manage and resolve conflict situations
advertisement

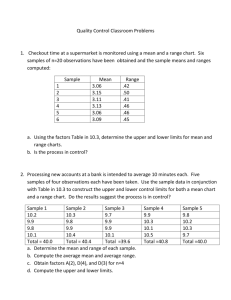
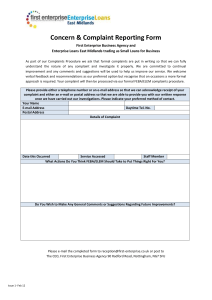
MANAGE AND RESOLVE CONFLICT SITUATIONS Unit Code: D1.HRS.CL1.09 D1.HOT.CL1.11 D2.TCC.CL1.06 Slide 1 Manage & resolve conflict situations This unit comprises three Elements: Respond to complaints Identify & manage conflict situations Resolve conflict situations. Slide 2 Assessment Assessment for this unit may include: Oral questions Written questions Work projects Workplace observation of practical skills Practical exercises Formal report from employer or supervisor. Slide 3 Respond to complaints Performance Criteria for this Element are: Handle complaints sensitively, courteously and discreetly Take responsibility for resolving conflict Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures. Slide 4 Handle complaints A complaint is made by a customer or guest because they are dissatisfied – causes may be: The business failing to keep a promise Service and or products Actions of others in the business. Slide 5 Handle complaints The list of possible causes for complaints is large. Following is a representative list of common causes of customer complaint: Levels of service Product standards (Continued) Slide 6 Handle complaints Processes Information given Charges and fees (Continued) Slide 7 Handle complaints Marketing materials Failing to keep promises Condition of the premises (Continued) Slide 8 Handle complaints The environment Issues relating to other patrons. Slide 9 Handle complaints When dealing with a complaint the objective is to: Convert a bad customer experience into a positive one. Slide 10 Handle complaints It is important to deal with complaints in a friendly, efficient and thorough manner characterised by: Sensitivity Courtesy Discretion. Slide 11 Handle complaints Being sensitive when handling conflict: Take a few seconds to assess the situation before acting Factor in all relevant issues Make requests and give suggestions Avoid issuing ultimatums (Continued) Slide 12 Handle complaints Take into account how the person feels about the situation See things from the other person’s point-of-view Understand their disappointment, annoyance and frustration Acknowledge the legitimacy of their complaint. Slide 13 Handle complaints Handling complaints with courtesy involves: Never shout at them Never interrupt them Never touch them Never threaten them (Continued) Slide 14 Handle complaints Never using or responding with bad language or behaviour Always demonstrate respect Use ‘please’ and ‘thank you’ Use the customer name. Slide 15 Handle complaints Handling complaints discretely involves: Talking in a soft voice Not discussing previous events Asking person to move to a private area. Slide 16 Handle complaints Always maintain a positive and cooperative approach: Adopt the ‘right attitude’ Let them talk (‘vent’) Demonstrate willingness to resolve the problem Create a friendly atmosphere Maintain positive customer relations. Slide 17 Take responsibility for resolving complaints Most common ways of identifying a complaint exists: Being informed by a customer Monitoring the business environment. Slide 18 Take responsibility for resolving complaints ‘Warning signs’ that there may be a complaint: Raised voices Facial expressions and or body language indicators Certain actions undertaken by guests at table (Continued) Slide 19 Take responsibility for resolving complaints ‘Unacceptable actions’ Overheard conversations. Slide 20 Take responsibility for resolving complaints Always apologise whenever a complaint is made: Give the apology freely Give it regardless of the nature of the complaint Even if you believe no legitimate grounds for complaint exists. Slide 21 Take responsibility for resolving complaints Providing an apology: Creates a positive environment Indicates a willingness to respond Demonstrates your involvement in the process Is very customer-focussed. Slide 22 Take responsibility for resolving complaints Taking responsibility for finding a solution: Must occur immediately after the apology Enables the resolution process to begin – never ignore a complaint Is necessary because this is usually what the customer wants. Slide 23 Take responsibility for resolving complaints Ways to take responsibility for resolving complaints include: Introducing yourself Making an offer of assistance Investigating the complaint: • Asking questions • Listening Suggesting or offering possible solutions. Slide 24 Take responsibility for resolving complaints Personal characteristics useful in resolving complaints and or conflicts: Being assertive – but not aggressive Being constructive Being well-informed (Continued) Slide 25 Take responsibility for resolving complaints Exercising patience Showing tolerance Understanding the total picture (Continued) Slide 26 Take responsibility for resolving complaints Being prepared to compromise Being consistent. Slide 27 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures All complaints must be dealt with in accordance with enterprise procedures: Individual ‘scope of authority’ (permission to take action without special