Unit 6 Review
advertisement

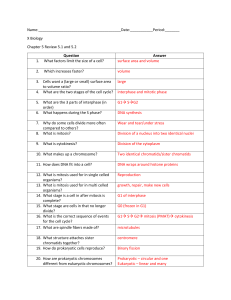
Unit 6 Review 30 Scantron Questions - Vocabulary Matching - True or False - Multiple Choice 1. What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid 2. What is the function of DNA? - Stores genetic (hereditary) information - Controls cell functions 3. Who id’d DNA structure? Watson & Crick in 1953 4. Three parts of nucleotide? - Phosphate, Deosyribose (sugar), Nitrogen base - Nitrogen base is different for each nucleotide (different shapes) 5. Pyrimidines: Single ring shape, Thymine and Cytosine 6. Purine: Double ring shape, Adenine and Guanine 7. Complementary Base Pairs - The two nitrogen bases that bond together - Purine always bonds with a pyrimidine - Adenine pairs with Thymine, Guanine pairs with Cytosine 8. What is the structure of DNA? - Structure - Double helix, two stands of nucleotides connected - Backbone - sugar and phosphate - Rungs (sticks out into center of molecule) - nitrogen-base – The order of bases is the genetic code, order codes for a specific gene (protein) 9. Parts of the Cell Theory • All living organisms are made up of one or more cells • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms • All cells come from the division of pre-existing cells 10. Cell Division – process where a cell splits (divides) into two cells 11. DNA Replication • Helicase (enzyme) breaks apart bonds between base pairs. This separates the left and right strands of the DNA molecule • DNA polymerase (enzyme) adds complementary base pairs to each separated strand. • Makes two new molecules of DNA 12. Can enzymes make mistakes – YES! • Mutation – change in the order of nucleotides in a molecule of DNA 13. Most common mutations: - Substitution – wrong nucleotide added - Addition – extra nucleotide(s) added - Deletion – nucleotide(s) removed 14. Prokaryotic Cell Division: - Binary Fission (DNA copied, Cell grows, Cytokinesis) 15. Eukaryotic Cell Division: - Mitosis or Meiosis then Cytokinesis 16. Main parts of the cell cycle: - Interphase (G1, S, G2), Division (M phase & Cytokinesis) 17. Interphase: - G1 (time gap 1)- cell grows & performs daily cellular activities - S Phase (synthesis) - DNA replication, all DNA is copied (identical DNA copies (chromatids) are held together at a centromere - G2 (time gap 2) - cell grows, gets ready to divide, duplicates organelles 18. DNA transform into a chromosome? How does this happen? • Prophae • DNA coils around proteins (histones) during Prophase, this structure is then called a chromosome • Chromosomes (in X shape) are actually two identical strands of DNA (sister chromatids) held together by a centromere 19. when does the nucleus disappear? Prophase Reappear? Telophase 20. How many times does the cell divide in mitosis? Once • How many cells are formed? Two Diploids • How many chromosomes (human cells)? 46 chromosomes 21. What happens during prophase? • DNA coils up into a chromosome (sister chromatids are attached by centromere) • Nucleus and nucleolus disappears • Centrosomes appear and begin to form spindle fibers 22. What are spindle fibers? Microtubules (proteins) Where do they form? Around centrosomes 23. What happens during metaphase? • Chromosomes (sister chromatids) line up in the middle of the cell • Spindle fibers elongate and attach to the centromere of each chromosome/chromatid 24. What happens during anaphase? • Spindle fibers shorten and pull on the centromere • Centromere breaks and the chromosome’s chromatids are separated • Chromatids are pulled to opposite ends of the cell 25. What happens during telophase? • Nucleus reforms around each grouping of chromatids (2 nuclei form) • Chromosome/chromatids unwind back into DNA • Cell gets ready to split in the middle 26. What is cytokinesis? How is it different in plants & animals? • Definition – division of the cytoplasm • Animals – cell membrane splits/pinches down the middle • Plants – after the cell membrane splits/pinches down the middle, the plant cell would then form cell plate in the center of the cells 27. How many times does the cell divide in meiosis? • Twice, Forms Four Cells • Each cell has 23 chromosomes, Cells known as Haploid/Gamete/Reproductive Cell 28. What happens in meiosis? • After completing Interphase (G1, S, G2), the cell would divide once (Meiosis I). The two cells would then each divide again (Meiosis II). This produces 4 haploid cells (reproductive cells) 29. How is spermatogenesis different from oogenesis? • Spermatogenesis - formation of sperm, cytoplasm divides equally within the two divisions, produces four equal sized cells • Oogenesis - formation of one egg and three polar bodies, cytoplasm does not divide equally Interphase Back to Interphase Prophase Cytokinesis Telophase Metaphase Anaphase