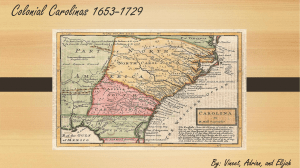
Carolina Colony

Proprietary Carolina
Chapter 5a
8-1.3: Summarize the history of English settlement in New England, the mid-Atlantic region, and the South, with an emphasis on South Carolina as an example of a distinctly southern colony
8-1.4: Explain the significance of enslaved and free Africans in the developing culture and economy of the South and South Carolina, including the growth of the slave trade and resulting population imbalance between African and European settlers; African contributions to agricultural development; and resistance to slavery, including the Stono
Rebellion and subsequent laws to control slaves.
8-1.5: Explain how South Carolinians used their natural, human, and political resources uniquely to gain economic prosperity, including settlement by and trade with the people of Barbados, rice and indigo planting, and the practice of mercantilism.
1
Chapter 5
Timeline
• 1566 Spain attempts Ft San Felipe on the remains of Charles Fort’s
• 1576 Spain attempts Ft San Marcos on the remains Ft San Felipe’s
• 1607 Jamestown, VA is the First permanent
English settlement in America
• 1619 Africans first arrive in America
1663 Carolina colony given to Lord
Proprietors
1566 Spain attempts
Ft San Felipe on
Charles Fort’s remains
1576 Spain attempts Ft San
Marcos on Ft
San Felipe’s remains
1607 Jamestown,
VA 1st permanent settlement in
America
1619 Africans first arrive in
America
1663 Carolina colony given to Lord
The Charter of Carolina
• In 1649, during a revolution in England, King
Charles I was executed
• His sons were able to escape to France
– Where they stayed until it was safe to come back
• On May 8, 1660, Charles
II (oldest son of Charles I) became King of England
King Charles I
King Charles II
3
The Charter of Carolina
King Charles II issued a charter that gave 8 men land in America
As thanks for helping him get the throne back
Opportunity for them to earn money
Charter of Carolina
They became known as the Lords Proprietors
4
The Charter of Carolina
The land given to the
Lords Proprietors:
Everything from the top of Florida to the bottom of Virginia,
From the Atlantic
Ocean to the Pacific
Ocean
They called the colony
Carolina
5
The Charter of Carolina
The proprietors were wealthy, titled land owners in England
(investors)
• The charter gave them control of the government of the colony
• Carolina colony started as a proprietary colony
BUT…
• The proprietors never left
England & made all of the laws for Carolina without ever seeing it
6
The Charter of Carolina
In 1664
Barbadians people from
Barbados Island
Attempted to establish
• a colony named Charles
Town near Cape Fear,
NC
• It failed within 3 years because of hostile Native
Americans and…
• Lacked the Lords
Proprietors’ support
Location of Cape Fear
7
• _____ ______ _______
________started the successful
Charles Town colony on Albemarle
Point.
• He got money to start the colony by asking the other proprietors to______ ______.
• How did the proprietors plan to get my from the colony?
8
Lord Anthony
Ashley Cooper
Charles Town Begins
Lord Anthony Ashley Cooper ,
One of the Lord’s Proprietors, started the successful Charles
Town colony on Albemarle Point by finally asking the other proprietors to invest money in the colony.
In return for their investment, they would make $$ from the settlers by collecting a
Quitrent = Rent
They had to pay the king a small amount each year, but
It was minimal compared to the $$ they were making
9
Charles Town Begins
Finding settlers to move to Carolina fairly easy
• The Bubonic Plague
– transmitted by fleas on the brown rat, swept through England
– started in part by houses being too close together & poor sanitation
• The Great London Fire burned a large portion of the city
– Helped to stop the spread of the plague
Brown Rat
Fleas would bite infected rats and give the disease to humans by biting them.
London, 1611
The Great
London Fire
10
Charles Town Begins
The settlers left
England in August,
1669
• They sailed to Ireland
• Then on to Barbados
– They picked up more passengers
– Including wealthy planters and their African slaves
Barbados
11
Charles Town Begins
• At 1st, the settlers headed for Port Royal near Beaufort
• Where Charlesfort and Ft
San Marcos were located
• They were welcomed by the Kiawah tribe on
Bull’s Island
But decided not to settle there after they inspected it
• They eventually landed on the area that is now known as Charles Town
Harbor
Bull’s Island
“Fundamental Constitution of
Carolina”
13
Charles Town Begins
The settlers carried with them the
“Fundamental Constitution of
Carolina”
1. Set up the nobility system the proprietors planned to set up
2. The government that the colonists were expected to follow
3. The most important thing :
It guaranteed religious freedom
This was the first time that a written constitution guaranteed this freedom
14
Charles Town Begins
Albemarle Point in April,
1670
The settlers eventually signed the Treaty of Madrid with Spain after the Spanish tried to destroy Charles Town
The treaty declared that all settlements NORTH of St.
