Viruses ppt 2013
advertisement

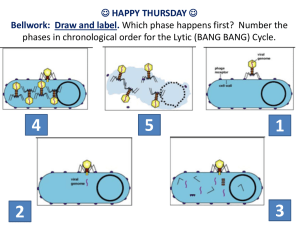
Viruses Section 21.1 Learning Targets Discuss the difficulties in classifying a virus. Describe, identify, and label the parts of a T4 Bacteriophage virus. Define:Virion, Lysis, Prophage, Bacteriophage, Host cell, Vector, Interferon, Virulence Discuss the characteristics in which a virus is classified. Describe how viruses multiply: lytic and lysogenic cycles (most likely will not get to this one) Discuss why viruses might be considered parasitic. Know the name of the person and the history of the first virus that we identified Are Viruses Alive? Do they go through metabolism? Do they grow and develop? Do they reproduce? On own? Viral Characteristics Smaller than the smallest known cell Carry on no life functions on own (must have host) Replicate ( reproduce) only if in a living cell – parasite) Found in air, soil, and water What is the structure of a virus? ( 2 main parts) NUCLEIC ACID CORE DNA or RNA contains instructions only for making copies of the virus PROTEIN COAT Capsid to protect DNA/RNA ENVELOPE (additional coat) outside the capsid – some Viruses, not all. Viral envelope surrounds the capsid of some large viruses consists primarily of phospholipids influenza and HIV Because of the UNIQUE shape of the protein coat and/or the envelope, viruses are usually very SPECIFIC as to what they attack. -some viruses are limited to attacking a SINGLE species of organism (1 type of host cell) Ex: SMALL POX is found only in humans Ex: POLIO only attacks the nerve cell Virus Classification SHAPE Type of NUCLEIC ACID (DNA / RNA) Whether they have an ENVELOPE or not? Type of HOST they infect How they are transmitted (i.e. = vectors) How they replicate lytic or lysogenic Viral shape (4 types) determines what cell can be infected & how the virus infects the cell Polyhedral viruses – many sided many are polygons with 20 sides –polio Other Examples: Herpes (cold sores) Chix pox Cold virus Spherical (i.e. HIV, some flu) Rod Shaped (TMV, herpes, flu) Polyhedral with a tail bacteriophage Body Defenses Against Viruses WHITE BLOOD cells ANTIBODIES (specific, commpounds that tie up specific viruses) - can remain in the body and “REMEMBER” viruses that have attacked before INTERFERON – protein that prevents viral replication VACCINES – harmless form of a virus that causes our body to produce antibodies History of Viruses Tobacco mosaic virus first virus to be discovered by Dimetri Ivanoski in 1880’s has a cylindrical shape infects plants, especially tobacco shows characteristic patterns (mottling and discoloration) on the leaves TMV crystallized in 1935 ( living organisms cannot be crystallized) http:/babylon.com Vector Organism or object that transmits a virus Ex’s: Rats insects birds Bacteriophage virus that infects bacteria has a polyhedral head containing DNA, a protein tail, and protein tail fibers T4 virus Virulence Degree in which a virus causes a disease Video: Flu Attack (love this video) – Rknot – reproductive rate how efficient the virus is at spreading - # people infected by one person R0 Viral Lecture part II Label the bacteriophage!! Viral Replication A virus needs the Nucleic acids and proteins found in living cells to replicate ( reproduce) 2 Types of Reproduction… Lytic Cycle: the virus destroys the host cell during reproduction What causes cold symptoms? 1. Adsorption/ Attachment every virus has a specifically shaped attachment protein each virus can only attach to a few kinds of cells like 2 pieces of a jigsaw puzzle fitting together 1. Virus attaches to cell with tail fibers, to adhere to receptors on the host cell. http://www.studyblue.com/notes/note/n/phage-lyticcycle/deck/2958162 Bacteriophages attaching to bacterium engineering.curiouscatblog.net 2. Entry and Invasion 1. Virus can inject its nucleic acid into the host cell Protein capsid stays attached to the outside of the host cell 3. Replication The viral genes take over the host cell and force the host cell to become a virus factory (coats and nucleic acids are made) 4. Assembly New viruses are assembled from the protein coats and nucleic acid made during replication Virions: newly replicated viruses 5. Lysis and Release Enzymes made by the invading virus causes lysis – bursting of the host cell The virions are released to go through this cycle in hundreds of more of the host’s cell HIV(green dots) emerging from white blood cell (littleenigma.tumblr.com) http://www.mcatzone.com/t2.ph Adsorption and Entry Lytic cycle video clip Lytic Cycle Examples Cold (rhinovirus, cornavirus, adenovirus) Flu (influenza) Herpes Simplex Virus Epstein Barr Virus ( cancer?) Lysogenic cycle – not immediate cell destruction Provirus = viral DNA that has been integrated into host cell’s chromosome does NOT interfere with normal functioning of host cell is replicated every time host cell reproduces can at any time pop out of host cell’s chromosome & enter a lytic cycle What are some diseases caused by proviruses? herpes simplex I virus causes cold sores hepatitis B chicken pox virus can cause shingles later in life Lysogenic Cycle Stages 1. 2. 3. Attachment and Entry – the viral DNA enters the host cell similar to lytic cycle Prophage formation ( DNA becomes part of host cell DNA) Eventual Lysis of infected host cells: some time in future the infected host cells enter the lytic phase and will cause lysis to release thousands of viruses and symptoms appear What is a retrovirus? RNA is its only nucleic acid contains reverse transcriptase enzyme that changes RNA into DNA viral DNA is integrated into host cell’s chromosome & becomes a provirus evidence for infection by a retrovirus What is HIV ( HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS)? retrovirus that causes AIDS new viruses are produced slowly because the viral genetic material is a provirus ( lysogenic) Transmission: through body fluid -sexual contact -needles and blood -mother to fetus infects white blood cells function until proviruses enter a lytic cycle & kill their host cells HIV Symptoms: swollen glands, loss of appetite and weight, night sweats, fatigue. Most people die of pneumonia or other disease. Facts on AIDS ( acquired immunodeficiency disease) CDC in Atlanta survey says: (updated 2012) 25% of teens report having 4 different sex partners in teen yrs 35% of teens consistently use birth control. 50% of teens are sexually active! 1 in 50 teenagers have injected drugs 93-98% of teens are aware AIDS is transmitted by sexual contact and I.V. drug use! 40,000-80,000 new cases each year 4,000+ from teenagers in high school For those who received HIV Today… Every 9.5 minutes someone new is infected with HIV 10% of you will see no symptoms of AIDS for 5 yrs. 50% will see no symptoms for 10 years. 40% will see no symptoms for 15 years. All will die within 10 years of the symptoms! AIDS is a DEATH SENTENCE! What are prions? particles that behave like viruses & cause infectious diseases made up of proteins but have no genetic material cause other proteins to malfunction responsible for mad cow disease What are viroids? particles that behave like viruses & infect plants single circular strand of RNA with no protein coat enter & infect host plant through wounds or insect bites cause beautiful patterns of color Viruses that live in animals without causing harm, but cause disease when they infect other animals or humans are a real threat to society.- Emergent Viruses – They are difficult to study because it is not always obvious where the source of the virus is, nor the means of transmission…..An example of this is Ebola….movie contagion WHAT IS THE CDC?