ch05xt
advertisement

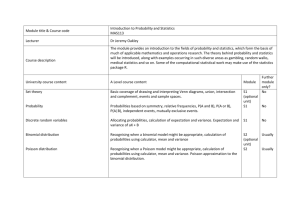
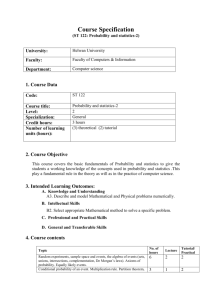
Guide to Using Excel For Basic Statistical Applications To Accompany Business Statistics: A Decision Making Approach, 6th Ed. Chapter 5: Discrete and Continuous Probability Distributions By Groebner, Shannon, Fry, & Smith Prentice-Hall Publishing Company Copyright, 2005 Chapter 5 Excel Examples Binomial Mean Catalog Sales Poisson Distribution Heritage Tile More Examples Chapter 5 Excel Examples (continued) Creating A Creating Binomial Table a Poisson Table Normal Distribution – State Bank and Trust Standard More Examples Chapter 5 Excel Examples (continued) Distribution – Haines Internet Services Exponential Creating A Standard Normal Table Binomial MeanCatalog Sales Issue: People who order items from catalogs can return the items for a refund. Historical return rate for one catalog has been 11 percent. Is this rate still valid? Objective: Use Excel to compute binomial probabilities based on a sample of 300 purchases. Binomial Mean – Catalog Sales Situation Sample Size is n=300 p = .11 Mean = np = 300(.11) = 33 44 returns were observed P(X > 44) = 1 – P(X < 43) Find P(X < 43) = ? Binomial Mean – Catalog Sales Click on Function Wizard – then select Statistical – then Binomdist Binomial Mean – Catalog Sales Binomial Probability function Binomial Probability Result Enter required values. Note, True indicates that you want the cumulative probability – False would indicate that you want the exact probability. Poisson Distribution Heritage Title Issue: The distribution for the number of defects per tile made by Heritage Tile is Poisson distributed with a mean of 3 defects per tile. The manager is worried about the high variability Objective: Use Excel to generate the Poisson distribution and histogram to visually see spread in the distribution of possible defects. Poisson Distribution – Heritage Tile Enter values of x ranging from 0 to 10. Poisson Distribution – Heritage Tile Click on the function button, then select Statistical and Poisson. Poisson Distribution – Heritage Tile Enter the value of x (located in cell a2), the value of the mean and finally false. Poisson Distribution – Heritage Tile Generate the remaining probabilities, then click on the Chart Wizard button. Poisson Distribution – Heritage Tile Enter the correct range of values in the chart wizard. Poisson Distribution – Heritage Tile Provide a title and label the axes as desired. Poisson Distribution – Heritage Tile Complete Histogram as shown in tutorials for Chapter 2. Creating A Binomial Table Issue: The binomial tables in this text contain specific probabilities for certain values of n and p. You may need to have more extensive tables. Objective: Use Excel to generate the Binomial table for n = 25 and p value of .01 to .50 in increments of .01 Creating A Binomial Table Sample size (n) in cell B1 P values in row 3 X values in column A Creating A Binomial Table P(X =0) = .777821 for n = 25, p = .01 Notice the use of absolute cell referencing – this allows you to copy the function across and down to complete this section of the binomial table Creating A Binomial Table Values for X > 11 are all zero – can be dropped from table to save space Creating A Binomial Table Expand the table to include more p values. Note, make sure your cell referencing is correct. – then copy cells Creating A Binomial Table Continue this process for all p values. For different sample sizes, replace n in cell B1 Creating A Poisson Table Issue: The Poisson tables in this text contain specific probabilities for certain values of . You may need to have more extensive tables. t Objective: Use Excel to generate the Poisson Table table for = 6.0 to 7.0 in increments of .10 t Creating A Poisson Table values in row 2 t Values of X in column A Creating A Poisson Table t P(X = 0) for = 6.0 equals .00248 Notice the use of absolute cell referencing – this allows you to copy the function across and down to complete this section of the binomial table Creating A Poisson Table t Continue this process for other values as desired. As increases, the possible values for X will have to increase. t Standard Normal DistributionState Bank and Trust Issue: State bank managers have studied the time customers spend at the bank on business. They plan to offer a gift certificate to any customer who is required to spend over 40 minutes on bank business. Objective: Use Excel to analyze to create histogram and determine the probability that a certificate will be given to any customer. The data file is State Bank.xls. Standard Normal – State Bank and Trust Open Data File: State Bank.xls Standard Normal – State Bank and Trust Create Bins (Upper Limits of each class) Standard Normal – State Bank and Trust Click on Tools – Data Analysis Histogram Standard Normal – State Bank and Trust Define Data and Bin ranges and specify where you want the output to go. Check Chart Output Standard Normal – State Bank and Trust Close Gaps in Histogram by selecting chart bars, right clicking and selecting Chart Object – Options – and then change Gap width to 0 Standard Normal – State Bank and Trust Add labels and format horizontal axis. Next, determine probability of a service time exceeding 30 seconds. Standard Normal – State Bank and Trust Select Function Wizard – Then Click on Statistical – then select Normdist function Standard Normal – State Bank and Trust Enter X =30, mean = 22.14, st dev = 6.09, and True for cumulative probability P(X <30) = .9016 Exponential DistributionHaines Internet Services Issue: The time between connect attempts averages two minutes and the distribution of time between attempts is assumed to be exponential. Objective: Use Excel to compute the probability that that the time between connect attempts will be less than 45 seconds (.75 minutes). Exponential Distribution – Haines Internet Services Click on Function Wizard – then select Statistical – then EXPONDIST Exponential Distribution – Haines Internet Services EXPONDIST function – note, that =.50 is used rather than the mean = 1 Exponential Distribution Probability Result P(X < .75) = .3127 Enter required values. Note, True indicates that you want the cumulative probability – False would indicate that you want the exact probability. Creating A Standard Normal Distribution Table Issue: The Standard Normal tables in the Appendix of this text were created using Excel. Objective: Use Excel to generate a standard normal table for z values below zero. Creating the Standard Normal Table Z value second decimal place Z value integer and first decimal place. Creating the Standard Normal Table Formula: ABS function is for absolute value Mean for NORMDIST function is -0.0 .01 = - .01 Notice use of absolute cell references to allow formula to be copied across and and down to finish the table Creating the Standard Normal Table Probabilities correspond to area on the standard normal table between the Z value and the mean = 0.