8.2 PowerPoint
advertisement

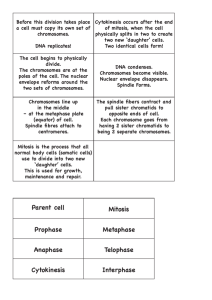
Remember…. • Cell Theory1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cells is the basic unit of structure. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. Cell Theory #2 In Detail • ORGANIZATION of LT – Cells -> Tissues – Tissues organize into organs – Multiple organs work together to for an organ system – All systems work together for survival of the organism Why does a cell need to divide? IN GENERAL• All organisms grow and change • Worn-out tissues are repaired or are replaced by newly produced cells. Why does a cell need to divide? SPECIFICALLY: Cell Size Limitations 1. Diffusion: short distances = efficient; long distances = inefficient • Think running 1/4mi vs. running 24 mi. 2. DNA: must be copied and made into protein to make necessities…can only be done so fast. • Think about copying homework for 1 class in 5 minutes vs. 7 classes in 5 minutes 3. Surface Area-to-Volume ratio: volume will become to much for the PM’s surface area to handle. • Think about a city growing, but no one builds new roads or bridges etc.= traffic jam http://openlearn.open.ac.uk/file.php/2815/S324_1_009i.jpg A Cell’s Life – Describe the cell cycle The Cell Cycle 1. Interphase – Longest Part of Cycle – – – “Growing Stage” - cell grows (G1, S, G2) carries on metabolism, spends most of its time here. (G1, S, G2) DNA is copied (S only) A Cell’s Life – Describe the cell Cycle 2. Mitotic Phase a.) Mitosis : chromosomes divide b.) Cytokinesis: cytoplasm divides into 2 HONORS • Chromatin - long strands of DNA wrapped around histones. • Must copy DNA • Supercoil to form chromosomes composed of two halves called sister chromatids: exact copies of each other held together by centromeres micro.magnet.fsu.edu/ cells/nucleus/images/chr... How do cells reproduce/divide? a.) MitosisI. Prophase – – – – longest phase Sister chromatids join Nucleus (envelope and nucleolus) disintegrate mg.sparknotes.com/ 8.2 Cell Growth and Reproduction Mitosis cont’ II. Metaphase – – Chromosomes pulled to the equator (middle) mg.sparknotes.com/ 8.2 Cell Growth and Reproduction Mitosis cont’ III. Anaphase– Chromosomes split and sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell mg.sparknotes.com/ 8.2 Cell Growth and Reproduction IV. Telophase– Chromatids reach the opposite poles (ends), What is Cytokinesis? b.). Cytokinesis - cytoplasm divides, cells separate into two daughter cells. mg.sparknotes.com/ Honors: What is cytokinesis? • Animal cells: plasma membrane pinches in along the equator • Plant cells: a cell plate is laid down across the cell’s equator and a cell membrane forms around each cell. New cell walls form on each side of the cell plate until separation is complete What is the end result of Mitosis? • Two identical cells that are identical to the original parent cell. – will carry out the same cellular processes and functions as those of the parent cell – will grow and divide too Specifically • Unicellular organisms = doubled number of organisms. Called asexual reproduction • Multicellular organisms = growth = more tissue. Can you find all the stages?