Energy Systems - PSE4U
advertisement

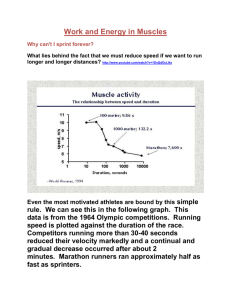
I will be able to explain how my body converts food into a usable form of energy for my cells and thus allows for movement. How does the human body generate energy? Carbohydrates Proteins Fats • Among the most common organic compounds on earth. Digestion breaks down carbohydrates into glucose. Glucose is stored in the liver and skeletal muscles in the form of glycogen. Glucose Metabolic pathways convert the chemical potential energy in foods we eat into ATP. ATP fuels cellular processes in our bodies. ADP + P + Energy → ATP ATP video Anaerobic process that occurs in the cytoplasm of cells. First of the two anaerobic energy pathways. Makes enough ATP to sustain intense activity for about 15 seconds. System involves breaking a phosphate group off of phosphocreatine (PC) molecule and adding it to ADP creating ATP. PC + ADP → ATP + creatine (Speed Skating Video – Men Team Pursuit) Allows athletes to participate in a high level of performance for an additional 1-3 minutes. Anaerobic process that occurs in the cytoplasm. Products of this reaction include ATP and a molecule called pyruvate. Pyruvate then moves on to the next pathway which is aerobic. Pathway Overview Video In the absence of sufficient oxygen, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid. Lactic acid builds up in the muscle fibres and causes pain and reduces movement. The exercise intensity at which lactic acid begins to accumulate within the blood is known as the anaerobic threshold. Anaerobic threshold level can be improved with exercise for athletes involved in endurance activities. Read Chapter 5 (pgs 81 – 84) 1. List the three key energy nutrients. 2. What is the role of carbohydrates as an energy source? 3. Why is ATP essential for life? 4. Compare anaerobic and aerobic systems. 5. List the type of activities that would use the ATP-PC system and Glycolysis. CHECK H/W