Law Vocab
advertisement

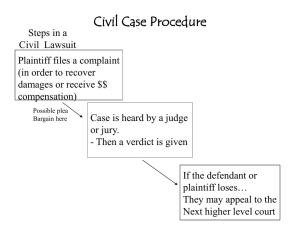
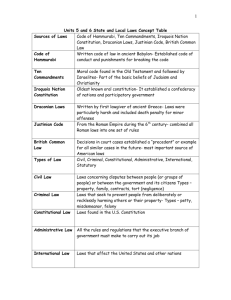
Law Vocab Common law Constitutional law Ex post facto law Lawsuit Tort Bill of Attainder Bail Complaint Juvenile Juvenile Delinquent Rehabilitate What is the Purpose of Laws? 1. Keep order in society 3. 2. 4. Provide a deterrence to disorder History of Law Code of ______________________________ King Hammurabi of Babylonia 282 laws regulating behavior Oldest written code of law that _______________________________ - 1760 BC Very harsh rules and punishments Religious Code Draconian Laws – 1 Justinian Code – Simplified Roman Code of law – based on jurisprudence – English Common Law Primary source of our laws Based on Statutes – Types of Laws Public or Constitutional Law– Administrative Law – Tax Law, example – Federal Trade Commission regulations to protect consumers from harmful products Statutory Law – Laws passed by legislatures Civil _______________________________ is paid as a result Criminal – ____________________________________ are the result Misdemeanors Felonies Civil Cases One person files a ________________ against another Plaintiff – Defendant – Suits of Equity – ________________ decide not juries (usually) Judge may issue an injunction – Most are settled ________________________________ < $5000 – < $10000 – Over $10000 2 Criminal Cases Prosecution & Defendant Burdon of Proof – is on the ________________________ Prosecution – must prove guild beyond a _______________________ Not a single doubt can exist. Innocent until proven guilty!! Civil Case Procedures Criminal Case Procedures 1. 1. Suspect is arrested - ________________________ Who files a civil suit? 2. Preliminary hearing - 2. 3. Defendant’s Response – Pleadings – 3. Indictment - 4. Arraignment 4. ____________________________ - each side gathers facts & evidence 5. What can be made at this time? - 5. ________________________________ - decide if a Defendant agrees to plead guilty to a lesser crime case should go to court or be settled Used to convict someone else 6. Trial – 6. Discovery - 7. Verdict – 7. Jury is selected If the plaintiff wins the judge sets a remedy – 8. Trial 8. Appeal - 3 Trial 1. Who makes an opening statement first? 2. Who makes an opening statement second? 3. Prosecution calls witnesses for testimony – Defense can cross-examine the witnesses – 4. Prosecution rests 5. Defense calls witnesses for testimony Prosecution can cross-examine 6. Defense rests 7. _____________________________ make closing statements 8. