FPGA for Dummies
advertisement

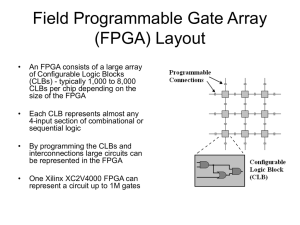
FPGA for Dummies Basic FPGA architecture ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA for Dummies • Historical introduction, where we come from; • FPGA Architecture: basic blocks (Logic, FFs, wires and IOs); additional elements; • FPGA Programming: Design flow; Software; • FPGA DSP: Digital filters examples; ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA for Dummies • Historical introduction, where we come from; • FPGA Architecture: basic blocks (Logic, FFs, wires and IOs); additional elements; • FPGA Programming: Design flow; Software; • FPGA DSP: Digital filters examples; ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) FPGAs initially were Similar to CPLDs, so a function to be implemented in FPGA is partitioned into modules (each implemented in a logic block) and then the logic blocks are connected with the programmable interconnection: ARRAY of logic GATES is the G and A in FPGA. By way of a configuration file or bit stream, an FPGA can be configured to implement the user’s desired function: this allows customization at the user’s electronics bench, or even in the final end product. This is why FPGAs are FIELD PROGRAMMABLE. ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna Complex Programmable Logic Devices (CPLDs) The key resource in a CPLD is the PROGRAMMABLE INTERCONNECT (Tradeoff between SPACE FOR MACROCELLS and SPACE FOR INTERCONNECT) ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA Architecture The basic structure of an FPGA is composed of the following elements: Look-up table (LUT): This element performs logic operations Flip-Flop (FF): This register element stores the result of the LUT Wires: These elements connect elements to one another, both Logic and clock Input/Output (I/O) pads: These physically available ports get signals in and out of the FPGA. ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA Components: Logic How can we implement any circuit in an FPGA? Combinational logic is represented by a truth table (e.g. full adder). Implement truth table in small memories (LUTs). A function is implemented by writing all possible values that the function can take in the LUT The inputs values are used to address the LUT and retrieve the value of the function corresponding to the input values ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA Components: Logic A LUT is basically a multiplexer that evaluates the truth table stored in the configuration SRAM cells (can be seen as a one bit wide ROM). How to handle sequential logic? Add a flip-flop to the output of LUT (Clocked Storage element). This is called Basic Logic Element (BLE): circuit can now use output from LUT or from FF. ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna Slice Flip-Flop Capabilities All flip-flops are D type All flip-flops have a single clock input (CLK) Clock can be inverted at the slice boundary All flip-flops have an active high chip enable (CE) All flip-flops have an active high SR input Input can be synchronous or asynchronous, as determined by the configuration bit stream Sets the flip-flop value to a predetermined state, as determined by the configuration bit stream ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna Slice Flip-Flop Timing Signal timing must satisfy Setup & Hold times; Propagation delay; At the maximum required frequency ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna Xilinx Configurable Logic Blocks (CLBs) Xilinx Configurable Logic Blocks (CLBs) usually contain more than 1 BLE: this is an efficient way of handling common I/O between adjacent LUTs and saves routing resources (eg. Ripple-carry adder). 2x1 3-in, 2-out LUT 3-in, 2-out LUT FF 2x1 FF 2x1 FF 2x1 FF 2x1 ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna Xilinx Configurable Logic Blocks (CLBs) The arithmetic logic provides a XOR-gate and faster carry chain to build faster adder without wasting too much LUT-resources. ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna Xilinx Configurable Logic Blocks (CLBs) The CLB is the modern Xilinx FPGA basic block: the number of CLB varies from devices to devices: Spartan 3, VirtexII, Virtex II-Pro Virtex 4: 4 slices 2 basic blocks per slice Virtex 5: 2 slices 4 basic blocks per slice Virtex 6: 2 slices (split in 2 columns) 4 6-inputs LUT 8 FF (storing LUT results) Virtex 7: 2 pairs of slices (split in 2 columns arranged symmetrically) 4 6-inputs LUT 8 FF (storing LUT results) ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna Altera FPGA Logic Array Blocks Altera’s FPGAs (Cyclone, FLEX) basic unit of logic is the Logic Element (LE) and is also LUT-based (4-LUT, flip flop, multiplexer and additional logic for carry chain) similar to Xilinx: LEs can operate in different modes each of which defines different usage of the LUT inputs. Altera LEs are grouped into Logic Array Blocks (LAB)). ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna Altera FPGA Logic Array Blocks Altera’s Stratix II FPGAs the basic computing unit is called Adaptive Logic Module (ALM): each LAB contains 8 ALMs. ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna Altera FPGA Logic Array Blocks ALM can be used to implement functions with variable number of inputs. This ensures a backward compatibility to 4-input-based designs. It is possible to implement module with up to 8 inputs. ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna LatticeSemiconductor FPGA Logic Blocks The Programmable Logic Cell (PLC) is the fundamental building block of the FPGA Fabric. The PLC consists of 2 components: PFU – Programmable Function Unit (Very simple logic!) Programmable Routing Block or Big Switch Box (Muxes) ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA Components: wires Before FPGA is programmed, it doesn’t know which CLBs will be connected: connections are design dependent, so there are wires everywhere (both for DATA and CLOCK)!!!!! CLBs are typically arranged in a grid, with wires on all sides. CLB CLB CLB CLB CLB CLB To connect CLB to wires some Connection box are used: these devices allow inputs and outputs of CLB to connect to different wires ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA Components: wires Connection boxes allow CLBs to connect to routing wires but that only allows to move signals along a single wire; to connect wires together Switch boxes (switch matrices) are used: these connect horizontal and vertical routing channels. The flexibility defines how many wires a single wire can connect into the box. Switch box/matrix ROUTABILITY is a measure of the number of circuits that can be routed CLB CLB HIGHER FLEXIBILITY = BETTER ROUTABILITY CLB CLB ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA Components: wires FPGA layout is called a “FABRIC”: is a 2-dimensional array of CLBs and programmable interconnections. Sometimes referred to as an “island style” architecture. 16-bit SR 16x1 RAM a b c d e 4-input LUT y mux flip-flop q clock clock enable set/reset In the switch boxes there are short channels (useful for connecting adjacent CLBs) and long channels (useful for connecting CLBs that are separated, this reduce routing delay for non-adjacent CLBs) ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA Components: memory The FPGA fabric includes embedded memory elements that can be used as random-access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), or shift registers. These elements are block RAMs (BRAMs), LUTs, and shift registers. Using LUTs as SRAM, this is called DISTRIBUTE RAM Included dedicated RAM components in the FPGA fabric are called BLOCKs RAM ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA Components: memory ALTERA Embedded Memory XILINX 36K/18K ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA Components: input/output The IO PAD connect the signals from the PCB to the internal logic. The IOB are organized in banks (depending on the technology and the producer the number of IOB per bank change). All the PAD in the same bank, share a common supply voltage: not all the different standard could be implemented at the same time in the same bank!!!! There are special PAD for ground (GND), supplies (VCC, VCCINT, VCCAUX, etc…), clocks and for programming (JTAG). ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna FPGA Components: input/output The IO Blocks (IOB) support a wide range of commercial standard (LVTTL, LVCMOS, LVDS, etc…) both single ended and differential (in that case pair of contiguous pad are used). In the PAD are available FF that are use to resynchronize the signal with the internal clock. ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna XILINX 7 serie families ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna ALTERA 10/V serie families ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna Vendor comparison ESS | FPGA for Dummies | 2015-12-08 | Maurizio Donna