permission from management) must be observed: • Ability to act on behalf of the business • Authority to act or respond in certain situations. Slide 28 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures Scope of authority may allow staff to: Offer a free product Offer a free service Offer a discount Implement a ‘programmed decision’. Slide 29 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures Enterprise (‘house’) policies are developed to: Provide guidance to staff on what can or should or must be done in certain situations Give consistency in dealings with customers Take pressure off staff Provide basis for in-house training. Slide 30 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures Enterprise complaint resolution process will address: Who should deal with complaints When management and or security should be notified The approved complaint resolution model to be used Limits of ‘scope of authority’ (Continued) Slide 31 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures Programmed decisions Situations where business will not entertain complaint resolution Documentation to be completed Mandatory training staff must receive before being allowed to deal with a complaint. Slide 32 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures Most complaints can be resolved in more than one way – you should strive for a solution that is: Quick, easy and practical to implement Satisfies the complainant Meets enterprise limitations. Slide 33 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures Programmed decisions: Are developed by management Are prepared for common complaints or situations May be applied to all complaints May be applied only after a legitimate complaint has been established Give consistency to the way customers are treated Must be applied ‘as written’. Slide 34 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures Situation Response/Programmed decision Guest complains their main course meal is not hot enough Apologise Offer to replace with meal of guest’s choice Provide complimentary coffee Customer complains the booking was Apologise not honoured Provide 25% discount voucher for next booking Patron complains the service was not Apologise as advertised/expected Deduct 25% from account Issue 25% discount voucher for next visit. Slide 35 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures One useful complaint resolution model is AQUA: A = Acknowledge Q = Question U = Understand A = Answer. Slide 36 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures There may be need to refer a complaint, where: Customer has insisted on ‘seeing the manager’ Complaint has ‘escalated’ You cannot deal with the complaint The required or requested resolution exceeds personal ‘scope of authority’. Slide 37 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures An ‘escalated complaint’ is one where one or more of the following applies: House policy demands it is handled by management Other efforts to resolve the situation have failed The customer is becoming agitated (Continued) Slide 38 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures Customer is engaging in unacceptable actions Allegations of dishonesty are made Legal action is threatened Involvement of authorities is mentioned Reference to media involvement is made. Slide 39 Handle complaints in accordance with enterprise procedures When referring an escalated complaint: Act swiftly Explain the context Refer to an appropriate person, or designated person. Slide 40 Summary – Element 1 When responding to complaints: Be alert to the wide-range of potential complaints people may make Realise complaints are individual in nature Apply sensitivity, courtesy and discretion when handling complaints Maintain a positive and cooperative manner (Continued) Slide 41 Summary – Element 1 Try to convert a negative customer experience into a positive one Take responsibility for resolving the complaint Look for warning signs – monitor customers and the business environment Apologise (Continued) Slide 42 Summary – Element 1 Read and understand workplace policies and procedures for handling complaints Determine your personal scope of authority for taking action Learn the programmed decisions which are in place and available to you Apply an approved model to assist in resolving complaints Refer complaints promptly where there is a need to do so. Slide 43 Identify and manage conflict situations Performance Criteria for this Element are: Identify potential for conflict quickly and take appropriate action to prevent escalation Identify threats to personal safety of customers or colleagues quickly and organise appropriate assistance. Slide 44 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation When managing conflict, prompt identification of the problem is key: It allows a more timely response Ignoring conflict only makes matters worse. Slide 45 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Conflict: A state of opposition between persons or ideas or interests A complaint which is not resolved can become a conflict Does not require physical aggression Can arise between almost anyone. Slide 46 