Shakespeare and Macbeth
advertisement

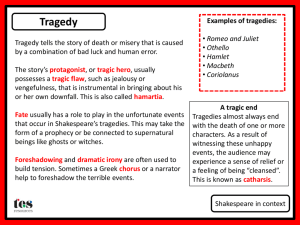
Shakespeare’s Biography Very little actually known about Shakespeare- most information is found through Church documents Born April 23, 1564 in Stratford-on-Avon (a guess even since only his baptism is recorded) Married to Anne Hathaway in December 1582 3 children- Suzanne, Judith and Hammnet Died on April 23, 1616 Playwright Performed most plays in The Globe Theater Began as a member of Lord Strange’s players acting company After that, joined Lord Chamberlain’s Men Transitioned to the King’s Men in 1603 Patronage and Monarchs Queen Elizabeth was on the throne when Shakespeare began writing his plays King James I assumed the throne in 1603 and was also a Patron to Shakespeare As a result, most of his plays written during that era are typically happier and include more comedies As a result, Macbeth is seen to appeal to James I (of Scotland) and a representative of a more turbulent time The Types of Plays The Comedy- purpose to entertain. Plot lines usually involve a love story and friends of the lovers (and a clown) EX: A Midsummer Night’s Dream The History- more serious purpose. Records the rise and fall of great kings. Served as a moral example EX: Julius Caesar The Tragedy- A play with a violent end-disaster as a result of breaching a fundamental moral law. EX: Macbeth Shakespeare’s language Blank Verse: Unrhymed lines of iambic pentameter This is the normal form of speech in Shakespearean plays for major characters Rhymed Verse: couplets of iambic pentameter, also called heroic couplets Used for supernatural characters (more than mortal) Used at the end of a scene Used when speaking of love Shakespeare’s Language Song Prose Used to create a particular mood Used for lower class characters and for reading from letters or documents The 5 Act Play Shakespeare’s Plays were divided into 5 acts by later publishers of the plays. His 5 acts are broken down by certain plot characteristics. The first complete publication of all 36 of Shakespeare’s plays is called the First Folio Act 1: ProtasisCharacters and situations are introduced, necessary exposition, conflict begins. Act 2/3: epitasiscomplication starts and reaches a frenzy Act 4: catastrophe- looks like everything will be solved, then the solution goes wrong Act 5: catastasis- solution to all conflicts Literary Terms to Know Anachronism: false assignment of event, person, scene, language to a time when that item was not in existence Equivocation: the use of expressions with double meaning in order to mislead the listener; a half truth Aside: dramatic convention that allows a character on stage to speak aloud his thoughts, unheard by other characters present Pathetic fallacy: nature reflecting the deeds of men Soliloquy: dramatic convention that allows a character alone on stage to speak aloud his thoughts Allusion: reference within literary work to person, historical event, work of art Patterns to Note Imagery Patterns Bird Deceptive appearances Animal Irony Color Sleeplessness Clothing Flattery to James I Darkness/Light Reversal of morality (“fair is foul, foul is fair”)