Gas laws
advertisement

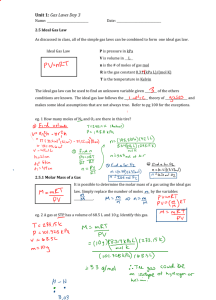
Gas laws 2 A spherical balloon with diameter 0.5 m contains a dry gas at 27°C. The balloon is heated up such that its diameter increases to 0.53 m while the gas pressure is kept constant. What is the new temperature? Neglect the surface tension of the balloon. A. 28.6°C B. 45.0°C C. 32.5°C D. 84.3°C 3. A sealed container of volume 1 m3 is filled with an ideal gas of temperature 22°C and pressure 140 kPa. What is the number of mole of gas molecules? The universal gas constant R = 8.31 J mol−1 K−1. A. 3.44×10−21 mol B. 5.71×10−2 mol C. 57.1 mol D. 766 mol 4. A fixed mass of an ideal gas has an initial pressure, volume and temperature of 100 kPa, 20 cm3 and 100°C respectively. What is the new volume of the gas if its pressure change and temperature change are +100 kPa and +100°C respectively? A. 6.51 cm3 B. 12.7 cm3 C. 20.0 cm3 D. 31.5 cm3 5 John breathes out under water and creates a bubble of volume 7 cm3. The gas inside the bubble has a pressure of 200 kPa and temperature of 37°C. The bubble ascends to a certain level where the gas volume becomes 12 cm3 and the temperature becomes 20°C. Assuming the gas is ideal, what is the gas pressure? A. 63.1 kPa 1 B. 123 kPa C. D. 324 kPa 110 kPa 6 A spherical bubble of diameter 1 mm rises from the bottom of a lake where the temperature is 4°C. The gas inside has an initial pressure of 9.01 × 105 Pa. When it reaches the water surface, the gas pressure becomes 1.01 × 105 Pa and the temperature increases to 20°C. What is the new diameter? Neglect the surface tension of water. (3 marks) 2 7. An experiment is carried out to investigate the relation between the pressure p and absolute temperature T of a gas of fixed mass and volume. The graph below shows the result obtained. (a) (i) If Celsius scale is used instead of Kelvin scale for the temperature axis, what would the x-intercept be? (1 mark) (ii) What is the significance of this temperature? (1 mark) (b) On the same graph, draw the graph obtained if the experiment is repeated with (i) half of the original volume but the same mass of gas. +(ii) one third of the original number of gas molecules but the same volume of gas. Explain your answer briefly. (3 marks) 3 8 A tank contains 50 kg of nitrogen gas (N2) at 0°C and 100 kPa. (a) What is the volume of the tank? (2 marks) (b) An additional 25 kg of N2 is added to the tank without a change in temperature. Find the new gas pressure. (2 marks) The molar mass of N2 is 28 g mol . The universal gas constant R = 8.31 J mol−1 K−1. −1 9. A tyre is filled with a gas at 20°C to a pressure of 300 kPa. The tyre is now heated up to 40°C. (a) What is the relation between the pressure p and Celsius temperature θ of the gas? (1 mark) (b) To maintain the original pressure, what fraction of the gas should be released from the tyre? Neglect the change in the volume of the tyre. (2 marks) 4