Accounting for Corporation
advertisement

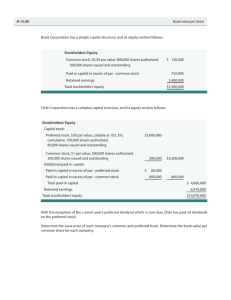
ACCOUNTING FOR CORPORATIONS I. Introduction What is the Corporation? A corporation is a separate legal entity chartered under law. Basically, upon the creation of a corporation, a 'new person' is created in the eyes of the law. This 'person' has similar rights and obligations that a real person would have and is expected to abide by the same laws and regulations that govern all business activity. Advantage and Disadvantage of Corporation: Advantage : 1. A Corporation is a separate legal entity. 2. The shareholders are not liable for the company's debts. 3. It is very easy to raise capital. 4. In the event the corporation fails, stockholders are only accountable for the amount they have invested. 5. Ownership may easily be transferred by selling the share held. 6. The corporation continue to exist even with the death of a stockholder. 7. Contacts can be entered into in the corporate name 8. Significant funds can be raised through the sale of stock to the public. Advantage and Disadvantage of Corporation: Disadvantage : 1. High taxes 2. Annual fees paid to the state in which the company corporate. 3. Double taxation in that the source of dividends, corporate income, is subject to corporate income taxes and the dividends received by stockholders are themselves subject to personal income taxes. 4. The cost of printing stock certificates. 5. Governmental regulation over affairs. 6. The filing of financial reports, as required by the Securities and Exchange Commission, that may disclose vital information to creditors. Study objective of Accounting for Corporation: 1. Analyze financial statement to identify the different types of business organizations. 2. Explain the characteristics of major types of stock issued by corporation. 3. Explain how to account for different types of stock issued by corporation. 4. Show how treasury stock transactions affect a company’s financial statements. 5. Explain the effects of declaring and paying cash dividends on a company’s financial statements. 6. Explain the effects of stock dividends and stock splits on a company’s financial statement. Who is a stockholder ? A stockholder is an owner of the company and as is entitle to vote , share in earning through the receipt of dividends, share in disposition of assets after creditors if the company becomes bankrupt, sell his or her ownership interest , and invest in additional shares on a proportionate basis if the company increases the amount of shares outstanding. Who is the board of director? Board of director is the person who was voted by the stockholder and overall responsibility for managing the company. Some of board of directors is the stockholders who was selected by the other stockholders. Right of stockholders : 1. Vote at stockholders’ meeting. 2. Sell stock. 3. Purchase additional shares of stock. 4. Receive dividends, if any. 5. Share equally in any assets remaining after creditors are paid in a liquidation. II. Share Stock certificate: Stock certificate is a legal document that certifies ownership of a specific number of stock shares in a corporation and typically has a par value printed on it. Stock certificates are divided into two forms : - registered stock certificates. - bearer stock. A registered stock certificate is normally only evidence of title, and record of the true holders of the shares will appear in the stockholder’s register of the corporation. A bearer stock certificates , as its name implies is a bearer instrument, and physical possession of the certificate entitles the holders to exercise all legal rights associated with the stock. Par value: Par value is a nominal value of a security which is determined by an issuing company as a minimum price . Shares are divided into five groups : -Authorized shares. -Issued shares. -Treasury stock. -Outstanding shares. -Subscribed shares. Authorized shares: Authorized shares are the maximum amount that can be issued according to the articles of incorporation. Issued shares: Issued shares are the amount of authorized shares that have been sold to the public. Treasury stock: Treasury stock represents the issued shares that have been reacquired by the company. Outstanding shares: Outstanding shares equal issued share less treasury stock. Subscribed shares: Subscribed shares are those shares under contact at a specified price for which a down payment has been given . The subscribed shares will not be issued until full payment is Received from the subscriber. Example of shares: Chan vatana company has an authorization (authorized shares) 200,000 shares. During 2008, 90,000 shares were issued. During the year, the company bought back 10,000 shares. The outstanding shares at year’s end are determined as follow: Issued shares 90,000 Less: Treasury stock 10,000 Outstanding shares 80,000 