Chapter 4: Prenatal development, birth, and newborns' readiness for
advertisement

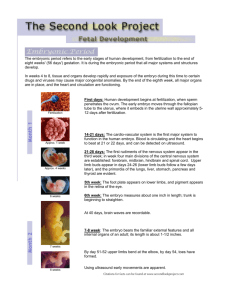
Chapter 4: Prenatal development, birth, and newborns’ readiness for life. Dr. Pelaez From conception to birth • Prenatal development is divided into 3 major phases: – Germinal period – Embryonic period – Fetal period Germinal Period • From conception to implantation (about 14 days). • Zygote moves toward uterus through fallopian tube • Implantation occurs • Support system develops (4 structures) Embryonic period • • • • • Lasts from week 3 to week 8. Neural tube development begins. Heart begins to beat Grows about 1/30 inches per day. External body structures form (ears, limbs, eyes) Fetal period • Lasts from week 9 to term. • By end of month 3, sex can be detected on ultrasound • Neural and muscular systems continue to develop • By second trimester (month 5-6), covered by vernix & lanugo (substance that protects fetal skin & fine hair which helps vernix to stick to body). • Third trimester (weeks 25-38) involve rapid growth and maturity of all organ systems. Teratogens • External agents such as viruses, drugs, and radiation that can be harmful to developing embryo or fetus. • Sensitive periods • Long-term effects depend on the quality of postnatal environment Maternal diseases • Diseases capable of passing through placenta and damage embryo/fetus • Rubella. 60-85% of babies exposed will have birth defects. • STD’s (AIDS, herpes, syphilis). • Toxoplasmosis • Influenza • Malaria • Tuberculosis Drugs • Drugs taken by mother can have harmful effects on children: (low birth weight, heart defects, brain & neurological defects, and death). • Thalidomide • Diethylstilbestrol (DES) • Alcohol • Cigarettes • Illegal, prescription, and over the counter drugs Environmental hazards • Environmental hazards that may cause low birth weight, miscarriages, or genetic defects to embryo/fetus: • Radiation • Lead • Zinc • Mercury • Other harsh chemicals Maternal characteristics • Maternal behavior can affect the outcome of her pregnancy • Mother’s diet • Mother’s emotional well-being • Mother’s age Birth Process • Perinatal environment: environment surrounding birth; includes influences such as drugs given to the mother, delivery practices, and the social environment. • 3 stage process: 1. first stage of labor: uterine contractions. Lasts about 3-8 hours. 2. second stage of labor: fetus moves through birth canal & emerges from mother’s body. 3. third stage of labor: expulsion of the placenta Three stages of child birth. Social environment at birth • First 12-16 hours are a sensitive period of emotional bonding. • Postpartum depression may inhibit emotional bonding. • Early father-infant interactions may make fathers feel more a part of the family. Assessing the baby’s condition • Apgar test: assess newborn heart rate, color, respiration, muscle tone, and reflexes. • Neonatal Behavioral Scale (NBAS): assess neonate’s neurological integrity and responsiveness to environmental stimuli. – NBAS administered a few days after birth – Assess 20 reflexes. – Low scores may indicate brain damage or other neurological problems Birth complications • Anoxia • Oxygen deprivation • Breech position • Rh factor • Premature delivery • Preterm: born 3 weeks or more before term. • Small for date babies • Low birth weight • Small for date: slow growth • Under 5 lbs • May experience respiratory distress syndrome Readiness for life • Healthy newborns display a number of reflexes. • Survival reflexes: breathing, sucking & swallowing • Primitive reflexes (disappear during first year of life): babinksi reflex, swimming, stepping reflex Readiness for life continued • Infant states. – – – – – – Regular sleep: 8-9 hours/day Irregular sleep: 8-9 hours/day Drowsiness: ½-3 hours/day Alert inactivity: 2-3 hours/day Alert activity: 1-3 hours/day Crying: 1-3 hours/day Reflexes in full term infants Table 4.6 Pg. 135