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Causes of conflict with customers may not be ‘obvious’ and can include: Lack of service or poor service Expectations not being met Dissatisfaction with products or services (Continued) Slide 47 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Unhygienic conditions Low comfort levels Actions of others (Continued) Slide 48 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Mistake with an account Error with a booking Special requests not met. Slide 49 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Conflict with suppliers can relate to: Business not paying their bills on time Business not adhering to Terms of Trade Late placement of orders Not signing for goods delivered (Continued) Slide 50 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Business delays delivery drivers when they make a delivery Changing suppliers Taking goods not meant for the business Failure of supplier to deliver as promised or expected. Slide 51 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Reasons for conflict with colleagues: Pressure of work Lack of or poor communication Prejudices (Continued) Slide 52 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Ineffective working procedures Differences in opinions or beliefs Team member not pulling their weight. Slide 53 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Warning signs of customer conflict: They look angry or aggressive They appear flustered or frustrated They display contorted facial expressions They glance around as if looking for help (Continued) Slide 54 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Physically touching someone Becoming too loud Slamming doors or throwing things – make sure you respond to the root cause and not the symptom Being argumentative. Slide 55 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Indicators there may be a staff conflict situation: They avoid verbal and visual contact The make negative facial expressions They make negative verbal remarks or comments They make rude gestures or remarks. Slide 56 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Generally, conflict may also occur where: Customer feels they are being treated unfairly Colleague feels they are being treated unfairly. Slide 57 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Always be ready to stop a conflict escalating: ‘Nip it in the bud’ Identify the issue as soon as possible Take action to address the identified situation/problem. Slide 58 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation To prevent escalation of conflict involving customers: Observe the situation for a few seconds before intervening Intervene – speak to the person Ask others to leave the area and or remove potential weapons – where necessary (Continued) Slide 59 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation Make an offer of help Try to contain the situation Involve others from within the business – if necessary. Slide 60 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation To prevent escalation of conflict involving colleagues: Think carefully about the situation • Is there really a conflict situation? Plan a response where one is deemed necessary: • What will you say? • Use ‘I statements’ • Identify specific examples you will refer to (Continued) Slide 61 Identify potential for conflict quickly and take action to prevent escalation • Where will you speak to the person? • When? • What do you want to happen? Have the conversation ‘as planned’ Be prepared for feedback Be prepared to compromise Only involve management as a ‘last resort’. Slide 62 Identify threats to safety and organise assistance Where your safety or the safety of customers is at risk: Try to identify these situations as soon as possible Always respond in some way Never put yourself in danger People take priority over property. Slide 63 Identify threats to safety and organise assistance Situations posing a threat include: Alcohol-affected persons People with guns or other weapons Where someone has already been injured by another person Individuals whose appearance or actions cause concern (Continued) Slide 64 Identify threats to safety and organise assistance People who are reluctant to leave the premises when asked to do so People who are physically fighting People who are arguing People engaging in erratic or irrational behaviour People who are harassing or intimidating others. Slide 65 Identify threats to safety and organise assistance House rules: Be aware of the house rules for your workplace Be aware of your scope of authority to implement house rules Apply house rules consistently to all patrons. Slide 66 Identify threats to safety and organise assistance When organising assistance to address threats to safety: Use common sense at all times • Think before you act Consider the consequences of your actions. Slide 67 Identify threats to safety and organise assistance Assistance may be obtained (subject to house policies and the nature of the conflict) by: Contacting Supervisor Contacting in-house Security Contacting Police. You may take action yourself but you are not obliged to do anything which puts