8-1.3
advertisement

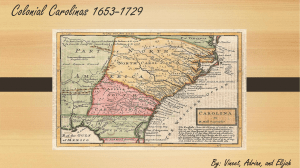
8-1.3: Summarize the history of English settlement in New England, the MidAtlantic, and the South, with an emphasis on South Carolina as an example of a distinctly South Carolina was founded as a proprietary colony when the king (Charles II) granted land to the eight Lords Proprietors in payment of debt Ex: Pennsylvania The proprietors hoped to make a profit by charging settlers a quitrent on the land. The proprietors commissioned John Locke to write the Fundamental Constitutions of Carolina A document that included policies, such as religious toleration design that attract settlers The fundamental constitution included provisions for establishing a social class system based on the granting of titles to large land holders Intended to make Carolina a society based on deference to the elites In order to encourage immigration, the proprietors granted large tracts of land to settlers through the headright system, just as in VA The headright system led to the establishment of large plantations based on cash crops that made South Carolina a distinctly southern colony Ex: Maryland, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Georgia The first SC settlers were Englishmen who emigrated from the British colony of Barbados and brought a well-developed slave system with them. Slavery made the plantation owners very wealthy Other settlers attracted to the prosperous Carolina colony came from France, Switzerland, Germany, Scotland and Ireland Assured of religious choices by the Fundamental Constitution settlers came from diverse religious backgrounds Fertile land Mild climate Many waterways The Lords Proprietor controlled the government through a governor and grand council which included, representatives of the Proprietors the Carolina Elite, and a smaller representation of the common people of the colony The Carolina colony had some degree of democracy from the beginning