Which combination of ionic charge and ionic radius give the largest
advertisement

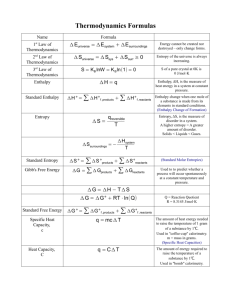
1. Which combination of ionic charge and ionic radius give the largest lattice enthalpy for an ionic compound? Ionic charge high high low low A. B. C. D. 2. 3. 4. Ionic radius large small small large Which reaction has a positive entropy change, ∆Sο? A. H2O(g) → H2O(l) C. 2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g) B. CaCO3(s) → CaO(s)+ CO2(g) D. N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) Some chlorine gas is placed in a flask of fixed volume at room temperature. Which change will cause a decrease in entropy? A. adding a small amount of hydrogen C. adding a small amount of chlorine B. cooling the flask D. exposing the flask to sunlight The lattice enthalpy values for lithium fluoride and calcium fluoride are shown below. LiF(s) CaF2(s) ∆Hο = +1022 kJ mol−1 ∆Hο = +2602 kJ mol−1 Which of the following statements help(s) to explain why the value for lithium fluoride is less than that for calcium fluoride? 5. I. The ionic radius of lithium is less than that of calcium. II. The ionic charge of lithium is less than that of calcium. A. I only C. II only B. I and II D. Neither I nor II Which reaction occurs with the largest increase in entropy? A. Pb(NO3)2(s) + 2KI(s) → PbI2(s) + 2KNO3(s) B. CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) C. 3H2(g) + N2(g) → 2NH3(g) D. H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g) 1 6. What is ∆H for the reaction below in kJ? CS2(g) + 3O2(g) CO2(g) + 2SO2(g) [∆Hf / kJ mol–1: CS2(g) 110, CO2(g) – 390, SO2(g) – 290] A. −570 C. −790 B. −860 D. −1080 7. Write all of the reactions for the formation of solid potassium oxide, K2O(s), from its elements in their standard states. The lattice energy of K2O(s) is 2238 kJ/mol. Use these data along with data in Appendix C and Figure 7.10 to calculate the “second electron affinity” of oxygen corresponding to the reaction O-(g) + e- O2-(g). 8. The standard enthalpy change of formation of Al2O3(s) is −1669 kJ mol−1 and the standard enthalpy change of formation of Fe2O3(s) is −822 kJ mol−1. (i) Use these values to calculate ∆Hο for the following reaction. Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) → 2Fe(s) + Al2O3(s) State whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… (ii) Draw an enthalpy level diagram to represent this reaction. State the conditions under which standard enthalpy changes are measured. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… 2 (iii) Estimate, without doing a calculation, the magnitude of the entropy change for this reaction. Explain your answer. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… 9. Define the term standard enthalpy of formation, and write the equation for the standard enthalpy of formation of ethanol, C2H5OH(l). …………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… 10. C2H6(g) ↔ C2H2(g) + 2 H2(g) Substance C2H2(g) H2(g) C2H6(g) S°(J mol-1 K-1) 200.9 130.7 -------- H°f (kJ mol-1) 226.7 0 -84.7 If the value of the standard entropy change, S°, for the reaction is 232.7 J mol-1 K-1, calculate the standard molar entropy, S°, of C2H6 gas. 11. Using the standard enthalpies of combustion, Table 12, calculate the determine the enthalpy of reaction of octane (C8H18) from its elements at standard conditions. 3