Functional Assessment and Behavior Intervention
advertisement

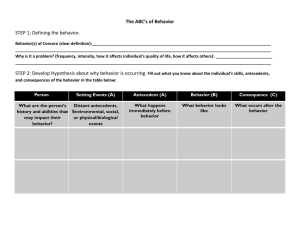
Functional Assessment and Behavior Intervention Planning: Practical Solutions for Problem Behavior Jane I. Carlson, Ph.D., B.C.B.A The May Institute Form vs. Function A Developmental Perspective The Communication Hypothesis The Basics of Applied Behavior Analysis A B C Antecedent: A stimulus condition or environmental event that precedes a behavior Example: Feeling hungry. A red light. Being asked to do a math problem. Seeing a friend. Dirty dishes in the sink. ANTECEDENT: An immediate “trigger” for the problem behavior. BEHAVIOR: Anything a person does that can be defined, observed, and measured. Example: Hitting self Writing Kicking Walking Throwing toys Crying Rocking CONSEQUENCE: A stimulus condition or environmental event that follows a behavior. Example: Social Interaction Edible item Token Check Mark Praise Gaining access to desired item. Consequences cause behavior to: Increase in frequency Maintain at the same rate Decrease in frequency Preferred Give Take Away Non-preferred Preferred R+ Give Positive Reinforcement Take Away Non-preferred Preferred Give Take Away Non-preferred Punishment (Type 1) Preferred Give Take Away Punishment (Type 2) Non-preferred Preferred Non-preferred Give RTake Negative Away Reinforcement Preferred Punishment (Type 1) Give Take Away Non-preferred Punishment (Type 2) Problems associated with punishment: No maintenance of effect without continued intervention. Not generalizable. Produces avoidance behavior Can evoke aggression. Often leads to coercion. Provides undesirable model of behavior. Preferred Non-preferred R+ Give Positive Reinforcment RTake Away Negative Reinforcement Positive Reinforcement Antecedent Homework assignment from school Behavior Consequence Child completes homework and shows to parent. Parent praises child and takes child out for ice cream Author is typing on the Author hits monitor computer and the several times. screen goes blank. Screen returns to normal. Mother and child are shopping for groceries. Mother gives child a cookie. Child begins crying. Negative Reinforcement Antecedent Behavior The classroom is very noisy. Child asks teacher to quiet everyone down. Consequence Classroom becomes quiet. Author is typing on the Author hits monitor computer and the several times. screen starts flashing. Screen returns to normal. Mother and child are Mother gives child a shopping for groceries cookie. and child begins to cry. Child stops crying. Deprivation and Satiation DEPRIVATION A state that occurs when a reinforcer has been withheld or unavailable. Temporarily increases the value of the reinforcer SATIATION A state that occurs when a reinforcer has been presented too frequently or in too great a quantity. Temporarily decreases the effectiveness of a reinforcer. POSITIVE/NEGATIVE REINFORCEMENT INTERACTIONS THE NEGATIVE REINFORCEMENT TRAP A B C ANTECEDENTS Give us important antecedents about the context in which problem behavior occurs. CONSEQUENCES give us important information about the function of a problem behavior. Functional Categories Attention Escape Tangible Other seeking ESCAPE When you ask the person to participate in a task or activity, the problem behavior occurs. When in an unpleasant situation, such as a crowded area, the problem occurs. When you make a request of the person. The behavior stops when you stop making demands. ATTENTION The person behaves appropriately in 1-1 situations. When an adult moves away, a problem occurs. Behavior occurs when teacher is talking to another person in the room TANGIBLE SEEKING When told “no”, a problem begins. If an adult “gives in”, the problem stops. When you take away a toy, food, or game. OTHER Sensory Medical SETTING EVENTS Establishing operations SETTING EVENTS Variables that affect the probability of a given stimulus-reinforcer relationship. Setting Events Physical discomfort Fatigue Negative life event Series of “hassles” Negative history with event/person Setting Event Setting Event Antecedent Behavior Consequence Just got back Teacher says, from the park. “Time for math.” In a good mood. Jack completes math paper. Aide gives Jack a work break and a small snack. Not feeling well. High pollen count today. Jack throws materials, hits his aide, and bites his wrist. Jack is asked to leave the classroom until he can calm down. Teacher says, “Time for math.” Conducting a Functional Assessment FA Tools Interview with relevant family/staff. A-B-C data collection Historical data analysis Experimental functional analysis Behavior Log 9/12/04 At 8:45 AM, Jamie was watching cartoons and I told him it was time to get dressed for school. He didn’t respond so I turned off the TV and told him to go get dressed. He started to scream and then he threw his toy at me. He continued to tantrum for about 10 minutes. I finally said, “Okay, you can have 10 more minutes of TV time but then you have to get dressed.” He stopped crying and turned the TV back on. A-B-C Sheet Date/time Antecedent Behavior Consequence 9/12/04 8:45 AM Jamie was watching TV and I turned it off and asked him to get dressed. He screamed and threw a toy, then had a tantrum for 10 minutes. I told him that he could watch TV for 10 more minutes but then he had to dress. 9/14/04 3:20 PM A neighbor came over and we were sitting and talking. Jamie started screaming and threw himself on the floor. I picked him up and talked with him for a few minutes. Intervention Planning Short-term prevention Long-term Intervention Short-term Prevention Interventions directed at setting events and antecedents identified during assessment. Long-term Intervention Educative strategies directed at the functions of problem behavior identified during functional assessment. Short-Term Prevention Strategies Alter Schedules Embed Demands Environmental Manipulation Extra supervision Mood Enhancement Offer Choice Reduce Demands Neutralize setting events Long-term Intervention Strategies Functional Communication Training Social skills Problem Solving Relaxation Skills Anger control training Tolerance for delay of reinforcement Shaping Systematic Desensitization Functional Communication Training (DRC) Functional Equivalence Interpretibility Effectiveness Efficiency