Augustine, FL, belonged to the
English
Helped pave the way for success for Charles Town
Original location of
Charles Town
15
Charles Town Grows
The settlers had a hard time the 1st year
• surviving disease
• a lack of knowledge about the climate and region
• Native American attacks
Charles Town had to be moved from Albemarle Point to Oyster
Point because is was poorly designed and was becoming overcrowded
New location of Charles
Town
The capital of the Carolina colony for many years
16
Charles Town Grows
Charleston Today
When Charles Town was moved, it was designed in a symmetrical grid to allow more room for growth.
Colonial Charles Town
17
Charles Town Grows
The Headright Method
Settlers got land based on the number of people in the family, or household
Slaves and indentured servants were included in the count
More people
=
More land
18
Drayton Hall
Plantation
Charles Town Grows
Not everyone could afford to move to Carolina colony
Wealthy landowners:
• Needed laborers
• Paid for passage in exchange for labor = indentured servants
– Would then have to work off their debt
Using the Headright Method, landowners received a lot of land
This helped start the large farms of the plantation system
19
• List the different groups that came to the Carolina Colony in the later
1600s.
(nationalities and religions)
• What was the largest group to come to Carolina?
20
Charles Town Grows
1st settlers of Charles Town
• Englishmen from Barbados
• They already had an established plantation system
Other colonists were from
Switzerland & Germany
Ireland & Scotland,
And even France
Religious groups:
Huguenots, Jews, Anglicans, and other
Christian denominations
Came to Carolina for freedom to worship
The largest group of people to come to the colonies were
African slaves from Barbados .
21
Describe how the following contributed to the Carolina colony economy:
1. Indian Trade
2. Cattle
3. Naval Stores
4. Rice
22
Carolina Economy
Carolina colony’s economy grew quickly
The Lords Proprietors wanted to make
$$ off of the colonists’ quitrent (rent)
BUT… settlers had to be able to make $
Colonists made money by trading with the Native Americans
Settlers traded guns, beads, trinkets, and alcohol
Native Americans traded furs & deerskins
Colonists shipped to England to make clothes
23
Carolina Economy
Settlers raised cattle
The cattle was traded to
Caribbean islands for sugar
African slaves were experienced herdsmen & horsemen
Their knowledge was used to help increase the cattle trade…$$$
Carolina African slaves were the first “cowboys”
24
Carolina Economy
Another way settlers got money was through naval stores which was used to make ships water tight
Pitch & tar were gotten from pine trees
grew all over the Carolina
Colony
Slaves would harvest the naval stores, as well as the wood from the trees to make barrels & buckets, hardwood for furniture, and shingles for English houses .
Pine trees tapped for pitch
Wooden shingles on the side of a house
25
Carolina Economy
Slaves in a rice field
Rice
Settlers made the most $$ from rice
It started out as a staple crop
– a crop that most people eat or can use
• The early colonial rice did not grow well
• Carolina Gold was brought over from Madagascar
• The African slaves had grown this rice for centuries and knew everything about planting rice.
26
• The good relationship between the settlers and the Natives was ruined when…
27
Carolina Economy
Native Americans were traded as slaves
Were kidnapped or captured by rivals and sold into slavery in the
Caribbean.
This ruined the settlers good relationship with the
Native Americans
28
Royal Colony of Carolina 5b
29
A Divided Colony
In the early years:
• There was only 1 governor in Carolina
• As the colony grew bigger the colonists started to argue
• They complained that the
Lords Proprietors were not spending the time and energy needed to effectively govern the colony
30
The Carolina Colony was ruled by _______
_________ and _________________.
• The Grand Council was considered
“____________________” because it controlled _________________________.
The Grand Council had three groups:
1. ____________
2. ____________
3. ____________
31
A Divided Colony
Carolina Colony:
The Lords Proprietors ruled through
A governor and a Grand Council
The Grand Council was considered the
“government for the colony ”
It controlled the law making & the courts
The Grand Council consisted of 3 groups:
1. Representatives chosen by the Lords
Proprietors
2. Representatives elected by Carolina Nobles
3. Representatives of the freemen (the regular colonists)
32
A Divided Colony
In 1682, the Council changed the power of the groups represented by the nobility and proprietors, and took away some of their power.
1. There needed to be a majority of EACH group to pass a law . (Majority Rule)
2. A jury system was established
Names were drawn out of a box by a child to ensure fairness. The jury would then make a decision about the case brought before them.
