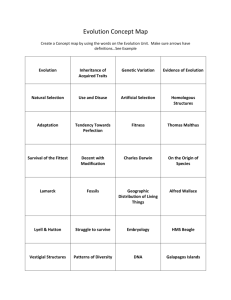
File
advertisement
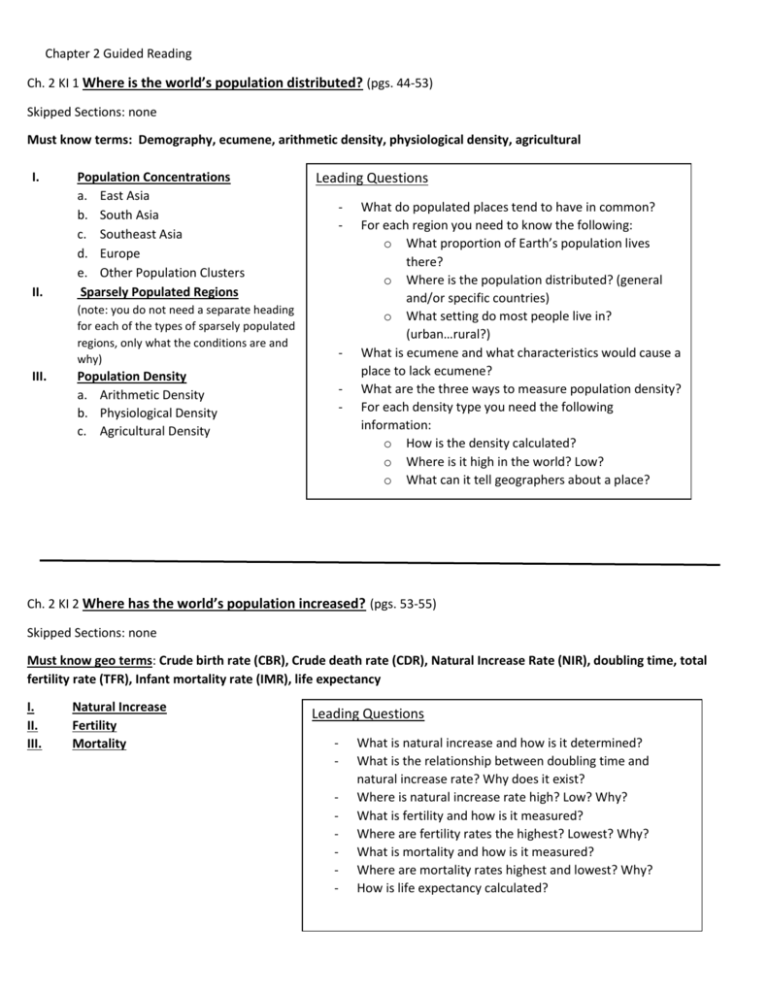
Chapter 2 Guided Reading Ch. 2 KI 1 Where is the world’s population distributed? (pgs. 44-53) Skipped Sections: none Must know terms: Demography, ecumene, arithmetic density, physiological density, agricultural I. II. Population Concentrations a. East Asia b. South Asia c. Southeast Asia d. Europe e. Other Population Clusters Sparsely Populated Regions (note: you do not need a separate heading for each of the types of sparsely populated regions, only what the conditions are and why) III. Population Density a. Arithmetic Density b. Physiological Density c. Agricultural Density Leading Questions - - What do populated places tend to have in common? For each region you need to know the following: o What proportion of Earth’s population lives there? o Where is the population distributed? (general and/or specific countries) o What setting do most people live in? (urban…rural?) What is ecumene and what characteristics would cause a place to lack ecumene? What are the three ways to measure population density? For each density type you need the following information: o How is the density calculated? o Where is it high in the world? Low? o What can it tell geographers about a place? Ch. 2 KI 2 Where has the world’s population increased? (pgs. 53-55) Skipped Sections: none Must know geo terms: Crude birth rate (CBR), Crude death rate (CDR), Natural Increase Rate (NIR), doubling time, total fertility rate (TFR), Infant mortality rate (IMR), life expectancy I. II. III. Natural Increase Fertility Mortality Leading Questions - What is natural increase and how is it determined? What is the relationship between doubling time and natural increase rate? Why does it exist? Where is natural increase rate high? Low? Why? What is fertility and how is it measured? Where are fertility rates the highest? Lowest? Why? What is mortality and how is it measured? Where are mortality rates highest and lowest? Why? How is life expectancy calculated? Ch. 2 KI 3 Why is population increasing at different rates in different countries? (pg. 56-66) Skipped Sections: Contemporary Geographic Tools: Spatial Analysis and the Census (62) Must Know Geo Terms: The Demographic Transition Model (DTM), the Agricultural Revolution, the Industrial Revolution, The Medical Revolution, zero population growth (ZPG), population pyramid, dependency ratio, census I. II. III. IV. V. Demographic Transition Model a. Stage 1 Low Growth b. Stage Two: High Growth c. Stage Three: Moderate Growth d. Stage 4: Low Growth e. Figure 2-17 Population Pyramids a. Age Distribution b. Sex Ratio Different Countries in Different Stages of Demographic Transition a. Cape Verde: Stage 2 b. Chile: Stage 3 c. Denmark: Stage 4 Japans Population Decline (case study on pg 65) Demographic Transition and World Population Growth Leading Questions - - - What is the demographic transition? What does it measure? For each stage (I. A-D) you need to include the following: o What is happening to CBR, CDR, and NIR? Why? o What major world events took place that would affect demographics? o When do countries go through each stage? What is a population pyramid? How are they constructed? What is dependency ratio? What can it tell geographers about a plcae? What is sex ratio? What can it tell geographers about a plcae? For each example under III. you must have the following information: o Describe the demographic structure of the country. o Explain why that country is in that stage. What demographic trends do we see in Japan? Why? What has been the effect? Generalize the global demographic trends the DTM predicts. Why do these trends occur? Ch. 2 KI 4 Why might the world face an overpopulation problem? (66-73) Skipped Sections: none Must Know Geography Terms: Thomas Malthus, epidemiologic transition, pandemic I. II. III. Malthus on Overpopulation a. Contemporary Malthusians b. Malthus’s Critics c. Malthus’s Theory and Reality Declining Birth Rates a. Reasons for Declining Birth Rates b. Reducing Births Through Contraceptives World Health Threats a. Epidemiologic Transition Stages 1 and 2 b. Epidemiologic Transition Stages 3 and 4 c. Epidemiologic Transition Possible Stage 5 Leading Questions - Who is Malthus? What did he believe? What parts of Malthus’s theory do people still believe today? What parts of Malthus’s theory do people think Malthus should have included? What do critics of Malthus claim? How have Malthus’s views stood the test of time? What was right and what was wrong? What is the Epidemiologic transition? What occurs in each stage of the transition? Why? What could the future hold in terms of the epidemiologic transition?