PPT
advertisement
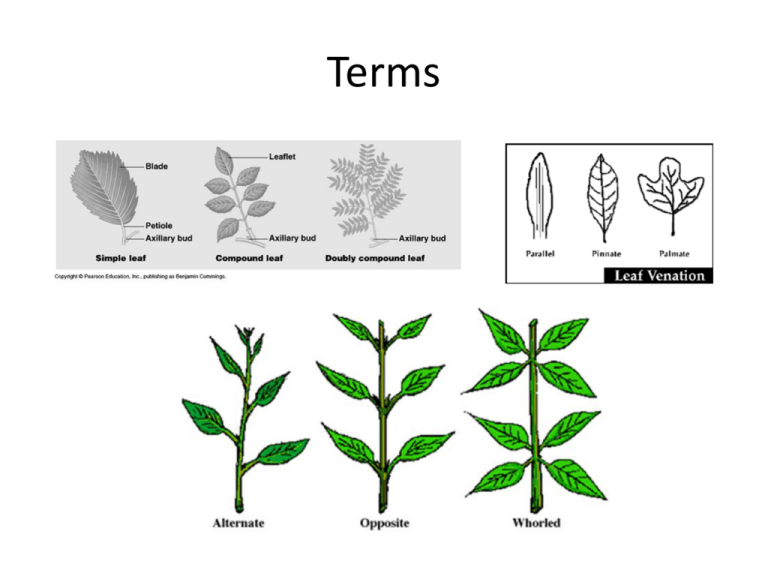
Terms Acacia (Golden Wattle) (Acacia pycnantha) • Description – Phyllodes: modified petioles (parallel veins) – Evergreen • Fruit – Legume • Flower – Yellow • Location – Australia • Chemical – Tannins • Uses – Perfume • Family – Fabaceae (pea family) Beavertail Cactus (Opuntia basilaris) • Description – Leaves modified into Glochids – Stems modified as Chladophylls • Fruit: fleshy red fruit (pear) • Flower: Yellow to red • Location: SW United States • Chemical – none • Use – Can be eaten • Family: – Cactaceae Bladderpod (Isomeris arborea) • Description – Compound leaves with 3 leaflets – Leaves alternate – Evergreen • Fruit: Capsule • Flower: Yellow • Location: – Endemic to California – Desert Regions • Chemical – Strong odor to reduce predation • Uses – None • Family – Capparaceae Brazilian Pepper (Schinus terebinthifolius) • Description – Pinnately Compound leaves – Leaves alternate – Evergreen • Fruit: Drupe • Flower: small white • Location: – Tropical and subtropical South America • Chemical – Aromatic sap that may burn – May act as a narcotic on birds who eat berries • Uses – Ornamental • Family – Anacardiaceae (Sumac family) Black Sage (Salvia mellifera) • Description – Simple leaves with small hairs – Drought Deciduous • Fruit: Schizocarp • Flower: blue or lavender in stacked balls • Location: – CSS & Chaparral • Chemical – Diterpenoids used as pain relievers • Use – Rub on sore feet – Chumash brewed as sun tea – Nectar used to make honey • Family – Lamiaceae (Mint family) Bulrush (Schoenoplectus californicus) • Description – Triangular leaf – Sedge-like • Fruit: grain • Flower: brown or tan panicle inflorescence • Location: – Indicator of Freshwater in North and South America • Chemical – none • Use – Used by Native Americans to make baskets, rope, canoes • Family – Cyperaceae California Buckeye (Aesculus californica) • Description – Palmately Compound with five leaflets – Deciduous • Fruit: Capsule • Flower: Large white to pink • Location: only Buckeye endemic to California • Chemical – neurotoxic glycoside aesculin, which causes hemolysis of red blood cells. • Use – Used by Native Americans to kill fish – Toxic to honeybees • Family – Sapindaceae California Buckwheat (Eriogonum fasciculatum) • Description – Leaves in clusters – Evergreen • Fruit: Grain • Flower: white or brown clusters • Location: Southwestern United States – CCS and Chaparral • Chemical – None • Use – treatment of headache, diarrhea, and wounds – Good for heart – Erosion control – Source of food for honeybees in summer months • Family – Polygonaceae California Redbud (Cercis occidentalis) • Description – Simple heart-shaped leaves – Deciduous • Fruit: Legume • Flower: Large Pink or red • Location: Western United States • Chemical – None • Use – Wood Veneer – Erosion control – Red bark used for baskets • Family – Fabeaceae (Pea family) California Sagebrush (Artemisia californica) • Description – Slender flexible stems with thin pinnate leaves – Evergreen • Fruit: achene • Flower: narrow inflorescence which are yellowish • Location: Native to California and Baja in CSS and Chaparral • Chemical – Terpenes to reduce competition and predation • Use – Erosion control – Reduce digestive issues • Family – Asteraceae (Sunflower family) Caster Bean (Ricinus communis) • Description – Palmate alternate Leaves – Evergreen • Fruit: Spiny capsule (not a true bean) • Flower: panicle-like inflorescence which are reddish in color • Location: Native to California and Baja in CSS and Chaparral • Chemical – Ricin (deadly) • Use – Source of Caster Oil used for digestive cleansing – lubricant • Family – Euphorbiaceae Catalina Cherry (Prunus ilicifolia) • Description – Simple toothed alternating leaves (vary) – Evergreen • Fruit: Drupe with large pit • Flower: small white • Location: Native to California and Baja in CSS and Chaparral • Chemical – Tannins • Use – Native