Law
advertisement

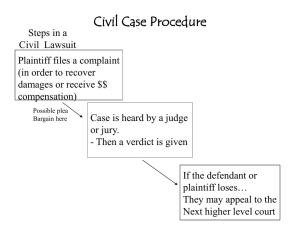
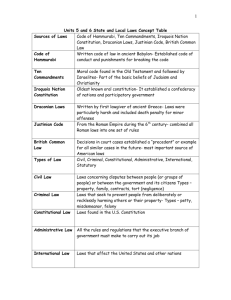
The American Legal System Chapter 15 & 16 Purpose of Laws • • • • To keep society in order To provide penalties for disorder To settle disagreements To provide deterrence to disorder History of Law • Code of Hammurabi • King Hammurabi of Babylonia • 282 laws regulating behavior • Oldest written code of law that applied to everyone– 1760 BC • Very harsh rules & punishments • Religious Code • Ten Commandments, Islamic Law • Draconian Laws – – Ancient Greek law that had extreme punishments for small crimes • Justinian Code • Simplified Roman Code of law – based on jurisprudence (theory of law) • English Common Law • Primary source of our laws • Based on precedent • Statutes – acts of parliament Types of Laws • Public or Constitutional –Involves Constitutional questions –Supreme Court • Administrative Law –Involves laws passed by government agencies –Tax law –Example – Federal Trade Commission has regulations to protect consumers from harmful products • Statutory Law –Laws passed by legislatures Types of Laws • Civil –Involve disputes –A fine or amount is paid as the result • Criminal –Violations of law –Jail sentences are the result –Misdemeanors –Felonies Civil Cases • One person files a lawsuit against another • Plaintiff – Person/party filing a lawsuit • Defendant - individual/group being sued or charged with a crime • Suit of Equity – special case when there are no existing laws or cases • Judges decide not juries (usually) • Judge may issue an injunction -a court order commanding a stop to an action • Most are settled out of court • Magistrate Judge less than $5,000, District Court less than $10,000, Superior Court more than $10,000 Criminal Cases • Prosecution & Defendant • Burden of Proof - is on the prosecution –Prosecution – party who starts the legal proceedings against another party for a violation of the law. • Must prove guilt beyond a reasonable doubt –Not a single doubt can exist –Innocent until proven guilty! Civil Case Procedures 1. Bringing the Suit Plaintiff files 2. Summons Sent to Defendant 3. Defendant’s Response Pleadings – a defendant’s response to the complaint by admitting fault or denying charges 4. Discovery – each side gathers facts & evidence 5. Pretrial Discussions – decide if case should go to court or be settled 6. Trial – both sides present their case 7. Verdict –decision of the judge or jury - if plaintiff wins the judge sets a remedy - fine paid by defendant if found guilty in civil case 8. Appeal – both sides have the right to appeal a decision Criminal Case Procedures 1. Suspect is arrested – Must be read their Miranda rights 2. Preliminary Hearing – judge reads charges & sets bail 3. Indictment – grand jury decides on evidence 4. Arraignment – defendant enters a plea & trial date is set 5. A plea bargain can be made at this time defendant agrees to plead guilty to a lesser crime Used to convict someone else 6. Discovery – both sides gather evidence 7. Jury is selected 8. Trial Trial 1. Prosecution makes an opening statement first 2. Defense then makes their opening statement 3. Prosecution calls witnesses for testimony – statement a witness makes under oath Defense can cross-examine – question a witness at trial or hearing to check or discredit testimony 4. Prosecution rests 5. Defense calls witnesses for testimony Prosecution can cross-examine 6. Defense rests 7. Both sides make closing statements Trial cont. 8. Jury Decision – Verdict –Jury first deliberates – jurors review evidence and legal arguments –Must decide guilt beyond a reasonable doubt –Acquittal – jury decides not guilty & defendant is released – can’t be retried for the same crime –Guilty – date is set for sentencing –Hung Jury – jury can’t decide – this is a mistrial and can be retried 9. Appeal - If the defendant is found guilty, the defense may appeal the verdict to a higher court Penalties for breaking the law • 4 functions of penalties –Punishment –Protect society –Make examples (deterrence) –Rehabilitation • State Penal Code – state’s written criminal laws. Crimes are defined. Punishments for each crime spelled out • Indeterminate Sentence – judge sets a minimum & maximum sentence • Determinate Sentence – judge sets a specific sentence • Mandatory Sentence – judge sets a sentence in accordance with state law