Worksheet A: KMT and Pressure Name Use kinetic theory to explain
advertisement

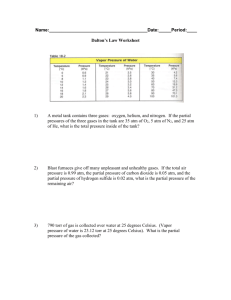
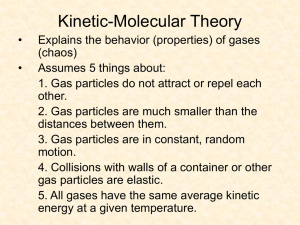
Worksheet A: KMT and Pressure Name _____________________ 1. Use kinetic theory to explain what causes gas pressure. 2. Convert the following Pressures: a. 600 mm Hg into atm b. 190 kPa into atm c. 2.3 atm into mm Hg d. 1.5 atm into kPa 3. What is the temperature at absolute zero 4. Use kinetic theory to explain the difference between evaporation and boiling of a liquid. 5. Use the chart to answer the following questions. a. What is the vapor pressure of ether at 40ºC? b. What is normal boiling point of water? c. What is the normal boiling point of benzene? 6. How is the average kinetic energy of water molecules affected when you pour hot water from a kettle into cups at the same temperature as the water? 7. Explain why a propane tank does not lose any pressure over time if unused and well sealed. Worksheet A: KMT and Pressure Name _____________________ 1. Use kinetic theory to explain what causes gas pressure. Kmt states that gas molecules are in constant motion, that motion causes constant collisions with container/other molecules. Collision = pressure 2. Convert the following Pressures: a. 600 mm Hg into atm 600mm Hg(1atm/760 mm Hg) = 0.789 atm b. 190 kPa into atm 190 kPa (1 atm/101.325 kPa) = 1.87 atm c. 2.3 atm into mm Hg 2.3 atm( 760 mm Hg/ 1 atn) = 1748 mm Hg d. 1.5 atm into kPa 1.5 atm( 101.325 kPa/1 atm) = 152 kPa 3. What is the temperature at absolute zero O Kelvins or -273oC 4. Use kinetic theory to explain the difference between evaporation and boiling of a liquid. Evaporation is when an individual atom at the surface of a liquid gaining enough energy to move rapidly enough to break free of IMF’s and go into the vapor state Boiling is when the entire liquid gains enough energy to move rapidly enough to break free of IMF and overcome atmospheric pressure and completely go into the vapor state. 5. Use the chart to answer the following questions. a. What is the vapor pressure of ether at 40ºC? 900 mm Hg b. What is normal boiling point of water? 100o C c. What is the normal boiling point of benzene? 80oC 6. How is the average kinetic energy of water molecules affected when you pour hot water from a kettle into cups at the same temperature as the water? Energy is transferred from faster moving particles (higher temperature) to slower moving particles (lower temperature) until an equilibrium is established (same speed same temperature). Since the temperature is the same in the water and cup there would be no affect. 7. Explain why a propane tank does not lose any pressure over time if unused and well sealed. The pressure inside the tank is caused by the gas particles colliding with the outside of the tank. When gas particles collide with other gas particles, the collisions are perfectly elastic. This means that the energy that these particles possess before the collision perfectly equals the energy that the particles possess after the collision.