you in danger. Slide 68 Identify threats to safety and organise assistance Ways to organise assistance: Face-to-face Internal telephone Pager PA system – using coded message Emergency alert devices. Slide 69 Summary – Element 2 When identifying and managing conflict: Realise conflict can occur with customers, suppliers and co-workers Always be alert to the potential for conflict to occur Understand there are many possible reasons for conflict (Continued) Slide 70 Summary – Element 2 Look for the warning signs of conflict – verbal and nonverbal Take action to prevent escalation of the conflict Seek to identify threats to safety as soon as possible Always take action when a threat has been identified (Continued) Slide 71 Summary – Element 2 Never put yourself in danger Put the protection of people above the protection of property Know the house rules, policies and procedures for handling threatening situations Obtain appropriate assistance when a threatening situation has been identified. Slide 72 Resolve conflict situations Performance Criteria for this Element are: Take responsibility for finding a solution to the conflict situations within scope of individual responsibility and job role Manage conflict by applying effective communication skills and anger management techniques Use conflict resolution skills to manage the conflict situation and develop solutions. Slide 73 Take responsibility for finding a solution to the conflict You can only respond to a conflict situation within your designated ‘scope of authority’: Ability to act generically for the venue Authority to spend money on behalf of the business Ability/authority to act in nominated circumstances. Slide 74 Take responsibility for finding a solution to the conflict Standard ‘scopes of authority’ may be given to allow staff to deal with: Refusal of service Asking person to leave Calling Security Contacting Police. Slide 75 Take responsibility for finding a solution to the conflict When taking responsibility for finding a solution to conflict: Realise some situations do not allow time to ‘find a solution’ Always use common sense and best judgement Sometimes you can negotiate a solution and sometimes you cannot Practice addressing these problem situations – you will not get every decision correct Observe and learn from others. Slide 76 Take responsibility for finding a solution to the conflict After your first few attempts at resolving conflict: Do a de-brief with others: • How did you go? • What did you do well? • What should be done differently next time? • What are the lessons to be learnt? Slide 77 Take responsibility for finding a solution to the conflict Causes of conflict: What are possible causes of conflict in the workplace? • List the answers identified by the class. Slide 78 Take responsibility for finding a solution to the conflict Addressing conflict with colleagues: Try to resolve without involving management If a resolution face-to-face with the colleague cannot be achieved, involve management Most conflict is easily resolved when people talk Do not be afraid to make the first move to resolve the situation. Slide 79 Take responsibility for finding a solution to the conflict Addressing conflict with customers: Respond immediately Adhere to limits of individual (personal & job) responsibilities and authority Give customers as much control as possible. Slide 80 Take responsibility for finding a solution to the conflict Taking responsibility: Approaching the person and talking to them Requesting they modify unacceptable behaviour Offering to help Showing a physical presence in the area Inviting people to explain or discuss the problem Realising it is your job to take responsibility. Slide 81 Manage conflict by using effective skills and techniques Two keys in dealing with: Use of appropriate communication skills Application of suitable anger management techniques. Slide 82 Manage conflict by using effective skills and techniques When communicating: Every message must have a purpose Messages should match the interests and abilities of the receiver Unnecessary words should be eliminated Chosen words should be within the experience range of the receiver Messages should be clear. Slide 83 Manage conflict by using effective skills and techniques When communicating: Consider verbal speech – it can be altered to suit requirements or situations Send appropriate non-verbal messages – there must be alignment between verbal and non-verbal messages. Slide 84 Manage conflict by using effective skills and techniques It is also necessary to: Apply active listening skills Ask questions Repeat, re-phrase and or paraphrase, as required. Slide 85 Manage conflict by using effective skills and techniques Language style is important when communicating to manage conflict: Use a language style the other person can relate to Reflect back to the other person the language style they are using A similar language style is less threatening and more likely to achieve positive communication. Slide 86 Manage conflict by using effective skills and techniques Other factors to consider include:: Cultural factors Socio-economic factors Health factors (Continued) Slide 87 Manage conflict by using effective skills and techniques Age Personality and mood. Slide 88 Manage conflict by using effective skills and techniques Important interpersonal skills when communicating in a conflict content: Face the person Maintain eye contact Use the person’s name Seek to establish a rapport. Slide 89 Manage conflict by using effective skills and techniques Anger management techniques to apply include: Manage personal emotions Empathise with the other person Be assertive (Continued) Slide 90 Manage conflict by using effective skills and techniques Taking control Looking for a win-win outcome Showing a willingness to resolve the issue (Continued) Slide 91 Manage conflict by using effective skills and techniques Defining common need Not telling them to ‘Calm down’ Using de-fusing techniques Moving the person to another place which is quiet and private. Slide 92 Use conflict resolution skills Five major ways to handle conflict: Avoidance Accommodation Forcing Compromise Collaboration. Slide 93 Use conflict resolution skills Communication and interpersonal skills required to resolve conflict = same as for managing conflict: Assertiveness Listening skills Non-verbal communication Language style Problem solving skills Negotiation De-fusing techniques. Slide 94 Use conflict resolution skills Determining solutions to conflict: Most conflict has more than one possible solution Aim for: • Quick, easy and practical solutions • Something which satisfies both or all parties • Meeting all applicable imposed requirements (Continued) Slide 95 Use conflict resolution skills What is best for the customer is often not best for the business – and vice versa Compromise is a common necessity Can exist for ‘customer’ and ‘colleague’ situations Requires willingness from both parties or sides. Slide 96 Use conflict resolution skills Two most common ways to resolve conflict: Use programmed decisions On a case-by-case basis. Slide 97 Use conflict resolution skills There are four basic options to choose from when addressing conflict resolution on a case-by-case basis: Ask the person what it will take to fix the problem and end the conflict Meet the other person half-way (Continued) Slide 98 Use conflict resolution skills Offer a formal apology Doing nothing. Slide 99 Use conflict resolution skills All conflicts must be resolved: With agreement the proposed solution will fix or end the issue In accordance with organisational constraints Within the law. Slide 100 Use conflict resolution skills The ‘Six-Step Method’ to conflict resolution: Listen carefully Acknowledge Respond Take action Report Follow-up. Slide 101 Use conflict resolution skills Step 1 – Listen carefully: Listen to everything said Tune in to body language Respect thoughts and emotions too Show genuine interest Demonstrate engagement and willingness to resolve the issue. Slide 102 Use conflict resolution skills Step 2 – Acknowledge: Establish and confirm nature and scope of issue Re-cap any relevant history Summarise the conflict Encourage further input. Slide 103 Use conflict resolution skills Step 3 – Respond: Tell customer what you intend doing to resolve the issue Verify proposal is acceptable and will fix the problem Check proposed action is acceptable to the organisation and you are authorised to implement it Involve other as necessary to authorise action Never blame anyone else in the organisation. Slide 104 Use conflict resolution skills Step 4 – Take action: This what the customer wants Tell customer of anticipated timeframe for resolution Under-promise and over-deliver Take action to implement the agreed solution Advise customer is there are unexpected delays. Slide 105 Use conflict resolution skills Step 5 – Report: Inform management of the conflict and the resolution A simple verbal report may be sufficient Advise other staff of progress as appropriate Record details of the conflict in writing where required. Slide 106 Use conflict resolution skills Step 6 – Follow-up: Return to the customer to check situation has been resolved Verify promises made have been kept Confirm person is satisfied with result or outcome. Slide 107 Summary – Element 3 When resolving conflict situations: Take responsibility for finding a solution Only operate within your designated scope of authority Realise conflict can occur with patrons or colleagues Recognise sometimes there can be no negotiated solution (Continued) Slide 108 Summary – Element 3 Try to give control to the customer when resolving customer conflict Be prepared to show a physical presence Use appropriate communication and interpersonal skills Factor in social, cultural and other relevant contexts (Continued) Slide 109 Summary – Element 3 Apply anger management techniques Use conflict resolution skills Develop solutions to address identified conflict Be prepared to ask the person what it would take to fix the problem (Continued) Slide 110 Summary – Element 3 Compromise can be an effective solution strategy Always be prepared to apologise Accept ‘doing nothing’ can be an appropriate response Work within organisational constraints and legal requirements. Slide 111