Americans made a fermented drink • Family – Rosaceae (Rose Family) Catalina Ironwood (Lyonothamnus floribundus) • Description – Compound Leaves (fernlike) – Evergreen • Fruit: Capsule • Flower: Cream • Location: Endemic to Catalina Island • Chemical – None • Use – Ornamental but seeds not very viable • Family – Rosaceae (Rose family) Cattail (Typha sp.) • Description – Flat simple leaf – Evergreen • Fruit: nut • Flower: Dense Brown Spike (wind dispersed) • Location: Indicator of fresh water in Northern Hemisphere • Chemical – None • Use – Rhizomes are edible • Family – Typhaceae Ceonothus (Mt. Lilac) (Ceonothus sp.) • Description – Simple leaf with three prominent veins – Evergreen • Fruit: Capsule • Flower: Blue • Location: Endemic to California in chaparral • Chemical – None • Use – Eaten by Deer – Used for teas – Baskets • Family – Rhamnaceae Coast Live Oak (Quercus agrifolia) • Description – Simple convex leaves with dentate margins – Hairs in axils in leaves – Evergreen – No undergrowth due to shade and Tannins • Fruit: Nut • Flower: Catkins • Location: Coast of California • Chemical – Tannins • Use – Food – Charcoal • Family – Fagaceae Coffee Berry (Rhamnus californica) • Description – Simple, reddish bark on stems – Evergreen • Fruit: Drupe • Flower: Greenish • Location – Southwestern United States, Chaparral • Chemical – none • Uses – Ornamental not as well liked by deer – Erosion control – Heal burns and rashed – Used as laxative • Family: Rhamnaceae Coyote Bush (Baccharis pilularis) • Description – Simple leaves that are often sticky – Various shapes determined by location – Large root system • Fruit: Achenes • Flower: small white or yellow • Location – Southwestern United States, Chaparral • Chemical – Oils to prevent predation • Uses – Secondary pioneer plant • Family – Asteraceae (Sunflower family) Elderberry (Sambucus sp.) • Description – Pinnately compound leaves with 5-9 leaflets – Deciduous • Fruit: True berry • Flower: Yellow in a umbella structure • Location – Temperate to subtropical regions of the world mostly Northern hemisphere • Chemical – none • Uses – Wine – Syrup • Family – Adoxaceae Encelia or Brittlebush (Encelia sp.) • Description – White leaves – Evergreen • Chemical – none • Uses • Fruit: Acene – Glue, Sealer, Gum, Incense – Treat toothaches • Flower: Yellow • Family • Location – U.S. Desert – Asteraceae (Sunflower family) Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus sp.) • Description – – – – – 700 species Alternate simple leaves Evergreen Gum Trees Peeling bark • Fruit: Capsule • Flower: vary in color with an operculum • Location – Australia • Chemical – Terpenoids (aromatic) • Uses – Planted to lower the water table – Make pulp for paper – Antiseptic – Food additives – Insect repellent • Family – Myrtaceae Flannel Bush (Fremontodendron sp.) • Description – Simple 3-lobed leaves – Evergreen – Fuzzy texture – modified hairs called trichomes • Fruit: Capsule • Flower: Large yellowish orange Flowers • Location: Southwest U.S. and Mexico • Chemical – None • Use – Water conservation gardens • Family – Malvaceae Fremont Cottonwood (Populus fremontii) • Description – Simple leaf with long flattened petiole – Deciduous • Fruit: Achene • Flower: Catkins • Location: Southwest U.S. and Northern Mexico in riparian areas • Chemical – None • Use – Erosion control – Fuel and fence posts • Family – Salicaceae Fringe Tree (Chionanthus virginicus) • Description – Simple leaf with long flattened petiole – Deciduous • Fruit: Drupe • Flower: Larger white • Location: Eastern U.S. • Chemical – None • Use – Dried bark and roots used to treat inflammation – Crushed bark used to treat sores and wounds • Family – Oleaceae Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba) • Description – Simple leaf which is fan shaped – Deciduous • Fruit: None • Flower: None • Location: China • Chemical – Butyric Acid • Use – Decorative – only males planted in this country • Family – Ginkgoaceae Horehound (Marrubium vulgare) • Description – Simple leaf with crinkled appearance • Fruit: Berry • Flower: White clusters on stem • Location: Europe, Africa and Asia • Chemical – Essential oils • Use – Antimicrobial and anticancer properties – Candy – Grasshopper repellent – Invasive Weed • Family – Laminaceae (Mint family) Incense Cedar (Calocedrus decurrens) • Description – Scaled leaves in flat sprays – Branches Flexible • Chemical – None • Use • Fruit: None • Flower: None • Location: North America – Pencils – Light fires • Family – Cupressaceae Indian Paintbrush (Castilleja sp.) • Description – Clover like leaves • Fruit: Capsule • Flower: red, orange to yellow (bracts) • Location: North America • Chemical – None • Use – Eaten as greens – Hairwash – Dye • Family – Orobanchaceae Jacaranda (Jacaranda sp.) • Description – Doubly compound leaves • Fruit: Capsule • Flower: Purple – often sticky • Location: Central and South America • Chemical – None • Use – Ornamental plants – Acoustic guitars • Family – Bignoniaceae Jimson Weed (Datura stramonium) • Description – Large simple toothed leaves • Fruit: Capsule • Flower: Large white to purple • Location: Americas • Chemical – Atropine • Use – Relieve asthma symptoms – hallucinogen • Family – Solanaceae Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis) • Description – Simple leaves that stand erect • Fruit: Capsule • Flower: small greenish yellow • Location: North America • Chemical – Oil (liquid wax ester) • Use – – – – Laxative Salve Biodiesel fuel Cosmetics • Family – Simmondsiaceae Laurel Sumac (Malosma laurina) • Description – Large Simple Leaves with reddish edges • Fruit: Drupe • Flower: Small white • Location: Southern California, CSS and Chaparral • Chemical – Volatile compounds • Use – Tea for dysentery – Crown sprouting – Fire adapted • Family – Anacardiaceae (Sumac family) Lemonade Berry (Rhus integrifolia) • Description – Large Simple and alternating – Evergreen – Reddish twigs • Fruit: Berry • Flower: Small rosy pink • Location: Southern California, Chaparral • Chemical – Tannins • Use – Lemonade like drink – Make candles • Family – Anacardiaceae (Sumac family) Liquid Amber (Lizuidamber styraciflua) • Description – Large Simple and palmate – Deciduous • Chemical – Styrax – • Use • Fruit: Woody Capsule • Flower: greenish • Location: Southwestern U.S. – Plywood, furniture, cabinets – Chewing gum • Family – Altingiaceae Mesquite (Prosopis sp.) • Description – Deciduous – Doubly pinnate compound leaves – Long Taproot (up to 200 ft) – Thorns • Fruit: Legume • Flower: Catkins with pale green or yellow flowers • Location: Southern Deserts • Chemical – None • Use – Food (flour) – Furniture – Barbecues • Family – Fabaceae (Pea family) Mulefat (Baccharis salicifolia.) • Description – Simple Leaves – Sticky foliage • Fruit: small achene • Flower: small fuzzy pink or red-tinged white flowers • Chemical – None • Use – Erosion control • Family – Asteraceaea (Sunflower family) • Location: Southwest United States CSS and Chaparral and deserts Mustard (Bassica sp.) • Description – Annual • Fruit: Silque • Flower: Yellow • Location: Native to Mediterranean Europe • Chemical – None • Use – Pioneer plant (indicator of distrubance) – Cooking oil – Spice – High in Vitamin C • Family – Brassicaceae (Mustard family) Palm Tree (Washingtonia sp.) • Description – Evergreen – Skirt – Near water (Oasis) • Fruit: Drupe • Flower: small and insignificant • Location: – California – Mexico • Chemical – None • Use – Food – Baskets – Thatch Roofs • Family – Arecaceae Palo Verde (Parkinsonia microphylla) • Description – Green bark – Small leaves that are drought deciduous • Fruit: Legume • Flower: pale yellow • Location: – Mojave Desert, Sonoran Desert • Chemical – None • Use – Food (flour) • Family – Fabaceae (Pea family) Pampas Grass (Cortaderia selloana) • Description – Tall grass with leaves that cut when going toward