ChemQuiz_Energetics
advertisement

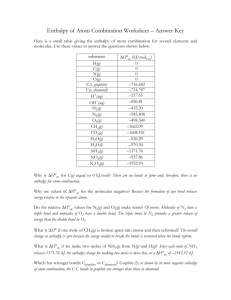
Energetics Click to start Question 1 Which statement about this reaction is correct? 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g) Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) ΔHƟ=+26.6kJ 13.3kJ of energy are absorbed for every mole of Fe reacted. 26.6kJ of energy are absorbed for every mole of Fe reacted. 26.6kJ of energy are released for every mole of Fe reacted. 53.2kJ of energy are released for every mole of Fe reacted. Wrong Answer! For 2 moles of Fe, 26.6kJ of energy is absorbed to break the bonds. 1 mole of Fe will require 13.3kJ of energy. Question 2 Which of the following is observed when the change in enthalpy is positive for the dissoving of a salt in water in an insulated copper beaker? Heat is evolved to the surroundings and the beaker feels cold. Heat is evolved to the surroundings and the beaker feels warm. Heat is absorbed from the surroundings and the beaker feels warm. Heat is absorbed from the surroundings and the beaker feels cold. Wrong Answer! A positve enthalpy change means that heat flows from the surroundings into the system. Question 3 All the following processes are exothermic except 2C2H5(g) C4H10(g) Cl(g) + e- Cl-(g) F2(g) 2F-(g) 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) 2Fe2O3 (s) Wrong Answer! Bond breaking is always endothermic. Question 4 What can be deduced about the relative stability of the reactants and products and the sign of ΔH, from the enthalpy level diagram below? Relative stability reactants ΔH Sign of ΔH products more stable - products more stable + reactants more stable - products reactants more stable + Wrong Answer! The vertical axis represents potential energy, energy or enthalpy. The reactants are high in energy and hence unstable; the products are lower in energy and hence more stable. The difference is the released in the form of heat energy. Question 5 What is the specific heat capacity of an alcohol in Jg-1K-1 if 560.0J of heat are required to raise the temperature of a 64.0g sample of ethanol from 295.0K to 310.0K? 0.583 0.194 8.75 0.292 Wrong Answer! Heat energy = mass x specific heat capacity x change in temp 560 = 64.0 x c x (310 – 295 ) c = 0.583 Jg-1K-1 Question 6 When 0.050 mol of nitric acid is reacted with 0.050 mol of potassium hydroxide in water, the temperature of the system increases by 13.70C. Calculate the enthalpy of reaction in kJmol-1 HNO3(aq) + KOH(aq) KNO3(aq) + H2O(l) Assume that the heat capacity of the system was 209.2J 0C-1. +57.3 kJmol-1 +2.87 kJmol-1 -2.87 kJmol-1 -57.3 kJmol-1 Wrong Answer! Heat energy = 13.7 x 209.2 = 2866.04J Enthalpy of reaction per mole of KCl = (1/0.05) x 2866.04 = 57328 Jmol-1 Sign is negative because energy is given out. Question 7 The bond energies for H2 , I2 and HI are 432, 149 and 295 kJmol-1 respectively. From these data, what is the enthalpy change(in kJ) for the reaction below? H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI(g) +286 +9 -9 -286 Wrong Answer! Enthalpy change = [(432 + 149)] – [(295 x 2)] = -9 kJ Question 8 Consider the following equation: 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) C6H12O6(s) + 6H2O(g) ΔH=2824kJmol-1 What is the enthalpy change associated with the production of 100.0g of C6H12O6? 157 kJ 282 kJ 508 kJ 1570 kJ Wrong Answer! Amount of C6H12O6= (100.0g/180gmol-1) = 0.55 mol-1 Enthalpy change = 0.55 x 2824 = +1568 kJ Question 9 The specific heat capacities of some metals are given below. Metal Specific heat capacity (Jg-1K-1) copper 0.385 magnesium 1.020 mercury 0.138 platinium 0.130 If 100kJ of heat is added to 10.0g samplesof each of the metals above, which are all at 250C, which metal will have the lowest temperature? copper mercury magnesium platinium Wrong Answer! Q = mcΔT, q/mc = ΔT, hence if c is increased, then ΔT will decrease. A high heat capacity means more energy is required to raise the temperature. Question 10 The bond energy for the H-F bond is equal to the enthalpy change for which process? HF(g) ½F2(g) + ½H2(g) HF(g) H(g) + F(g) ½F2(g) + ½H2(g) HF(g) H+(g) + F-(g) HF(g) Wrong Answer! The H-F bond enthalpy is the amount of energy (in kJ) required to break 1 mole of HF covalent bond into gaseous hydrogen and fluorine atoms (under standard thermodynamic conditions) Question 11 When a sample of a pure hydrocarbon (melting point 850C) cools, the temperature is observed to remain constant as it solidifies. Which statement accounts for this observation? The heat released in the change of state equals the heat loss to the surroundings. The solid which forms insulates the system, preventing heat loss. The temperature of the system has fallen to room temperature. Heat is gained from the surroundings as the solid forms, maintaining a constant temperature. Wrong Answer! During freezing intermolecular forces (van der Waals’ forces) are formed and heat energy is released to the surroundings. Question 12 Consider the following reactions: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) Bond enthalpies (in kJmol-1) involved in the reaction are: NΞN a H-H b N-H c Which expression could be used to calculate the enthalpy of reaction? a + 3b - 2c a - 3b + 6c 6c – a + 3b a + 3b – 6c Wrong Answer! Enthalpy change = ∑(bond broken) - ∑(bond made) = (NΞN + 3 x H-H) – (6 x N-H) Question 13 The enthalpy changes for two different hydrogenation reactions of C2H2 are: C2H2 + H2 C2H4 ΔHƟ1 C2H2 + 2H2 C2H6 ΔHƟ2 Which expression represents the enthalpy change for the reaction below? C2H4 + H2 C2H6 ΔHƟ = ? ΔHƟ1 + ΔHƟ2 ΔHƟ1 - ΔHƟ2 ΔHƟ2 – ΔHƟ1 - ΔHƟ1 - ΔHƟ2 Wrong Answer! Using the energy cycle by Hess law, the enthalpy change is obtained by reverting ΔHƟ1 and adding to ΔHƟ2 C2H4 + 2H2 C2H6 ΔHƟ ΔHƟ1 ΔHƟ2 C2H2 + 2H2 Question 14 2KHCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) K2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) + 2HCl(aq) Ɵ ΔH 2 ΔHƟ1 2KCl(aq) + 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) This cycle may be used to determine ΔHƟ for the decomposition of potassium hydrogen carbonate. Which expression can be used to calculate the ΔHƟ ? ΔHƟ = ΔHƟ1 + ΔHƟ2 ΔHƟ = ΔHƟ1 - ΔHƟ2 ΔHƟ = ½ ΔHƟ1 - ΔHƟ2 ΔHƟ = ΔHƟ2 – ΔHƟ1 Wrong Answer! Congratulations!