III. Stock Stock are divided into two types : -Common stock. -Preferred stock. Common stock: Common stock are the shares in a corporation with no preference or priorities over other classes of stock. The rights in these shares Include: voting rights, distribution rights, liquidation rights, and Other rights. Preferred stock: Preferred stock are the shares in a corporation that are entitled to a preference above shares of common stock. The shareholders of preferred stock have the following rights: -Special voting or veto rights. -A priority on distribution of dividends. -A priority on the corporation’s assets upon liquidation or merger. -A right to convert to common stock based on a formula. -A right to force the corporation to buy back shares at some time in the future . -A possible separate right to elect a designated number of Example of Stock: On January1, Korn chantha company has authorized shares 55,000 shares of common stock and 44,000 shares of preferred stock. On January 1 , it issued 6,600 shares of common of $10 par value common stock for cash. On Jane 20. the company issued an additional 5000, shares of common stock and also 2,000 Shares of preferred stock. All shares were issued at par value. Jan 1. Cash $66,000 Common stock Jan 20. Cash $66,000 $70,000 Common stock $50,000 Preferred stock $20,000 IV. Stockholders’ equity Stockholder’s equity section of the balance sheet consists of capital stock, paid-in capital, retained earnings and total stockholder’s equity. Capital stock shows the par value of the stock issued. Preferred Stock is listed before common stock because of its preference in liquidation. Paid-in capital shows the amount received over the par value of stock issued. Retained earning presentations the accumulated earning of the company since inception less the dividends declared. Total stockholders’ equity sums of the above. V. Issuance of stock When stock is sold at an issuance price that is different than par value, cash is debited for the amount received and the particular security (common or preferred stock) is credited at par value. When is sold above par value, the excess is called a premium. The premium account is shown under the paid-in capital section of stockholders’ equity because it relates to the issuance of stock’s company. In the case where the issuance price is less than par value, the excess is called discount. Discount is shown under paid-in capital as a reduction. Example of premium stock: Kuy Rotha corporation issued 6,000 shares of $10 par value of preferred stock for $16 a share. Cash $96,000 Preferred stock $6,0000 Premium on Preferred stock $3,6000 Example of discount stock: Pen Ret Co.,Ltd issued 30,000 shares of $15 par value common stock for $14 a share. Cash $420,000 Discount on common stock $30,000 Common stock $450,000 VI. Subscribed stock Stock may be acquired under an installment plan. The journal entry for the down payment is : Cash ( down payment) Subscription Receivable ( balance due) Common Stock Subscribed (par value) Premium on Common Stock ( subscription price over par value When full payment has been received , the subscribed stock will be issued. The journal entry are: Cash $$$ Subscription Receivable Common stock subscribed Common Stock $$$ $$$ $$$ On July 10, Lay Soklun Corporation received subscription for 10,000 shares of $15 par value common stock. The subscription price is $18 per share. A down payment of 40 percent was made. On August 5, the balance due from the subscribers was received. July 10 Cash $72,000 Subscriptions Receivable $108,000 Common stock subscribed $150,000 Premium on Common Stock August 5 Cash $108,000 Subscriptions Receivable $108,000 $30,000 VII. Treasury Stock Treasury stock or reacquired stock is the stock is bought back by the issuing company, reducing the amount of outstanding stock. The journal entry is : Treasury stock Cash $$$ $$$ When the treasury stock is resold, the difference the selling price and the cost is reflected in an account called Paid-in Capital-treasury stock. Cash $$$ Treasury Stock $$$ Paid-in Capital- treasury stock $$$ Example of Treasury Stock: ADB Corporation had the following transactions during 2009 January 7 Purchased 1,000 shares of outstanding common stock at $18 per share February 8 Sold 400 shares of treasury stock at $20 per share March 10 Sold 250 shares of treasury stock at $16 per share Journal entry of example of treasury stock: January 7 Treasury stock $18,000 Cash February 8 March 10 Cash $18,000 $8,000 Treasury stock $7,200 Paid-in capital- treasury stock $800 Cash $4,000 Paid-in capital-treasury stock $500 Treasury stock $4,500 When a company experience financial problems, stockholders may DonateCash shares back to the company so that$$$ they may be resold. Paid-in Capital-donation $$$ On April 1 , animal corporation received 1,500 shares of $10 on par value of