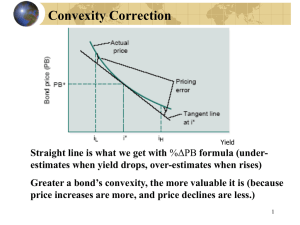
Learning Objectives - University of South Carolina
advertisement

FINA 469 Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management Spring 2015 Professor Steven Mann Office: 456I Office Hours: T/R 2:00-3:30 Office Phone: 777-4929 E-mail: svmann@moore.sc.edu Textbook Bodie, Z., A. Kane, and A. Marcus, Essentials of Investments. Ninth Edition. McGrawHill Irwin, 2013. Recommended Text The Wall Street Journal Course Objectives 1. Organize the student’s thinking processes about investment decision making. 2. Introduce the student to the tools utilized in investment analysis. 3. Give the student the opportunity to solve problems encountered in the marketplace by portfolio managers. Administrative Notes Office hours: Although I have formal office hours on Tuesday and Thursday afternoons, I encourage you to call or stop by my office whenever you have a question or problem. The following caveats to the preceding: 1. I am occasionally under time pressure on a project and will need to answer your question at a mutually convenient time. 2. If you expect you will need a long meeting, please attempt to arrange a mutually convenient meeting time with me first. 1 Performance Evaluation Exam I Exam II Exam III Project/Paper 100 100 100 100 Total 400 points Exam I will be on Thursday, February 12, during the regularly scheduled class period. Exam II will be on Thursday, April 2, during the regularly scheduled class period. According to the official final exam schedule, Exam III will be on Tuesday, May 5, at 9:00 AM for section 1 (10:05 class) and on Monday, May 4, at 12:30 pm for section 2 (11:40 class). No make-up exams will be given, i.e., no exam will be administered at a different time. Chapters to be Covered in the Course 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 13, 15, 16, 17, 19 A quick glance at the above list indicates that we will be reading numerous chapters in our text not to mention the Wall Street Journal, Standard & Poor’s Stock Guide, Value Line, etc. This seems like a lot of reading. It is! Do not worry. Some things we will read only for content while on others we will concentrate considerable effort. I will help you decide which is which. Portfolio Project We will be using STOCK-TRAK, an investment simulation game. Each student will manage a $500,000 portfolio. This portfolio could include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, cash, etc. Portfolio managers will make trades over the Internet or by calling a toll-free number and speaking with brokers who will record your trades. The first day of trading is Monday, February 2. Students must participate actively in project in order to receive a passing grade in the course. Grading Policy The course grades will be computed to obtain a class grade point average of approximately 3.25. I base the course grade on total points. I start with a straight scale 90% and above is an A, 80% and above is a B, and so forth. The class grade point average is calculated. If the class grade point average is 3.25 or higher, I assign grades based on that scale. If the grade point average is below 3.25, I drop the scale by one percent and repeat the process. When the target grade point average is achieved, I assign 2 grades. Problem sets will receive a “+”, “0” or “-“. Any student receiving three or more minuses on these assignments will not pass the course Re-grade policy: If you think that a serious error has been committed in grading your exam, you must submit the exam for a complete re-grade along with a detailed written explanation of your objection within 10 business days of receiving the graded exam. There is absolutely no guarantee that the re-grade will result in a higher score. The score may be higher, lower or the same. 3 Learning Objectives, Part I FINA 469 Professor Steven V. Mann The following represents a list of things that we will discuss in the first part of our course. I. Securities and Markets What is a security? What is a complicated security? What attributes of expected cash flows do investors care about? Fixed-income vs. variable-income securities U.S. Treasury securities Agency securities/Mortgage-backed securities Corporate bonds International bonds U.S. pay vs. foreign pay Eurodollar bonds Yankee bonds Domestic issues Foreign bond market Eurobonds Primary vs. secondary markets Money vs. capital markets 4 What is liquidity? What is depth, breadth and resiliency? bid-ask spread as a pair of options market impact costs organized exchange vs. over-the-counter market what is a market maker? specialists vs. competitive market makers II. Portfolio Building risk aversion, risk neutral, and risk lovers portfolio’s expected rate of return long vs. short position mechanics of short selling portfolio’s variance what is the role covariance, correlation? diversification efficient set portfolio opportunity set minimum variance set minimum variance portfolio How do we locate the efficient set? In practice, what do we need to estimate the efficient set? What is asset allocation? What is the security selection decision? 