CHAPTER15
advertisement

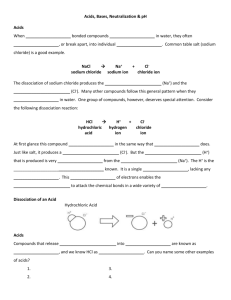
Chemistry Raymond Chang 10th edition Chapter 15 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Question 1 Which is true regarding the equilibrium below? HF(g) + H2O(l) ↔ F- + H3O+(aq) A) HF is acting as a Bronsted base. B) Water is acting as a Bronsted base. C) The reaction goes to completion leaving little HF. D) The Fluoride ion is acting as Bronsted acid. Question 2 Which of the following is(are) true? A) pH can never be greater than 14. B) pH can never be less than 0. C) At room temperature, pH + pOH = 14. D) All of the above. Question 3 Which of the following is a neutral salt (neither acidic nor basic)? A) KCl B) NaCN C) NH4NO3 D) NaF Question 4 The hydroxide ion is the conjugate base of the hydronium ion. A) True B) False Question 5 Which of the following has an impact on the percent ionization of a weak acid? A) The acid ionization constant. B) The concentration of the acid. C) Both A and B. D) None of the above. Question 6 Which of the following best describes the acid strengths of the hydrohalic acids? A) HF>HCl>HBr>>HI B) HF<<HCl<HBr<HI C) HF=HCl=HBr=HI D) HF=HCl<HBr=HI Question 7 Which of the following will produce a basic solution when dissolved in water? A) Na2O B) NaOH C) Both A and B D) None of the above Question 8 The substance that is largely responsible for acid rain is A) calcium carbonate. B) sodium chloride. C) ozone. D) sulfur dioxide. Question 9 A Lewis base is a(an) A) substance that contains the hydroxide ion. B) proton acceptor. C) electron pair donor. D) none of the above Question 10 In a 0.100 M solution of sodium hydroxide, what are the equilibrium concentrations of sodium hydroxide, sodium ions, hydroxide ions, and hydronium ions, respectively? A) 0.100; 0.100; 0.100; 0 B) 0.100; 0.100; 0.100; 1X10-13 C) 0; 0.100; 0.100; 0 D) 0; 0.100; 0.100; 1X10-13 Question 11 The chloride ion in aqueous solution is a A) strong conjugated acid. B) weak conjugated acid. C) strong conjugated base. D) weak conjugated base. Question 12 Water can act as a A) weak acid. B) strong acid. C) weak base. D) strong base. E) two of the above. Question 13 Which pH region is most likely for a sample of vinegar? A) 0 to 1 B) 1 to 6 C) 8 to 13 D) 13 to 14 E) none of the above Question 14 Calculate the pH of a 0.018M solution of Ca(OH)2. A) 12.56 B) 1.8 C) 1.44 D) 12.25 E) none of the above Question 15 Identify the Bronsted acids and bases in the following reaction: A) option 1 B) option 2 C) option 3 D) option 4 E) option 5 Question 16 When KOH and HNO3 are mixed, a reaction occurs. What are the spectator ions in the reaction? A) K+ and H+ B) H+ and OHC) K+ and NO3D) H+ and NO3E) there are no spectator ions in this reaction Question 17 What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid? A) a strong acid contains strong covalent bonds whereas a week acid does not B) a strong acid has more hydrogen atoms in its molecule than a weak acid C) a weak acid is nonpolar, whereas a strong acid is polar D) strong acids react with both strong and weak bases, whereas weak acids do not E) none of the above Question 18 What will be the pH of a 1.0 × 10-8 M solution of HCl? A) 8.0 B) 6.0 C) cannot be calculated D) it will be slightly less than 7.0 E) it will be slightly more than 7.0 Question 19 Which of the following salts is expected to produce a basic solution upon hydrolysis? A) calcium chloride B) ammonium sulfate C) sodium acetate D) ammonium acetate E) ferrous bromide Question 20 Calculate the mass in grams of 0.0504 moles of an acid having the molar mass equal to 100.5. A) 5.1 B) 19.84 C) 5.07 D) 5.065 E) none of the above Answer Key – Chapter 15 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. B C A B C B C D C D 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. D E B A C C E D C C