3. People who were not members of the Anglican
Church wouldn’t be taxed to support the
Anglican Church
33
The Commons House of Assembly
“ “
The Council (not Grand Council)
• Consisted of _____________
The Commons House and the Council became known as the __________.
Over time the Commons house gained _____
________.
34
A Divided Colony
In 1692 -
The proprietors set aside the Fundamental
Constitutions & created the Commons
House of the Assembly
– Became the voice of the people
The Council then only consisted of representatives of the Proprietors
• The 2 bodies (Commons House of Assembly and The Council) became known as the
Assembly a bicameral legislature
• Bicameral – a legislative (law making) body containing 2 houses
• The Commons House gained more power
35
Northern Carolina differed from
Southern Carolina
• Primary northern crop…
• Northern coast had…
• Northern Carolina aligned itself with…
What did these differences lead to?
36
A Divided Colony
Geographically –
The northern part of the
Carolina colony never fit in:
• It had sounds not harbors
• Tobacco was the cash crop, not rice
• It had close ties with Virginia shipping ports
1689, Carolina colony was split
North Carolina &
South Carolina
37
A Divided Colony
In 1680,
The Proprietors stopped using the headright method
Decided it was time to stop granting free land
Proprietors made settlers sign contracts that required them to pay rent on the land
Colonists became upset because they wanted to own the land free of rent
38
A Divided Colony
Other Problems:
The Barbadians
• About ½ of the population of the colony
• Thought they deserved more power
• Got angry when the governor that they liked was forced out by the Lords Proprietors
The colony needed strong leadership, but got fighting instead
39
Fighting the Spanish
• In 1702 Carolina attacked __
___________.
• Describe the attack and a mishap
40
Conflicts in the Colony
The Spanish had been attacking settlers in the southern part of
Carolina colony.
• When the Spanish king died,
England attacked Spain to keep his land from going to his closest relative who was French.
• With 500 colonists, Carolina attacked St. Augustine in 1702
• They laid siege against the city for six weeks, which ended when South
Carolinians burned the settlement .
Unfortunately, they also burned their own ships and had to walk home
In 1706 the Spanish retaliated, attacking Charles Town.
The fighting finally ended in 1714
41
The Tuscarora War
• Where and When?
• Describe what happened and why
• Phase 1
• Phase 2
• Phase 3
42
The Indian Wars
Colonists were constantly fighting with Native
Americans
One conflict with the Tuscarora tribe occurred in 1711 in North Carolina
The Tuscarora massacred several families when they heard that Swiss colonists were going to push them off their land
South Carolina responded by sending 500 friendly Native Americans and 30 settlers .
A peace treaty was signed but by 1712, they were fighting again
South Carolina stayed until the end of the war, and Tuscarora were wiped out as a threat
43
The Yemassee War
• When and Where?
• Describe what happened
44
Conflicts in the Colony
The Yemassee War (1715-1717)
Involved almost every Native American tribe that traded with the settlers
This was fought entirely within South
Carolina.
The Yemassee attacked Port Royal
– Because traders had charged high prices and cheated them in business deals
1 st the militia defeated the Yemassee
After a 2nd attack, the Cherokee
helped the settlers
The 3 rd phase of this war lasted until the peace treaty was signed
Thomas Hepworth House in
Beaufort has gun ports in basement on the back of the house to help defend against Yemassee attacks
45
• What happened to the Yemassee after the war?
• What did the colonist gain after the war?
46
Proprietors
Conflicts in the Colony
By the end of the war…
Most of the Yemassee were dead
The survivors moved back to Florida and were absorbed into the Seminoles
Colonists
This war lasted longer & cost more:
$$ and lives than any other Native American war
In the end more land was open to settlement
Colonists learned to depend on themselves, and not the Lords
Proprietors, for protection
47
• The Proprietors thought the colonists
1. ___________________
2. ____________________
• The colonist thought the Proprietors
1. _______________
2. ________________
48
Conflict Between Proprietors and
Colonists
Colonists felt:
The proprietors were too far away
Not investing enough money or supplies in the colony
Proprietors
The Proprietors felt:
That the colonists were not obedient enough
Where costing them valuable profits
Colonists
49
• Describe the difference between a proprietary colony and a royal colony.
• What happened to SC in 1729
50
Chapter 5
Change in Government
The Council
Protested to the king about the neglect of the proprietors
Appealed to the king to make
Carolina a royal colony
Whose governor would be appointed by the king rather than proprietors
In 1729 the king reached a financial agreement with the
Proprietors
Both North and South Carolina became royal colonies
51