Gross pay
advertisement

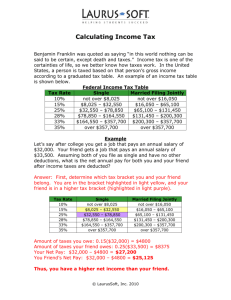
Let’s calculate some paychecks! 1. Math: Reminder: Gross pay is calculated by multiplying regular hours times regular pay and adding any overtime hours multiplied by overtime pay. Do you remember HOW OVERTIME PAY IS CALCULATED?? Net pay is determined by subtracting any deductions from gross pay -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- EXAMPLE: You worked 45 hours last week and pay is $10/hr. What is your gross pay? Deductions: 10% federal income tax, 6.2% social security, 1.45% Medicare What is your NET PAY? 40 x $10 = $400 regular pay 5 x $15 = $75 overtime pay (1 ½ x regular pay) Gross Pay = $475 $475 x 10% = $47.50 federal income tax $475 x 6.2% = $29.45 social security $475 x 1.45% = $6.89 medicare Totals Deductions = 47.50 + 29.45 + 6.89 = $83.84 $475 – 83.84 = $391.16 net pay (a.k.a. take home pay) See Page 74 in your book: Making Academic Connections: Complete a.- d. with a partner Answers to Page 74, Math a.Gross Pay = $368 b.Gross Pay = $478.40 c.Net pay = $304.47 d.Net pay = $307.58 Opener Get signed on to computer Go to IRS.gov Who Must File? Handout # IRS Website: Forms and Publications Tab Search 1040EZ Instructions- See Page 7 Also see pages 30-38 for tax tables – how much will you owe? Double the Salary An employee starting a new job has the option to choose how he is paid for the first twenty days of work. He works five days a week, for four full weeks. Make the best choice for the new employee after comparing the two options. Payment Option 1: For the first twenty days of work, the new employee will be paid $500 a day. Payment Option 2: The pay will be $0.01 for the first day. Each day the pay will double. So, it will be $0.02 the second day, $0.04 the third day, $0.08 the fourth day, etc. By the end of twenty days, how much money will the employee have made? Double the Salary Payment Option 1: $500.00 a day * 20 days = $10,000 Payment Option 2: Day 1 $ 0.01 Day 11 10.24 Day 2 .02 Day 12 20.48 Day 3 .04 Day 13 40.96 Day 4 .08 Day 14 81.92 Day 5 .16 Day 15 163.84 Day 6 .32 Day 16 327.68 Day 7 .64 Day 17 655.36 Day 8 1.28 Day 18 1310.72 Day 9 2.56 Day 19 2621.44 Day 10 5.12 Day 20 5242.88 Total: $10,485.75 Solution Payment Option 1: $500.00 a day * 20 days = $10,000.00 Payment Option 2: This is a better choice for the new employee as he will be making $10,485.75 This is $485.75 more than if he would have chosen Payment Option 1 Chapter 2 Income, Benefits, and Taxes Chapter 2 Objectives • List and discuss types of earned income and unearned income • Discuss types of self employment, advantages and disadvantages • Describe the types of taxes we pay and the benefits of paying taxes • Read a paycheck, noting required and optional deductions from gross pay • Discuss common federal tax forms Slide 9 What Are the Sources of Earned Income? • A wage is pay for each hour worked. o Minimum wage – lowest rate by state law o Overtime – 1½ times regular rate • A salary is pay for each month or year worked (no timecards used) • A tip is a gift of money for a service. • A commission is a set fee or percentage of a sale paid to the salesperson. 2-1 Earned Income and Benefits Slide 10 What Is Self-Employment? • Self-employment is working for yourself. • An entrepreneur is someone who is selfemployed and owns a business. Lifestyle businesses o hobby, intends to keep it small, local, work it themselves Venture businesses – ointends to grow into corporation and expand 2-1 Earned Income and Benefits Slide 11 Self- Employment Small Business Advantages • ability to make decisions about running business • can set your own hours • can keep all the Profits: (Profits are the amount left after all expenses are deducted from the revenues or sales of the business). • • • • • Disadvantages If business fails, invested money is lost must take risks (risky) hard to get credit initial startup requires long hours and a lot of work money is tight at first What Are Employee Benefits? Benefits are forms of pay other than salary or wages. • Pay without work- vacations, holidays, sick leave • Education-tuition reimbursement • Perks-parking spot, office with view, car, coffee station • Insurance-health, dental, worker’s comp • Retirement plans • Profit-sharing plans • Stock option plans 2-1 Earned Income and Benefits Slide 13 