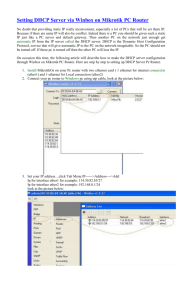
dhcp - mastii
advertisement
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol 1 Objectives Describe the DHCP lease and renewal process Understand and describe the purpose of a DHCP relay Install DHCP Configure DHCP scopes, superscopes, reservations, vendor classes, and user classes Manage and monitor DHCP Troubleshoot DHCP Install and configure a DHCP relay 2 The DHCP Process Used to automatically deliver IP addressing information to client computers on a network Can also deliver IP address information to servers and other devices such as printers Use of DHCP reduces time spent configuring computers on network Client computers use DHCP by default unless static IP address is specified during installation 3 Windows XP TCP/IP Properties 4 Processan to lease an address is composed of four Leasing IP Address packets DHCPDISCOVER: sent from the client computer to the broadcast IP address 255.255.255.255 DHCPOFFER: response sent after receiving DHCPDISCOVER packet DHCPREQUEST: response of DHCP client after receiving DHCPOFFER packet DHCPACK: response sent by chosen DHCP server indicating confirmation that lease has been chosen and client can now use the lease 5 The Four Packets in the DHCP Lease Process 6 Renewing an leased IP Address An IP address using DHCP can be either permanent or timed Permanent address DHCP server never reuses the address for another client Timed lease Allows clients to use an IP address for a specified period of time Windows clients attempt to renew their lease after 50% of lease time has expired ipconfig /release command is used to force the release of a DHCP address 7 The DHCP Lease Renewal Process 8 DHCP packets DHCP Relay Are broadcast packets during the leasing process Cannot travel across a router DHCP relay Receives broadcast DHCP packets from clients and forwards them as unicast packets to a DHCP server Must be configured with IP address of the DHCP server to deliver unicast packets DHCP Relay Service cannot be installed on the same server as the DHCP Service 9 Installing DHCP 10 Authorization Control over DHCP is very important An unauthorized DHCP server can quickly hand out incorrect IP addressing information to hundreds of client computers To exercise control over DHCP Windows Server 2003 must be authorized to start DHCP Service Authorization of a DHCP server takes place in Active Directory 11 Authorization (Continued) To authorize DHCP server Must be a member of Enterprise Admins group or Member of Enterprise Admins group must delegate permissions to you 12 Unauthorized DHCP server error in Event Viewer 13 The DHCP Management Snap-In 14 Authorized DHCP server information in Event Viewer 15 Configuring DHCP Normally accomplished with the DHCP management snap-in NETSH Command used to configure DHCP Used in larger organizations where there is a need to make changes programmatically using batch files 16 Configuring DHCP (Continued) DHCP elements that can be configured include Scopes Superscopes Multicast scopes Reservations Vendor and user classes Scope, server, and reservation options 17 Used to define a range of IP addresses for the Scopes DHCP server to hand out to client computers Each scope is configured with Name Description Starting IP address Ending IP address Subnet mask Exclusions Lease duration 18 Name and description Scopes (Continued) Appears in the DHCP management snap-in Starting and ending IP addresses Define range of IP addresses that can be handed out by the DHCP server Strategies when defining starting and ending IP addresses Configure scope to use all available addresses on a subnet, then exclude the static IP addresses being used by hosts Configure scope to use addresses that are not already in use 19 Exclusions Scopes (Continued) Used to prevent some IP addresses in a scope from being handed out dynamically Lease duration Defines how long client computers are allowed to use an IP address Default lease duration used by Windows Server 2003 is eight days DHCP server Does not begin using a scope immediately after creation Scope must be activated before DHCP Service can begin using the scope 20 Scope Settings 21 Superscopes Used to combine multiple scopes into a single logical scope Used when a single physical part of the network has two subnets 22 A Superscope Containing Two Scopes 23 Multicast Scopes Used to deliver multicast addresses to applications that require it Time To Live (TTL) Defines the number of routers through which a multicast packet can move Exclusions Define addresses between the start and end IP addresses that are not handed out Lease duration The length of time that an application can use a multicast address Default lease length is 30 days 24 Reservations Used to hand out a specific IP address to a particular client computer or device on the network Can also be beneficial when firewalls are in place Created based on the MAC address of the network card 25 Creating a Reservation 26 Configuring Options DHCP can hand out the following IP configuration options Default gateway DNS server WINS server DNS is often configured at the server level 27 Summary DHCP Dynamically assigns IP addresses Can assign multicast IP addresses DHCP lease process Composed of DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, DHCPREQUEST, and DHCPACK DHCPNAK: used by DHCP servers to decline renewal of lease DHCPRELEASE: used by clients to inform DHCP server that lease is no longer required 28 Summary (Continued) Renewing lease Clients attempt to renew at 50%, 87.5%, and 100% of lease time Commands ipconfig /release and ipconfig /renew Can release and renew DHCP leases DHCP server Must be authorized in Active Directory to lease addresses Must be member of Enterprise Admins to authorize DHCP 29 Summary (Continued) Scope Defines range of IP addresses that are leased to clients Must be activated before DHCP server leases addresses in the scope Superscope Combines two scopes into single scope Exclusion in scope Used to stop a DHCP server from handing out specific addresses or range of addresses within a scope 30