summary page
advertisement

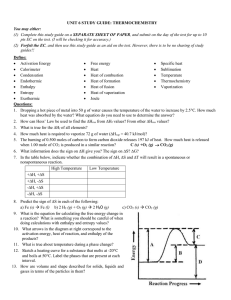
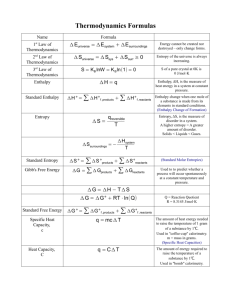
Thermodynamics Cheat Sheet Specific Heat In Phase Energy Change –: q=mcT q=energy m=mass c=specific heat constant T=change in temperature Between Phase Energy Change –: q=mHf or q=mHv Hf=enthalpy of fusion Hv=enthalpy of vaporization units: J/g, J/mol, etc –Melting=-fusion –Condensation=-vaporization Calorimetry -mmetalcT = mwatercT -mmetalc(Tf-Ti) = mwaterc(Tf-Ti) c for water is 4.18 J/g*C Breaking and Forming Bonds Breaking bonds requires energy Forming bonds releases energy Exothermic reactions release energy after forming products Endothermic reactions take energy from the surrounding system to start reaction Bond Energies : E= +(reactant bonds)-(product bonds) Any arithmetic combination of various reactions that gives a matching net rxn and enthalpy Ex. Want: C + 2H2 --> CH4 DH= ? 2H2+ O2 --> 2H2O H= -572 kJ C + O2 --> CO2 H= -394kJ CO2 + 2H2O --> CH4 + 2O2 H= +890kJ C + 2H2 --> CH4 DH= -76kJ Enthalpy Equation: DHrxn=S DHproducts – SDHreactants Decreasing enthalpy of a system is favorable because increased enthalpy cannot rely on surroundings for energy Hrxn=- for exothermic Hrxn=+ for endothermic Reverse rxns have same number and different signs Ssystem = S*products - S*reactants S units: J/K * mol Gas has highest and solids have lowest entropy Solids and liquids have almost same magnitude of entropy Increasing # of moles of gas in reaction from reactants to products makes more entropy and vice versa Product-favored reactions have higher entropy and vice versaG = H - T S* Favored if negative G < 0 spontaneous G > 0 non-spontaneous Solve for threshold temp with G=0 and given H & S G* is standard condition G=0 is equilibrium G = G* + RTlnQ OR G =G* + RTlnK (at equilibrium) Q=reaction quotient Q=K at equilibrium K= e-G*/RT G < 0 ~ large K G>0 ~ small K G=0 ~ K=1 ++ is spontaneous at high temperatures - is spontaneous at low temperatures EntropyS + increase + increase - decrease Maybe Never Always Maybe Enthalpy H - decrease