Measuring Gases
advertisement

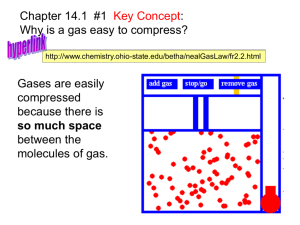
Measuring Gases Objectives: • 1. Explain what gas pressure means and describe how it is measured. Key Terms: • atmospheric pressure, barometer, manometer, STP Gas Variables - Amount • Amount of Gas (n) - a mole is a standard amount of a substance – n = mass / molar mass (molar mass = atomic mass in grams) • In order to do this you need to calculate the molar mass of the substance. – If the amount of gas in a closed system is increased then the pressure is also increased. • Increases the amount of collisions per unit time Gas Variables - Volume – Volume of Gas (V) - values are recorded in liters (1000cc or 1000ml) • if the amount (n) of gas is constant the pressure will increase if the volume of the container is decreased – Increases the number of collisions per unit time as the molecules must travel a shorter distance Gas Variables – Temperature • Temperature (T) – Represents the kinetic energy of a gas – all measurements will have to be converted to Kelvin before calculations. (K = C + 273) – the pressure in a closed container increases as the gas is heated • Number of collisions per unit time increases as the KE of each molecule increases Gas Variables – Pressure • Pressure (P)- Pressure in a container is created by collisions of molecules on the walls of the container. – it is created by manipulating the other 3 variables. • (n) … directly related • (V) … inversely related • (T) … directly related Standard Temp and Press • STP – This is a standard from which the properties of gases are determined. • Its values are: – 273K (0oC) – 1 atm (101.3 kPa or 760mmHg).