Define biology
advertisement

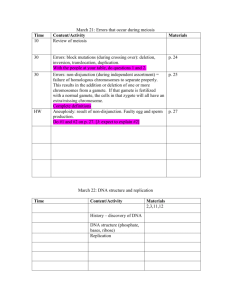
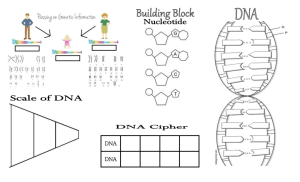
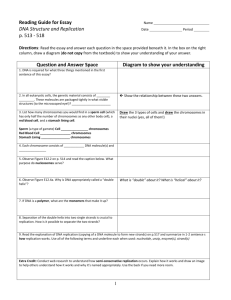
Supplement to lecture exam#2 Ch. 4, 5, 6 and parts of 8 Note that not all material is included in this list and your best study guide are your lecture notes! Chapter 4 Definition of metabolism What is cellular respiration? State the first and second laws of thermodynamicsUnderstand that energy from the sun fuels almost all of life on earth. Know that chemical reactions in the cell either require or release energy Understand that energy is stored in chemical bonds Know the three major processes in cell metabolism, where they occur and major products of each. Glycolysis- glucose- pyruvate Kreb cycle Electron transport system Define activation energy Define ATP Know the definition and function of enzymes Know the factors that affect enzyme functioning Define selective permeability and state the importance in cell membranes Diffusion Osmosis Concentration gradient Tonicityisotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic solutions and how and why it affects the cell shape active transport compared to passive transport aerobic anaerobic fermentation Explain the function of electron carriers (NADH and FADH) and where they are produced Chapter 5 Know the chemical reaction and process of photosynthesis Know the major reactants and products of each major process of photo-synthesis (Light dependent and light independent- Calvin cycle) Dark reaction Carbon fixation Autotroph Heterotroph Chloroplast, stroma, thylakoid membrane, and chlorophyll Explain the function of electron carriers (NADH and FADH) Chapter 6 Define the term chromosome and sister chromatid 1 Centromere Histones DNA double helix shape Know the components of a Nucleotide Know the nucleotide strand backbone (sugar-phoshpate-sugar-phosphate) Know the four DNA Nitrogenous bases Know Nucleotide base pairing rules What is a Karyotype Know the total number of chromosomes in a human body cell. Know the total number of chromosomes in a human sex (gamete) cell Compare and contrast autosomes and sex chromosomes Know the difference in sex chromosomes of males versus females Draw a simple representation of two parent DNA strands, two separated strands and two strands that have replicated from the parents. Understand the cells replicate their DNA (create sisters chromatid) before they divide during interphase of the cells life cycle Chapter 8 Interphase Diploid Haploid Asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction Alleles Zygote Egg Sperm Fertilization Crossing over Gamete Gametophyte Sporophyte Compare and contrast Mitosis and Meiosis Why is mitosis considered conservative cell replication? Why is meiosis considered division reduction cell replication? Difference in male and females produce gametes. 2