Unearned vs. earned income • Earned • Wage/Hourly (minimum wage and overtime) • Salary (no time cards or counting hours) • Tips • Commission (earned on amount of sale) • Unearned • • • • Interest Dividends (cash and stock) Pension (retirement income) Government Transfer Payments: (EX: social security benefits, unemployment benefits, workers’ compensation) Slide 14 What Type of Taxes Do You Pay? • Taxes are based on consumption, income, and wealth. • Direct taxes are paid directly to the government. o Examples: income and property taxes • Indirect taxes are charged on goods or services bought by the consumer. o Examples: use, excise, and sales taxes 2-2 Unearned Income and Benefits Slide 15 What Types of Taxes Do You Pay? CONSUMPTION TAXES Use taxes – paid when is a Progressive tax – using certain good and the more you earn the services provided by more you pay in tax government. Ex: toll road (tax brackets) Excise taxes – charged on the purchase of specific Property Tax goods. Ex: phone, utilities paid by those who Sales taxes – added to own real estate. purchase price of goods Income Tax: How Do You Benefit from Paying Taxes? • Direct benefits o Examples: roads and highways, social security, police protection, national parks • Indirect benefits o Examples: security from armed forces, public education for citizens, free vaccines 2-2 Unearned Income and Benefits Slide 17 Public Goods are paid for by your taxes • Three unique qualities of public goods: – We all benefit (they raise the overall standard of living in our country) – No one can be excluded from the benefits – People don’t necessarily benefit in proportion to taxes paid Slide 18 Opener: Calculate and reflect the following: 1. Figure out weekly and yearly earned income if working a job at minimum wage ($7.25/hr.) for 40 hours a week for 1 year. W= Y= 2. Next figure out your weekly and yearly income if working a job at $12.00/hr for 40 hours a week for a year. W= Y= 3. Now calculate the weekly and yearly income for a job with median starting pay for a Bachelor’s degree ($24/hr) for 40 hours a week for a year. W= Y= Sum up your thoughts about these results Communication Skills – see pg. 53 Critical Listening • Evaluate the information you hear. • Consider only important or relevant information. • Make good decisions *Remember the example based on what is of the used car salesman accurate and useful. 2-2 Unearned Income and Benefits Slide 20 Focus On . . . Social Security Benefits • Workers pay into the social security fund through payroll deductions. • A social security number is assigned to each person. • Employers match the payments. • Upon retirement, workers receive a monthly benefit check. 2-2 Unearned Income and Benefits Slide 21 Methods for Paying Employees 1. 2. 3. Paycheck • Paper check with stub • Least secure payment method because the employee is responsible for handling the paycheck Direct Deposit • Employers directly deposit employee’s paycheck into the authorized employee’s bank account Payroll Card • A payroll card electronically carries the balance of the employee’s net pay Where Does My Money Go? • Imagine you have just started your first job! After the first week, you have earned $100. About how much money would you receive in your first paycheck?? – – – – A) $100 B) $84 C) $69 D) $55 Where Does My Money Go? • Up to 31% of an individual’s paycheck is deducted. Your net paycheck many only be about $69! • How do you get from $100 all the way down to $69? • Let’s take a look… What Are Paycheck Deductions? • A deduction is money withheld from a paycheck. o Required deduction examples: income tax, social security tax, Medicare tax o Optional deduction examples: health insurance, life insurance, savings plan • Gross pay is total salary or wages. • Net pay is gross pay minus deductions. 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 25 What is the Gross Pay? If Miss Patty Paycheck worked at Terrific Tacos for $6.00/hour for 15 hours a week what will her gross pay be? # hours worked x wage = gross pay 15 hours x $6.00/hr = $90.00/week What is Miss Patty Paycheck’s gross pay for a two week pay period? 