net sales Cash Flow Margin it expresses the relationship between cash generated from operations and sales. It measures the ability of a firm to translate sales into cash. Profitability Ratios (return) RETURN ON ASSET =net income / total asset The Return on Assets ratio measures the efficiency with which the company is managing its investment in assets and using them to generate profit. It measures the amount of profit earned relative to the firm's level of investment in total assets. RETURN ON EQUITY =net income / stockholder’s equity It measures the return on the money the investors have put into the company. This is the ratio potential investors look at when deciding whether or not to invest in the company. In general, the higher the percentage, the better, with some exceptions, as it shows that the company is doing a good job using the investors' money. Profitability Ratios (return) CASH RETURN ON ASSET =cash flow from operating activities / total assets It is used as a comparison to return on assets since it is a cash comparison to this ratio as return on assets is stated on an accrual basis. The higher the percentage, the better. Liquidity Ratios ACID TEST RATIO (QUICK RATIO) =(current asset – inventory) / current liabilities The most basic definition of acid-test ratio is that, “it measures current (short term) liquidity and position of the company”. CASH RATIO =cash and cash equivalents / current liabilities Cash ratio (also called cash asset ratio) is the ratio of a company's cash and cash equivalent assets to its total liabilities. Cash ratio is a refinement of quick ratio and indicates the extent to which readily available funds can pay off current liabilities. Liquidity Ratios CURRENT RATIO =current asset / current liabilities The current ratio indicates a company's ability to meet short-term debt obligations. The current ratio measures whether or not a firm has enough resources to pay its debts over the next 12 months. The current ratio can also give a sense of the efficiency of a company's operating cycle or its ability to turn its product into cash. WORKING CAPITAL =current asset – current liabilities Working capital is the amount by which the value of a company's current assets exceeds its current liabilities. It measures how much in liquid assets a company has available to build its business. Working capital is a common measure of a company's liquidity, efficiency, and overall health. Solvency Ratios DEBT RATIO =total debt / total assets A ratio that indicates what proportion of debt a company has relative to its assets. The measure gives an idea to the leverage of the company along with the potential risks the company faces in terms of its debt-load. SOLVENCY RATIO = (after tax net profit + depreciation) / (long term liabilities + short term liabilities) Solvency is a measure of the firm's ability to pay all debt, particularly long-term debt and is a measure of the firm's long-term survival. Thank you. Reference: www.investopedia.com www.readyratios.com www.bizfinance.about.com