ch 1-2 notes
advertisement

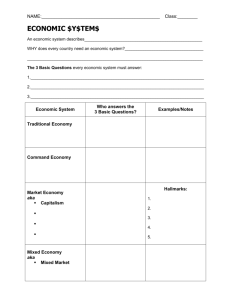
What is Economics? Chapter 1 Section 1, Ch 1 Economics-study of the choices that people make to satisfy their needs and wants. 2 Categories: 1. Microeconomics: study of the choices made by economic actors such as households, companies, and individual markets. 2. Macroeconomics: examines the behavior of entire economies. Who makes decisions? 1. Consumers-people who decide to buy things. 2. Producers-people who make the things that satisfy our needs & wants. You make choices based on your needs & wants, that reflect your desires for goods and services. 1. goods-physical objects that can be purchased. 2. services-actions/activities that are performed for a fee. 3. needs-basic things food, shelter, clothing, etc. 4. wants-everything other than needs (car) Economic Resources: Resources-anything that people can use to make or obtain what they need or want. Resources that can be used to produce goods and services are called factors of production. -natural resources -human resources -capital resources -entrepreneurship Section 2, Ch 2 Three basic economic questions: 1. What to produce? 2. How to produce? 3. For whom to produce? Section 3, Ch1 Trade-off: exchanging one thing for the use of another opportunity cost: the next best alternative that had to be given up for the alternative that was chosen. productions possibilities: are all the combinations of goods and services that can be produced from a fixed amount of resources in a given period. Chapter 2 Economic Systems Types of Economic Systems: A. Traditional: things are done the way they have always been done; based on customs and beliefs. B. Command (Controlled): individual has little influence on how economic questions are answered. Gov’t controls. Central Planners decide who will receive the product what will be produced and how. C. Market (Capitalism) Individuals answer basic questions. Gov’t doesn’t intervene. Market between buyers and sellers. Private individuals own the factors of production. D. Mixed Economies: combines elements of traditional, market, and command. Authoritarian Socialism-closest to pure command model. Also known as communism. Gov’t owns or controls nearly all the factors of production. Capitalism-closest to the market model. Individuals owns the factors of production and answer the economic questions. Democratic Socialism-between authoritarian socialism an capitalism. Gov’t owns some of the factors of production. Ch 2 , Section 2 5 features of the free-enterprise system of the U.S. 1. Own private property and enter into contracts. 2. Make individual choices. 3. Engage in economic competition. 4. Make decisions based on self-interest 5. Participate in the economy with limited government involvement and regulation. Ch 2, Section 3 U.S. Economic Goals: -freedom -efficiency -equity -security -stability -growth