30 hours x $6.00/hr = $180.00 for 2 weeks Miss Patty Paycheck’s Paycheck • Miss Patty Paycheck’s paycheck includes: – Gross Pay $180.00 – Payroll Withholdings: • Federal Withholding Tax $14.10 • State Withholding Tax $5.45 • FICA $13.77 • What is her Net Pay? • Gross Pay – Payroll Withholdings = Net Pay $180.00 – ($14.10 + $5.45 + $13.77) = $146.68 Federal Withholding Tax On-The-Go Employee SSN Check # Beakens, Joe 201-92-4856 164 Check Amount $1,102.98 Employee Address 293 Michael Grove Billings, MT 59102 Pay TypeGross Pay Deductions Current Year-to-date $1,353.33 Federal Withholding State Withholding Fed OASDI/EE or Social Security Fed MED/EE or Medicare Medical 401K $106.00 $40.82 $83.91 $19.62 $0.00 $0.00 $503.46 $117.72 $636.00 $244.92 $0.00 $0.00 Totals $250.35 $1,502.10 Pay Period 6/11/2004-7/11/2004 Federal Withholding Tax – The amount required by law for employers to withhold from earned wages to pay taxes (Tax Brackets based on income: 10%, 15%, 25%, 28%, 33%, 35%) – The amount of money deducted depends on the amount earned and information provided on the Form W-4 (In this case under 10% was deducted) – Largest deduction withheld from an employee’s gross income State Withholding Tax On-The-Go Employee SSN Check # Beakens, Joe 201-92-4856 164 Check Amount $1,102.98 Employee Address 293 Michael Grove Billings, MT 59102 Pay TypeGross Pay Deductions Current Year-to-date $1,353.33 Federal Withholding State Withholding Fed OASDI/EE or Social Security Fed MED/EE or Medicare Medical 401K $106.00 $40.82 $83.91 $19.62 $0.00 $0.00 $503.46 $117.72 $636.00 $244.92 $0.00 $0.00 Totals $250.35 $1,502.10 Pay Period 6/11/2004-7/11/2004 State Withholding Tax (Approx. 3% in this case) – The percentage deducted from an individual’s paycheck to assist in funding government agencies within the state – The percentage deducted depends on the amount of gross pay earned FICA (Federal Insurance Contribution Act) On-The-Go Employee SSN Check # Beakens, Joe 201-92-4856 164 Check Amount $1,102.98 Employee Address 293 Michael Grove Billings, MT 59102 Pay TypeGross Pay Deductions Current Year-to-date $1,353.33 Federal Withholding State Withholding Fed OASDI/EE or Social Security Fed MED/EE or Medicare Medical 401K $106.00 $40.82 $83.91 $19.62 $0.00 $0.00 $503.46 $117.72 $636.00 $244.92 $0.00 $0.00 Totals $250.35 $1,502.10 Pay Period 6/11/2004-7/11/2004 FICA – This tax includes two separate taxes: Fed OASDI/EE or Social Security and Fed MED/EE or Medicare – These two taxes can be combined as one line item or itemized separately on a paycheck stub Social Security On-The-Go Employee SSN Check # Beakens, Joe 201-92-4856 164 Check Amount $1,102.98 Employee Address 293 Michael Grove Billings, MT 59102 Pay TypeGross Pay Deductions Current Year-to-date $1,353.33 Federal Withholding State Withholding Fed OASDI/EE or Social Security Fed MED/EE or Medicare Medical 401K $106.00 $40.82 $83.91 $19.62 $0.00 $0.00 $503.46 $117.72 $636.00 $244.92 $0.00 $0.00 Totals $250.35 $1,502.10 Pay Period 6/11/2004-7/11/2004 Social Security – Nation’s retirement program, helps provide retirement income for elderly and pays disability benefits – Based upon a percentage (6.2%) of gross income, employer matches the contribution made by the employee Medicare On-The-Go Employee SSN Check # Beakens, Joe 201-92-4856 164 Check Amount $1,102.98 Employee Address 293 Michael Grove Billings, MT 59102 Pay TypeGross Pay Deductions Current Year-to-date $1,353.33 Federal Withholding State Withholding Fed OASDI/EE or Social Security Fed MED/EE or Medicare Medical 401K $106.00 $40.82 $83.91 $19.62 $0.00 $0.00 $503.46 $117.72 $636.00 $244.92 $0.00 $0.00 Totals $250.35 $1,502.10 Pay Period 6/11/2004-7/11/2004 Medicare – Nation’s health care program for the elderly and disabled, provides hospital and medical insurance to those who qualify – Based upon a percentage (1.45%) of gross income Tax Forms – see pages 66-68 • W-2 – reports a worker’s taxable income for the year • 1040EZ – a tax return for filers with no dependents or itemized deductions • 1040A – a tax return that allows more options for income and deductions • 1099- – reports interest earned and selfemployment income (Ex: Landscaper, PT) 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 33 E-Filing – see page 66, 67 • It is a fast and safe way to file a tax return. • You can e-file yourself or hire an authorized e-file provider. • Those who meet adjusted gross income requirements can e-file free. • Refunds are often received much quicker. 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 34