File
advertisement

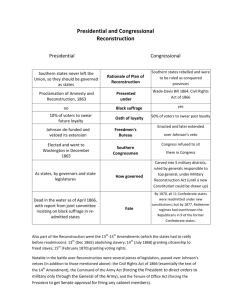
RECONSTRUCTION 1865 - 1877 The 12 years of readjustment following the Civil War when the nation faced the problems of rebuilding and reuniting the country, while also ensuring the protection of newly freed African Americans. 1863 - 1865 Lincoln's 10 % Plan or Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction http://www.american-historama.org/1860-1865-civil-war-era/ten-percent-plan.htm GOAL: restore the Union quickly 10% of state voters must take an oath of loyalty to rejoin the Union Form new state governments (1/10th of number of voters who participated in the 1860 election) Amnesty for Confederates, Restore property (except slaves) EXCEPT for the highest Confederate officials and military leaders Accept abolition of Slavery (1865 - 13th Amendment) CRITICS: Republicans in Congress felt Lincoln's plan was not tough enough and didn't protect the newly freed slaves properly 1864 Wade-Davis Bill GOAL: create a Reconstruction plan that would penalize Confederates more and better protect blacks created by Radical Republicans, Senator Benjamin Wade of Ohio and Representative Henry Winter Davis of Maryland Majority of state's white males must pledge loyalty to the Union and Constitution Guarantee black equality before the law (but not the right to vote) - abolish slavery Elections would create a new state constitution Conventions would be restricted to those who swore an Ironclad oath (never aided the Confederacy) No Confederate officials could participate in the new governments Lincoln used pocket veto and bill FAILED AP Study Notes: http://www.apstudynotes.org/us-history/topics/presidential-and-congressional-reconstruction-plans/ 1865 March Freedman's Bureau - agency to help former slaves transition to freedom O.O. Howard – commissioner Succeed in establishing education and healthcare Help slaves find work, get educated, and medical aid Fail to distribute land – Johnson takes back land and returns to former owners Program ended by 1870 William T. Sherman's Special Field Order 15 set aside the Sea Islands and 40 acres for black families in SC and GA http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/reconstruction/40acres/ps_so15.html Johnson ends up evicting freedmen off of Sherman land to return it to former owners 1865 April 14th Lincoln is Assassinated by John Wilkes Booth Background of Assassination: http://memory.loc.gov/ammem/alhtml/alrintr.html Timeline: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/americanexperience/films/assassination/ 1865 May 29 Andrew Johnson assumes the Presidency - Presidential Reconstruction Confederates take an oath of loyalty to the Union Exclude Confederates with property worth over $20,000, But Pardon individual Confederates (13,000 pardons) (felt wealthy Southerners led the South into secession) State Conventions repeal ordinances of secession Ratify 13th Amendment - abolish slavery State's Rights - allowed new state governments freedom to manage their affairs CRITICS: Confederacy back to same old ways. Prominent Confederate leaders returned to power. AP Study Notes: http://www.apstudynotes.org/us-history/topics/presidential-and-congressional-reconstruction-plans/ 1865 Black Codes Freedmen made up 40% of population in former slave states; Southern Legislators feared their voting power, passed several 'Black Codes' creating barriers to voting: literacy requirements, poll taxes, residency requirements Southern states pass repressive "Black Codes" to preserve something close to slavery Created a separate class for blacks: (vary state to state) Can: black marriage recognized, testify in court with other blacks, own certain property Cannot: travel without permits, serve on a jury, vote, carry firearms, marry whites, testify against whites Arrested on vagrancy charges if former slave failed to sign yearly labor contracts (assigned to gang labor if don't sign a contract) CRITICS: Republicans felt that free labor principles were violated and former slaves not truly freed. Sharecropping https://www.gilderlehrman.org/history-by-era/reconstruction/timeline-terms/sharecroppers was preferred to gang labor (heavy supervision), but wasn't a means to betterment a system where black families and poor whites would rent part of a plantation, raise a crop and divide it with the owner dominate in the