center of plant • Fruit: Grain • Flower: dense white panicles • Location: – Southern South America • Chemical – None • Use – Flower arrangements • Family – Poaceaea (Grass family) Pine Tree (Pinus sp.) • Description – Leaves are needles grouped into fascicles – Branches flexible • Fruit: None • Flower: None • Chemical – None • Use – wood – Furniture, floors • Family – Pinaceae • Location: – Worldwide Sago Palm (Cycas Revoluta) • Description – Palm-like • Fruit: None • Flower: None • Location: Old World • Chemical – Alkaloids, tannins, steroids • Use – Ornamental • Family – Cycadaceae Southern Black Walnut (Juglans nigra) • Description – Compound leaves – Deciduous – Slight odor • Fruit: Drupe • Flower: green catkins • Location: New World • Chemical – None • Use – Flooring, furniture – Food • Family – Juglandaceae Southern Magnolia (Magnolia grandiflora) • Description – Thick Waxy Leaves – rusty pubescence underneath • Fruit: Follicle • Flower: Large White • Location: Southeastern U.S. • Chemical – None • Use – Ornamental – Make furniture, pallets and veneer • Family – Magnoliaceae Sugar Bush (Rhus Ovata) • Description – Large simple leaves with reddish twigs – Ovate leaves that are folded along the midrib • Fruit: drupe • Flower: small, pink • Location: Southern California in chaparral. • Chemical – Tannins • Use – Ornamental • Family – Anacardiaceae (Sumac family) Sweet Bay (Laurus sp.) • Description – Glossy simple leaves – Evergreen • Fruit: True berry • Flower: Pale yellow green • Location: Native to Mediterranean climate • Chemical – Cineole oil • Use – Astringent – Olympic Wreaths – Cooking (spices) • Family – Lauraceae Toyon (Heteromeles (Photonia) arbutifolia) • Description – Christmas Berry – Simple leaf - dentate – Evergreen • Fruit: pome • Flower: small, white • Location: Southern California in chaparral and CSS. • Chemical – Tannins – Glycocides • Use – Ornamental – Jelly from fruit – Tea for stomach ailments • Family – Rosaceae (Rose family) Tree Tobacco (Nicotiana glauca) • Description – Heart shaped leaves • Fruit: Capsule • Flower: Yellow tubular • Location: South America • Chemical – Nicotine • Use – Smoked – Treat swelling and bruises – Biofuel • Family – Solanaceae Western Sycamore (Plananus racemosa) • Description – Large palmate leaves that are pubescent – Deciduous – Peeling Bark • Fruit: achene • Flower: inflorescence • Location: California and Baja • Chemical – None • Use – Ornamental • Family – Platanaceae White Alder (Alnus rhombifolia) • Description – Simple alternate leaves with serrate margins – Deciduous – Bark with “eyes” • Fruit: Strobili (females) • Flower: Catkins (male) • Location: California and Baja • Chemical – None • Use – Ornamental • Family – Betulaceae White Ash (Fraxinus americana) • Description – Compound leaves that are made of 5-9 leaflets – Leaves are opposite – Deciduous • Fruit: Samara • Location: – Eastern North America – Moist habitats • Chemical – None • Uses – Baseball bats, oars, flooring, tool handles • Family: Oleaceae White Sage (Salvia apiana) • Description – Large white leaves with an odor • Fruit: Achene • Chemical – Terpenes to reduce competition and predation • Use – Food (Pinole) • Flower: white to lavender • Location: CSS and Chaparral of southwestern U.S. • Family – Lamiaceae (Mint family) Wild Radish (Raphanus raphanistrum) • Description – Annual – Small simple leaves – Invasive species • Chemical – None • Use – Food • Fruit: Silques • Family • Flower: white to lavender • Location: Native to Asia – Brassicaeae (Mustard family) Willow (Salix sp.) • Description – Narrow simple leaves – Usually Deciduous – Moist soils • Fruit: capsule • Chemical – Salicylic Acid • Use – Aspirin • Family • Flower: catkins • Location: Northern hemisphere – Salicaceae Plant families Mustard (Brassicaceae) Cactus (Cactaceae) Mint (Lamiaceae) Rose (Rosaceae) Pea (Fabaceae) Sumac (Anacardiaceae) Sunflower (Asteraceae) Grass (Poaceae)






