Shearman & Sterling
advertisement

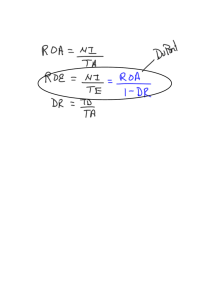
Friday: Financial Restructuring Cap des Biches AshantiBogoso Feng-Shui Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 1 Mt Cameroon Ecotours Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 2 Mt Cameroon Mount Cameroon Ecotours Last Year Tourists Revenue/Tourist Revenues Expenses Profit Capex Working Cap Free cash flows: Expected Return Terminal Value PV (Cashflows) NPV Cash Firm Value Equity to Raise Equity to Firm Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy 700 0.65 455.00 (305.00) 150.00 12,357 1,300 13,657 5,000 8,657 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 850 0.65 552.50 (442.50) 110.00 (2,100.00) (500.00) (2,490.00) 935 0.65 607.75 (463.75) 144.00 1,100.00 (50.00) 1,194.00 2,550 2,805 3,086 1.30 1.30 1.30 3,315.00 3,646.50 4,011.15 (867.50) (931.25) (1,001.38) 2,447.50 2,715.25 3,009.78 25% 25% 25% (1,992.00) 764.16 1,224.96 (55.00) (55.50) 2,392.50 2,659.75 Year 5 Terminal 3,240 1.30 4,211.71 (1,039.94) 3,171.76 (55.55) 2,954.23 (27.78) 3,143.99 25% 25% 1,089.43 968.04 15% 31,439.86 10,302.21 = 5,000 - 2,200 - 1,000 -500 37% Percentage of equity to investors 63% Percentage of equity to owners Financial Restructuring 3 Leveraged Finance Cost of the Deal Estimating cost of deal Shares Price Premium Equity cost Debt cost Fees Capex & restructuring Total cost of deal $ $ 5% $ 10% $ $ 10 45 15% 518 $ 55 29 57 658 lbocapacity.xls Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 5 LBO Financing NEWCO Cost of purchasing the business Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Senior debt $457 Mezzanine What securities? What returns? What investors? Equity $25 Financial Restructuring 6 Case Study: Cap des Biches (B) The LBO Proposal Devise a recommended financing plan GTI (owner) Buyers Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Other Investors Financial Restructuring 7 Cap des Biches (B) Cap des Biches (B) Evaluating a Leveraged Buy-Out (LBO) Given Share price Number of shares GTI ownership Public ownership NOI Interest Coverage Tax Earnings Per share Growth rate 30% LBO data Management equity Bank coverage ratio needed Bank rate Seller's debt amount Seller's debt rate Premium for shares Sale NOI multiple 24 9 million 35% 65% 30.00 1.00 30.00 8.70 20.30 2.26 3.60% Acquisition data Flexics P/E Free cash flows next year Free cash flows last year Raise growth to Upfront costs 18 10.64 $2.57 per share $2.48 per share 5.50% $2.00 per share 20 2 12% 30 15% 5% assumption 12 www.stern.nyu.edu/~igiddy/dakar Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 8 Corporate Financial Restructuring Prof. Ian GIDDY Stern School of Business New York University What is Corporate Restructuring? Any substantial change in a company’s financial structure, or ownership or control, or business portfolio. Designed to increase the value of the firm Restructuring Improve capitalization Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Improve debt composition Change ownership and control Financial Restructuring 10 It’s All About Value How can corporate and financial restructuring create value? Assets Fix the business Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Operating Cash Flows Liabilities Debt Or fix the financing Equity Financial Restructuring 11 Restructuring Figure out what the business is worth now Use valuation model – present value of free cash flows Fix the business mix – divestitures Value assets to be sold Fix the business – strategic partner or merger Value the merged firm with synergies Fix the financing – improve D/E structure Revalue firm under different leverage assumptions – lowest WACC Fix the kind of equity What can be done to make the equity more valuable to investors? Fix the kind of debt or hybrid financing What mix of debt is best suited to this business? Fix management or control Value the changes new control would produce Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 12 Corporate Finance CORPORATE FINANCE DECISONS INVESTMENT FINANCING PORTFOLIO RISK MGT MEASUREMENT CAPITAL DEBT M&A Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy EQUITY TOOLS Financial Restructuring 13 Capital Structure: East vs West Intel VALUE OFTHE FIRM TPI Optimal debt ratio? DEBT RATIO Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 14 Fixing the Capital Structure Too little debt Managers like to control shareholders’ funds Underestimate the cost of equity Produces Less discipline Excessive cost of capital Takeover risk Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Too much debt Close control of equity Easy money Underestimate business or financial risks Produces Risk of financial distress Excessive cost of capital Destroy operating value Takeover risk Financial Restructuring 15 Fixing the Capital Structure: Distress Restructuring The Three Excesses Labor Capacity Debt Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 17 TPI’s Refinancing Asia’s biggest debtor Almost $4 billion in foreign currency debt financing domestic revenues Protracted rescheduling results in $360 million debt/equity swap No change in management or effective control Still needs $1.2 billion new equity Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 18 Debt-Equity Swaps Cosmetic or real? Choices for company under siege Raise new equity to pay off creditors Example: Iridium Give creditors equity in place of debt Example: Sammi Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 19 What Do Debt-Equity Swaps Do? Overleverage creates financial distress Actual or potential default Lenders take