Cotton Belt and Tobacco Belt of NC and VA Crop-lien system farmers didn't own land, so put their crop up as credit to purchase supplies for cultivation crop was collateral if farmer couldn't pay merchant for supplies later Debt - cotton prices decreased, couldn't pay back loan, so grow more cotton to pay Page 298 Case Study of Matt Brown 1865 December Congress Reconvenes Reconstituted southern states sent representatives to the Capitol and Congressional Republicans denied seats to all members of the eleven former Confederate states AP Study Notes: http://www.apstudynotes.org/us-history/topics/presidential-and-congressional-reconstruction-plans/ 1866 Civil Rights Act 1st major law to be passed over a Presidential veto (2/3rds vote in Congress) defined rights of citizens regardless of race Equality before the law No state could deprive a citizen the right to make contracts, bring lawsuits, enjoy equal protection 1866 June 14th Amendment (proposed by Congress, ratified in 1868) empowered the federal government to protect rights of all citizens provided for equal protection under the law regardless of race (guarantee legal equality) most important change in the U.S. Constitution since the Bill of Rights 1867 March Reconstruction Act Congressional Reconstruction OR Radical Reconstruction ends 1877 Reconstruction Act passes over Johnson's veto South divided into 5 military districts, occupied by Union troops Create new state governments - grant black men right to vote (suffrage) Ratify 14th Amendment 1877, last federal troops left the south 15th Amendment - ratified in 1870 guaranteed black suffrage and ensured states couldn't remove this from their new state constitutions later Tenure of Office Act - bar President from removing officeholders / cabinet members without Senate consent 1868, Andrew Johnson removed Secretary of War Edwin Stanton (Radical Republican) and the House of Representatives impeached him for violated the Tenure of Office Act Senate acquitted him because his lawyers promised Republicans he would behave and stop interfering in the Reconstruction policy. AP Study Notes: http://www.apstudynotes.org/us-history/topics/presidential-and-congressional-reconstruction-plans/ 1868 Election of 1868 - Ulysses S. Grant (Civil War hero) elected as President 1870 - 1871 Enforcement Acts stop the activities of terrorist groups - Ku Klux Klan KKK - terrorist organization founded in Tennessee in 1866 Grant sent federal marshals and troops into southern areas to arrest Klansmen 1873 - Colfax, Louisiana bloodiest act of violence where armed whites killed hundreds of former slave 1870's Reconstruction fades Republicans become more complacent about Reconstruction due to the loss of Radical Republicans like Thaddeus Stevens http://www.biography.com/people/thaddeus-stevens21011351 Redeemers (Democrats of the South who "redeemed" the white South from corruption, misgovernment, and northern and black control) Grant Administration became complacent about enforcing maintaining Reconstruction in South Example - Governor Adelbert Ames of Mississippi asked Grant for help when white rifle clubs drilled in public and assaulted and murdered Republicans - Grant responded that the northern public was "tired out" by southern problems 1875 Civil Rights Act prohibit discrimination in jury selection, transportation, restaurants, and other public areas (didn't have enforcement for 90 years) 1876 - 1877 Presidential Election of 1876 / Bargain of 1877 Republicans nominate Governor Rutherford B Hayes (OH) Democrats nominate Governor Samuel J. Tilden (NY) Republicans still in control of SC, FL, LA Bargain of 1877 brings Hayes in as President, led to the appointment of a southern postmaster general https://www.boundless.com/u-s-history/reconstruction-1865-1877/the-grant-presidency/the-compromise-of-1877/ AP Study Notes: http://www.apstudynotes.org/us-history/topics/presidential-and-congressional-reconstruction-plans/ Compare and contrast the efforts for and against the increasing of guarantees for equal rights for all during Reconstruction. To save time, write a thesis statement then write only the body of an essay. Use example from above to reflect the varied efforts for equality during Reconstruction. THESIS: BODY: AP Study Notes: http://www.apstudynotes.org/us-history/topics/presidential-and-congressional-reconstruction-plans/