donation common stock from its stockholders. And then on April 10 the corporation sold 500 share at $15 per share. April 1 Memorandum: received 1,500 shares of donated common stock having a par value of $10 April 10 Cash $7,500 Paid-in Capital-donation $7,500 VIII. Dividends A dividend is a distribution of the assets of a corporation to its shareholders. Three important dates associated with dividends are: - Declaration date: the date upon which a divided is declared by the board of directors. - Date of record: the date upon which a stockholder must hold the stock in order to entitled to receive the dividend. - Payment date : the date the stockholder receives the dividend. Journal entries are made on the declaration date and payment date. No entry is made on the date on record. Dividends are divided into two forms: - Cash dividends - Stock dividends. Cash dividends: A cash dividend is a payment made by a company out of its earning to investor in the form of cash. Example of Cash dividends: On October 2 ,2008, a cash dividend of $2 per share on 5,000 shares of $10 par value common stock. The record date is October 20,2008. Payment is to be made on December 5 , 2008. October 2 Retained Earnings $10,000 Cash dividends payable $10,000 October 20 No entry December 5 Cash dividends payable Cash $10,000 $10,000 Stock dividends: A stock dividend : is an increase in the amount of shares of a company with a new shares being given to the shareholders Stock dividends are divided into two kinds : - Small stock dividends - Large stock dividends. A small stock dividend : when amount to be distributed are less than 20-25 percent of the outstanding stock. Retained Earnings ( based on the market value of the shares) Stock dividend distributable( based on the par value of shares) Premium on Common Stock A large stock dividend : when amounts to be distributed are more than 20-25 percent of the outstanding stock.( Retained Earnings ( based on the par value of the shares) Stock dividend distributable The entry for the actual stock issuance is the same whether there is a small or large stock dividend. Stock dividend distributable Common Stock $$$ $$$ Example of Stock dividends: Chan Vatana Corporation has 40,000 shares of $10 par value common stock outstanding. On August 5,2007, it declared a 5 percent stock divided to the shareholders to record on August 25. On August 5, the market price of the stock was $25 per share. The issuance date is September 10,2007. Aug. 5 Retained Earning $50,000 Common stock dividend distributable $20,000 Premium on Common Stock $30,000 Aug.25 No entry Sep.10 Common stock dividend distributable $20,000 IX. Retained Earnings Retained earnings is the accumulated earnings of the business that have not been distributed to stockholders. Retained earnings may be either un appropriated and appropriated . Un appropriated retained earnings is free for dividend distribution. Appropriated retained earnings is reserved and unavailable for dividend distribution. Retained Earning Appropriation of Retained Earning $$$ $$$$ When the appropriation is no longer needed, the above entry is reversed: Appropriation of Retained Earning $$$$ Retained Earning $$$ ABC Corporation has a balance in retained earnings of $70,000. The company decides to establish a reserve for plant expansion of $20,000. Retained Earnings $20,000 Appropriation for Plant Expansion $20,000 The company acquires $6,000 of treasury stock. The entry for the appropriation is : Retained Earnings Appropriation for Treasury Stock 5,000 5,000 The Treasury stock costing $3,000 is sold: Appropriation for Treasury Stock Retained Earning $3,000 $3,000 Under the stockholder’s equity section, retained earning would be broken down as follows: Un appropriated retained earnings $48,000 Appropriated retained earnings: For Plant Expansion $20,000 For Treasury Stock $2,000 Total Retained Earnings $60,000 Stockholders’ Equity Capital Stock: Preferred stock Common stock Common stock subscribed Common stock dividend distributable Paid-in Capital: Premium on Preferred stock Premium on Common stock Paid-in Capital-donation Paid-in Capital-Treasury stock Retained : Un appropriated retained earnings Appropriated Retained Earnings Subtotal: Less: Treasury Stock Total Stockholders’ Equity Exercise of Accounting for Corporation: Pen Ret Corp. completed the following transaction in 2009 : 1. Issued 20,000 shares of $10 par common stock at par 2. Issued 2,000 shares of $30 started value preferred stock at 32 per share. 3. Purchased 500 shares of common stock as treasury stock for $15 per share. 4. Declared a 5 percent dividend on preferred stock. 5. Sold 300 shares of treasury for $18 per share. 6. Paid the cash dividend on preferred stock that was declared in event 4. 7. Appropriated $6,000 of retained earnings. Prepare journal entry and stockholders’ equity of December 31,2009