5 What is an indexed portfolio? What is the capital allocation line? (equation, graph) What is the capital market line? (equation, graph) What is a complete portfolio? What is the distinction between market and unique risk? 6 Learning Objectives Exam II FINA 469 Professor Steven V. Mann Part III Asset Pricing Models Security Market Line (equation, graph) How do we locate mispriced securities in the CAPM? What causes the Security Market Line to change? How is expected return estimated with the security market line? Law of One Price How does arbitrage work? What is the fundamental assumption of the APT? Factor risk premium Factor portfolio Multifactor APT How is APT used in practice? What are the empirical problems with APT? Compare/contrast the CAPM vs. the APT Part IV Stock valuation models discounted cash flows vs. relative value approach Gordon growth model two-stage dividend growth model H-model Three-stage model 7 What type of investment strategies did Long-term Capital Management pursue? Financial ratio approaches P/E ratios P/S ratio P/Book ratio Different styles of equity investing – value vs. growth Part V Market Efficiency Explain the logic of market efficiency? How is the idea of market efficiency tested? Explain the role of transactions in EMH tests? Explain the role of the asset pricing model in EMH tests? What are the different kinds of anomalies? Examples of EMH anomalies Active vs. passive portfolio management 8 Learning Objectives for the Final Exam FINA 469 Professor Steven V. Mann Part VII Fixed-income Securities What factors affect a bond’s required yield? Price a bond Explain why bonds change in price What are day count conventions? Explain how bonds are priced between coupon payment dates How is accrued interest calculated? What is the difference between the full and flat price of a bond? Explain the three sources of dollar returns from investing in bonds Calculate current yield Explain how to calculate yield to maturity with the bond pricing formula Explain how to calculate yield to call with the bond pricing formula Calculate the total return of a bond (formula provided) Explain scenario analysis What is par curve and how is it calculated? What is spot curve and how are spot rates calculated Calculate a spot rate What is a forward rate and how are they calculated? Calculate a forward rate (formula provided) Explain how par rates, spot rates and forward rates are related to each other 9 What are the types of yield curve shifts and how are they related? Explain the importance of the curvature of the price/yield relationship Calculate Modified duration (formula provided) Explain what dollar duration tells us? Calculate the convexity of a bond (formula provided) What does convexity tell us? How are convexity and duration related? What are the properties of convexity? What is negative convexity? What is the value of convexity? What is effective duration/convexity? What is securitization? Explain the role of a special purpose vehicle in an ABS transaction? Why can ABS issuers borrow at lower rates than if they issued debt directly? What is/are the differences between the cash flows of amortizing vs. non-amortizing assets? Part VIII Derivative Securities Basic definitions of calls and puts What are the payoffs of calls / puts at expiration? What are the basic option strategies? (covered call, protective put, straddle, etc.) How can one hedge with options? What is the current exercisable value? What is the premium over current exercisable value? Basic intuition about option pricing 10 What is the option pricing model in a world of perfect certainty? Explain how changes in the five fundamental variables affect call values? (i.e., the Greeks) What is a synthetic call? What is a synthetic put? Explain put-call parity What is a forward contract? How much is forward contract worth at expiration? What are the risks of forward contracts? What is a futures contract? How do forwards and futures differ? Explain how marking-to-market works What are futures used for? Explain how stock index arbitrage works Explain how portfolio insurance works What are options on futures and how do they work? What are contracts-for-differences and how do they work? Please adhere to the Honor Code in your study of fixed-income. University of South Carolina Honor Code: It is the responsibility of every student at the University of South Carolina Columbia to adhere steadfastly to truthfulness and to avoid dishonesty, fraud, or deceit of any type in connection with any academic program. Any student who violates this Honor Code or who knowingly assists another to violate this Honor Code shall be subject to discipline. 11