KINGDOM PLANTAE
advertisement

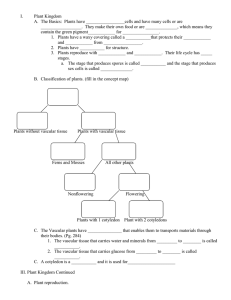
A. Autotrophs - use sun’s energy directly (plants) B. Heterotrophs - obtain energy by the foods they eat. (animals) * all organisms use the energy from the Cellular Respiration ALL organisms obtain usable energy (ATP) in a process called cellular respiration. The equation for cellular respiration is the opposite of the equation for photosynthesis. KINGDOM PLANTAE Characteristics • Multicellular • Eukaryotic • photosynthetic (autotrophic) • most reproduce sexually and asexually • Contain cell walls (cellulose), chloroplasts, and large central vacuole Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Comparison Diagram Introduction to Plants Plant adaptations: Plants evolved from aquatic algae Had to gain the ability to conserve water Cuticle – waxy covering, helps prevent the water loss and is a barrier to microorganisms Stomata - openings in the outer cell layers of leaves for gas exchange Roots - take in water and dissolved minerals Stems - Transport water and dissolved substances, stores food and water, contains vascular tissue (xylem and Phloem) Leaves (blade) – site of photosynthesis Vascular Tissue – allows faster transport of water and nutrients, provides structure (xylem and phloem) Seeds - contains an embryo, nutrients, and protective coat; allows seeds to survive in harsh conditions and sprout when favorable Transpiration • evaporation of water from plants. • occurs chiefly at the leaves while their stomata are open for the passage of CO2 and O2 during photosynthesis. Classification of Plants Divided into 3 basic groups based on evolutionary adaptations. 1. Nonvascular plants (mosses) 2. Seedless vascular plants (ferns) 3. Seed plants (gymnosperms and angiosperms) 1. Non-vascular Plants • Ex. Mosses (Bryophyta), liverworts and hornworts • 400 million years old; 16,000 species • Gametophyte is dominant • Required water to reproduce – swimming sperm • No vascular tissue to low to ground • Evolutionary adaptation – Cuticle; stomata 2. SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS • Ex. Ferns (pterophyta), whiskferns, lycopods and horsetails • All are seedless, sperm must swim (no pollen) • sporophyte is the dominate generation. • Evolutionary adaptations – roots, stems and vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) 3. Seed Plants • Gymnosperms “cone-bearers” (conifers, ginkos) and angiosperms (flowering plants) • Gametophyte becomes more reduced • Evolutionary adaptations Pollination replaces swimming sperm, seed evolved, flower