Economic Systems McFarland

Economic Systems
McFarland
Types of Economic Systems
• Every country in the world must make economic choices in order to use their natural, human, and entrepreneurial resources efficiently.
Types of Economic Systems
• The leaders of each country must address the 3 basic economic questions – what, how, and for whom?
4 Types of Economic Systems
• Traditional
• Command
• Market
• Mixed
What to Produce?
• Traditional
– Determined by tradition
– Economic roles passed from generation to generation
• Command
– Determined by government officials
• Market
– Determined by individuals
How to Produce?
• Traditional
– Determined by custom
• Command
– Determined by government officials
• Market
– Determined by individuals
For Whom to Produce?
• Traditional
– Usually centered around traditional family and social units such as tribes
• Command
– Determined by government officials
• Market
– Determined by individuals
Examples
• Traditional
– Aborigines of Australia
– Inuit of Canada
• Command
– Middle Ages in Europe
• Market
– U.S.
– Canada
Mixed
• A mixed economy combines elements of all the other 3 economic systems
3 Main Categories of Mixed
Economies
• Communism – the government owns or controls nearly all the factors of production – leans towards the command model – ex. Cuba
• Capitalism – the individuals own the factors of production – leans toward the market model – ex.
U.S.
• Socialism – the government owns some of the factors of production – ex. France
Features of the U.S. Economy
• Individuals in the U.S. are free to exchange their goods and services, seek jobs of their own choosing, use their resources as they wish, and own and operate businesses.
Features of the U.S. Economy
• Because of these freedoms, the capitalist economy of the U.S. is sometimes called a free enterprise system, a system under which business can be conducted freely with little government intervention.
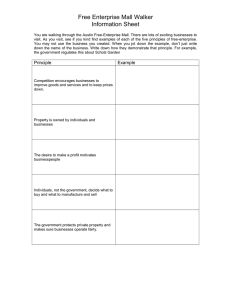
Free-Enterprise
• Free-enterprise is based on 5 main features
• In the U.S. individuals have the right to…
5 Main Features of Free-Enterprise
• Own private property and enter into contracts
• Make individual choices
• Engage in economic competition
• Make decisions based on self interest
• Participate in the economy with limited government involvement and regulation
Private Property
• Goods that are owned by individuals and by businesses, rather than by the government are considered private property
• Ex. Clothes, CD’s, books, factories, machinery, etc.
Contracts
• Individuals have the right to enter into agreements with one another to buy and sell goods and services
• These agreements are called contracts – ex.
If John agreed to sell a CD to Jamie, they have a contract
• Contracts can be oral or written
Choice
• Property owns, laborers, producers, and consumers in the U.S. enjoy freedom of choice
• Ex. Producers are free to make whatever they wish
Competition
• Sometimes 2 or more people decide to make the same product or provide the same service
• This leads to competition, or the economic rivalry that exists among businesses selling the same or similar products
• The more competition there is, the lower the price of the product
• Free-enterprise allows producers and consumers to make economic choices for their own benefit.
6 Goals of U.S. Economy
• Freedom
• Efficiency
• Equity
• Security
• Stability
• Growth