Mr. Sheehan Economics Class 12
advertisement

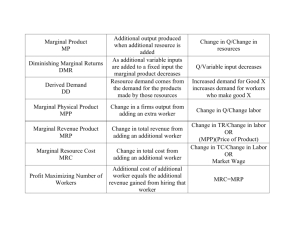
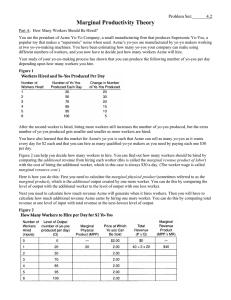
Economics: Class 12 9/29/14 Plan for the Week Monday – Review Chapter 1 Tuesday – Review Chapter 3 & 4 Wednesday – Review Chapters 5 Friday – Exam 1 - Chapters (1, 3, 4, and 5) Definition of Key Terms Economics The study of how people choose to allocate their scarce resources. The study of the production, distribution , and consumption of goods and services Economic Growth Marginal Analysis The additional benefit derived from producing one more unit of a good or service Marginal Costs The analysis of the benefits and cost of the marginal unit of a good or input. If increasing the output adds more to total benefits than to total costs. The output should be increased. Marginal Benefits The growing ability of the economy to produce economic growth. The main ways to have growth are to invest more, innovate, increase specialization, and increase inputs The additional cost incurred by producing one more unit of a good or service Net Benefits Net Benefits = Total Benefits (Revenue) – Total Costs Definition of Key Terms Opportunity Cost Value of the best alternative that had to be forgone in order to undertake a given course of action. The real cost of an item: what you must give up in order to get it. Production Possibility Curve A graph showing combinations of goods that an individual, a firm, or an economy is capable of producing Scarcity A condition that exists when current resources are inadequate to provide for all of people’s wants. A good is scarce if another unit of the good would benefit someone Trade-offs A comparison of the costs and benefits of doing something. Production Possibility Curves and Opportunity Cost The worker is currently spending one hour making chairs and three hours making benches. What is the opportunity cost per chair of spending a second hour in chair making (assuming the worker is still limited to four hours)? What is the dollar value of this opportunity cost if benches sell for $12. If chairs sell for $25, how many hours should be spent making chairs? Hint: the opportunity cost per unit of the good gained is the loss divided by the gain Chairs Benches Time Spent (hours) Product Made Time Spent (hours) Produc t Made 0 0 4 20 1 4 3 18 2 7 2 14 3 9 1 8 4 10 0 0 Marginal Analysis Key Procedure for Using Marginal Analysis Identify the control variable (which good is being increased by one more unit) Determine what the increase in total benefits would be if one more unit of the control variable were added. This is known as the marginal benefit of the added unit Determine what the increase in total costs would be if one more unit of the control variable were added. This is the marginal cost of the added unit If the unit’s marginal benefit exceeds (or equals) its marginal cost, it should be added. Marginal Analysis Problem Acme Manufacturing has trained Worker A at a cost of $30,000 and Worker A is worth $70,000 to Acme. A worker’s worth to a firm refers to how much the firm presently values all the future profits it expects to make from the worker, these profits being the revenues produced by the worker less wages and fringe benefits. Later, Acme has the opportunity to hire Worker B. Worker B would cost $30,000 to train but would be worth $90,000. However, to hire Worker B, Acme must fire Worker A. Should Acme hire Worker B? Do Later Work on the Practical Application Questions: Do numbers 1-9 skip 5 and 7