Spelling, punctuation and grammar in year 3
advertisement

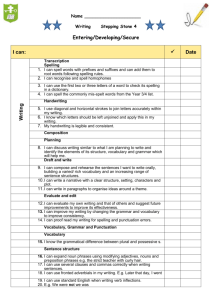
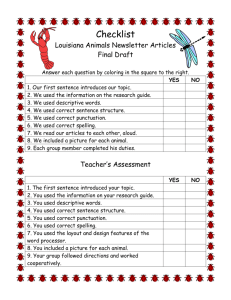
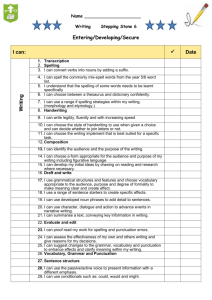
SPELLING, PUNCTUATION AND GRAMMAR IN YEAR 3 A BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE YEAR 3 EXPECTATIONS IN ENGLISH ENGLISH • Spoken Language • Reading (Word-reading, comprehension) • Writing (Transcription, Composition and ‘Spelling, Punctuation and Grammar’) NATIONAL CURRICULUM “Pupils should be able to write down their ideas with a reasonable degree of accuracy and with good sentence punctuation. Teachers should therefore be consolidating pupils’ writing skills, their vocabulary, their grasp of sentence structure and their knowledge of linguistic terminology”. TIMETABLE 8:40 8:50 9:00 9:15 Class assembly Monday 9:15 9:45 9:45 10:45 10:45 11.00 11.10-12.10 12:10-12.30 Numeracy Guided reading Assembly 13:45 15:25 Literacy Phonics (KS1) Topic Guided reading ICT Literacy Numeracy with DP French With LM Guided reading Numeracy Phonics (KS1) SPAG Phonics (KS1) LUNCH SPAG Literacy BREAK Assembly Music Literacy RE With L Coca Music Assembly Numeracy R4P Thursday REGISTRATION – Handwriting Wednesday 13:30 13:45 R4P SPAG Phonics (KS1) SPAG Tuesday 12:30 13:30 Guided reading SPAG PE with SPORTS COACH 2.20-3.25 Science R4P Guided reading Assembly Friday Phonics (KS1) Numeracy Literacy Topic SPELLING Pupils’ spelling of common words should be correct, including common exception words and other words that they have learnt. Pupils should spell words as accurately as possible using their phonic knowledge and other knowledge of spelling, such as morphology and etymology. STATUTORY SPELLING LIST • Words that are taught through spelling lessons, writing lessons and other lessons across the curriculum • Used as a measure of proficiency in spelling, in line with age-related expectations SPELLING Pupils Should Be Taught To: • Use further prefixes and suffixes and understand how to add them • Spell further homophones (e.g. to, two, too) • Spell words that are often misspelt (English Appendix 1) • place the possessive apostrophe accurately in words with regular plurals [for example, girls’, boys’] and in words with irregular plurals [for example, children’s] • use the first two or three letters of a word to check its spelling in a dictionary • write from memory simple sentences, dictated by the teacher, that include words and punctuation taught so far. PUNCTUATION • using commas after fronted adverbials • indicating possession by using the possessive apostrophe with plural nouns • using and punctuating direct speech (using inverted commas, not ‘speech marks’) GRAMMAR Pupils should be taught to develop their understanding of the following concepts: extending the range of sentences with more than one clause by using a wider • range of conjunctions, including when, if, because, although • choosing nouns or pronouns appropriately for clarity and cohesion and to avoid repetition • using conjunctions, adverbs and prepositions to express time and cause • using fronted adverbials FRONTED ADVERBIALS Here is an example of a fronted adverbial: TERMINOLOGY • use and understand the grammatical terminology in English Appendix 2 accurately and appropriately when discussing their writing and reading. Vocabulary, grammar and punctuation Year 3: Detail of content to be introduced (statutory requirement) Word Formation of nouns using a range of prefixes [for example super–, anti–, auto–] Use of the forms a or an according to whether the next word begins with a consonant or a vowel [for example, a rock, an open box] Word families based on common words, showing how words are related in form and meaning [for example, solve, solution, solver, dissolve, insoluble] Sentence Expressing time, place and cause using conjunctions [for example, when, before, after, while, so, because], adverbs [for example, then, next, soon, therefore], or prepositions [for example, before, after, during, in, because of] Text Introduction to paragraphs as a way to group related material Headings and sub-headings to aid presentation Use of the present perfect form of verbs instead of the simple past [for example, He has gone out to play contrasted with He went out to play] Punctuation Introduction to inverted commas to punctuate direct speech Terminology for pupils preposition, conjunction word family, prefix clause, subordinate clause direct speech consonant, consonant letter vowel, vowel letter inverted commas (or ‘speech marks’) QUESTIONS