Chapter 27 Sec 4 Notes - jWorldHistoryCreditRecovery

Chapter 27 Sec. 4: Upheavals in China Notes
Focus Question: How did China cope with internal division and foreign invasion in the early 1900s?
China’s Qing dynasty collapsed in 1911
President Sun Yixian (also called Sun Yat-sen) hoped to rebuild China on the 3 Principles of the People- nationalism, democracy, and economic security for everyone
China falls into Chaos in face of “twin evils” of warlord uprisings and foreign imperialism
1912 Sun Yixian stepped down as President in favor of Yuan Shikai, a powerful general o Yuan tries to set up a new dynasty and the country becomes divided o Yuan died in 1916 creating more chaos o Warlords seize power and the economy collapses
During period of upheaval foreign powers increase influence o During WWI Japanese officials present China with Twenty-One
Demands which seeks to make China a Japanese protectorate
China gives into some demands
Following WWI the Allies gave Japan control over former
German possessions in China o Students in China respond with protests known as the May 4 th
Movement
Reject Confucian traditions and learning from the West
Want to end foreign domination o Some Chinese turn to ideas of Marx and Lenin
Soviet Union trains Chinese students and military officers to become the vanguard , or elite leaders, of communist revolution
1921 Sun Yixian (Sun Yat-sen) and his Guomindang , or Nationalist party, established a government in south China o Sun joins forces with the Chinese Communists in forming an army to defeat the warlords but still believed a govt should be based on his ‘3
Principles of the People’ o Sun died in 1925 and is replaced by Jiang Jieshi (Chiang Kai-Shek)
o Jiang Jieshi (Chiang Kai-Shek) leads Northern Expedition in 1926 with Chinese Communists seizing Beijing
Takes control of government led by Guomindang without
Communists
Mid-campaign Jiang turns on Communists and in 1927 orders slaughter of Communist party members and their supporters
Marks beginning of civil war that lasts 22 years
Mao Zedong (Mao Tse-tung) rises to lead Communists and begins recruiting among large peasant masses o In southeastern China Mao redistribute land to peasants and promise other reforms
-
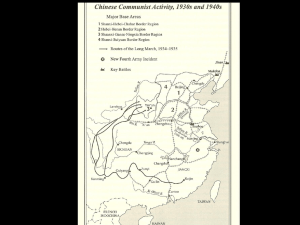
Determined to defeat Communists, Jiang Jieshi leads “extermination campaigns” o Leads to Long March from 1934 to 1935 as Mao’s forces retreat using guerrilla tactics to fight back o Communists set up new base in remote region of Northern China o Communists enforce strict discipline on march among peasants making them welcomed by many
In 1931 Japan invaded Machuria in northeastern China o Communists unite with Guomindag against Japanese aggression o 1937 Japanese invade again starting the Second Sino-Japanese War
Japanese overwhelm Chinese in eastern China taking Beijing
Dec 13 th Japanese seize Nanjing after lengthy siege killing hundreds of thousands of soldiers and civilians
United Guomindang and Communist front stays intact till end of war with Japan
WWII ends with Jiang and Guomindang controlling China’s central government o Communist Party controlled much of northern and central China o Soon Mao and Communists seize power and bring revolutionary change