equity in lieu of repayment Lenders hold equity passively Lenders replace management Change of control means restructuring Existing management buys time Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Lenders sell equity Financial engineering Bottom line “rationalization” Divestitures & outsourcing Financial Restructuring 20 What Are The Alternatives? Key: Make the new securities attractive to: Existing lenders New lenders New bond investors New equity investors Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 21 The Financing Spectrum Equity Expected Return Residual returns after contractual claims Control through voting rights Senior Debt Returns independent of the value of the business Control through covenants Risk Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 22 The Financing Spectrum Expected Return Equity Preferred equity Convertible debt Subordinated debt Senior unsecured debt Senior secured debt Risk Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 23 The Financing Spectrum Expected Return Equity Preferred equity Convertible debt Subordinated debt Senior unsecured debt Asian bank NPLs Senior secured debt Risk Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 24 What Are The Alternatives? Asset-backed or cash flow-backed debt Senior debt Subordinated debt Subordinated debt with upside participation Subordinated debt with equity option Preferred equity Restricted shares Common stock Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 25 Subordinated High Yield Debt “Junk bonds” – like equity, but allow increased financial leverage Tax advantage over equity Big market in USA (institutional investors) and increasing in Europe Leveraged loans favored by certain commercial banks Often used in connection with M&A and LBOs Behave like equity – and often have equity participation Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 26 Sub Debt -- Motivations Optimization of financial leverage Regulatory-driven capital requirements Rated asset securitizations (senior-sub structure in asset-backed securities) Insider or supplier-credit subordination (eg in project finance) Work-outs and restructurings (existing borrowers agree to seniority of new loans, to buy time) Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 27 Sub Debt’s Big Problem: High Interest! Solutions Deep discount subordinated debt Subordinated debt with equity warrants Convertible subordinated debt Participating subordinated debt Puttable subordinated debt Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 28 Preferred Equity Legally a form of equity Claim senior to ordinary equity May have fixed dividend, or may be “participating” But cannot trigger liquidation if payment missed Par value determines liquidation claim Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 29 Convertible Preferred Used by venture capital firms Permit investors to participate in growth But give preference in liquidation if the venture fails And disguise share value (tax!) A variant – PERCS* give issuer right to convert into common stock *Preferred equity redemption cumulative stock Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 30 Preferred Stock: Pros and Cons Advantages No dilution of control Dividends conditional on availability of earnings Omission cannot force liquidation Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Disadvantages Higher after-tax cost than debt Lower return on equity Limited investor interest Financial Restructuring 31 Restricted Stock: Pros and Cons Advantages Overcome foreign control restrictions Insiders retain control If company well run, value of control may be low Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Disadvantages Nonvoting stock trades at a discount Dual-class recaps hurt stock price May allow management to avoid needed reforms Financial Restructuring 32 The New Equity Option Key: Make the new equity attractive to: Portfolio investors Domestic International Reduce agency costs or we’ll “Just say no!” Strategic/direct investors Domestic International Cede Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy control or we’ll go elsewhere Financial Restructuring 33 The Difference “The Ministry of Finance received a preferred share while investors received a preferred share and a warrant allowing them to purchase the ministry's share at a 13.3% premium (equivalent to the cost of carry) during a three-year period. The preferred shares carry a 5.25% dividend and full voting rights” "When institutions started buying the story, they bought the convertible bonds, the sub debt - you name it, they bought it." Alternatives: Thai Farmers Bank: SLIPS, Bankok Bank: CAPs Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 34 Transparency and Disclosure A 275-page prospectus, which provided a breadth and depth of information previously unseen in an Asian issue. "We went and looked back at US bank holding company offers - those that were US SEC Grade 3 compliant. We also went back and looked at a lot of the prospectuses for the recaps of US banks, like Mellon and Citibank. We looked at the level of disclosure they achieved and committed ourselves to exceeding that -- which SCB did." Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 35 What Globally Mobile Investors Look At Macro Factors Structural Factors Firm-level Factors Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy • Currency overvaluation • Capital restrictions • Acctg & disclosure requirements • IAS compliance • Bankruptcy regime • Creditor rights • Govt-corporate nexus • Trading infrastructure • Price-Value ratio, Sharpe ratio, EVA • D/E ratio • Currency & maturity mismatch • IAS conformity • Insider control • Objective research coverage • Trading liquidity Financial Restructuring 36 Fixing the Capital Structure: Distress Restructuring Cap des Biches (C) The Creditors are Prowling Trouble! Reason The financing is bad Business mix is bad The company is bad Remedy Raise equity or Change debt mix Sell some businesses or assets to pay down debt Change control or management through M&A Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 38 Financially Distressed Firms Lose customers Get less favorable terms from suppliers Are forced to discount products Reduce new investment to below the optimal level Example: Hynix (Korea) Source: Altman (1984), Opler and Titman (1994) Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 39 When Default Threatens, Value the Company Highest Valuation of Company? Merged Value Sale to Strategic Buyer Going Concern Value Auction Voluntary Reorganization Existing Management Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Ch 11 Reorganization Liquidation Value Voluntary Liquidation Ch 7 New Management Financial Restructuring 40 Zombie, Inc Does it make sense to dissolve the company? Is it better to sell the company? How much debt can the company afford to have? Assume you have been brought in as the new CEO-CFO team. What terms of restructuring can you propose to the banks? Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 41 Debt Restructuring in Distress Can a debt restructuring create value? Assets Operating Cash Flows Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Liabilities Debt Equity Banks give up some creditor rights in exchange for equity Financial Restructuring 42 Example Earnings at Zombie Inc., have suffered in recent years. The private company now faces a financial crisis, as a result of its possible inability to repay a principal repayment on its debt coming due in the next quarter. The company's summary balance sheet is as follows: Assets Cash Accounts receivable Other short term assets Property, plant and equipment Total Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy 100000 900000 5100000 8000000 14100000 Liabilities Accounts payable Short term secured debt Long term bank debt Shareholders equity Total 1000000 100000 9000000 4000000 14100000 Financial Restructuring 43 Example The company faces a takeover, but management has made a restructuring proposal to its unsecured bank lenders, namely that they convert one half of Zombie's bank debt into equity at the current book value per share. Should the banks take the offer? Assets Cash Accounts receivable Other short term assets Property, plant and equipment Total Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy 100000 900000 5100000 8000000 14100000 Liabilities Accounts payable Short term secured debt Long term bank debt Shareholders equity Total 1000000 100000 4500000 8500000 14100000 Financial Restructuring 44 Example of Valuation: Before-and-After Zombie, Inc Share Valuation Shares Book Value Acquisition Value Management Est. NPV, based on EBITDA WACC Growth Debt Going Concern Value $ $ $ Before 400,000 10.00 $ 8.00 20.00 $ After 850,000 10.00 9.41 1,100,000 1,100,000 17.48% 11.22% 2.5% 2.5% 10,100,000 5,600,000 $ (6.43) $ 8.62 Option value? Bank lenders Debt (at market) Equity (NPV value) Total Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Before 7,182,749 0 7,182,749 After 4,500,000 3,876,905 8,376,905 Financial Restructuring 45 Cap des Biches (C) CDB, two years after the successful LBO, is having difficulty meeting its debt service obligations. The banks are putting pressure on management to make a restructuring proposal. Can Cap des Biches afford to pay its required interest and principal this year? Next year? What is the debt capacity of Cap des Biches Power Company? Please suggest a way in which the debt could be restructured to keep the banks satisfied and keep the company alive. Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 46 Fixing the Capital Structure: Making Use of Cash Flows Leveraged Finance Company has unused debt capacity Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Takeover? Share buyback? Leveraged recapitalization? Financial Restructuring 48 Leveraged Recapitalization Strategy where a company takes on significant additional debt with the purpose of paying a large dividend (or repurchasing shares) Result is a far more leveraged company -- usually in excess of the "optimal" debt capacity After the large dividend has been paid, the market value of the shares will drop. Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 49 Leveraged Recapitalizations Motivations: Defensive Proactive Ownership transition/liquidity Which produces what value? Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 50 Cap des Biches (D) CDB, after its debt restructuring, has achieved a turnaround. Net cash flows are now positive and steady, and the shareholders are looking for ways in which they can realize the benefits of their investments. Should they pay a dividend, buy back shares, or sell the company? Group report due by Wednesday 11th June Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 51 What is Corporate Restructuring? Any substantial change in a company’s financial structure, or ownership or control, or business portfolio. Designed to increase the value of the firm Restructuring Improve capitalization Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Improve debt composition Change ownership and control Financial Restructuring 52 Copyright ©2003 Ian H. Giddy Financial Restructuring 53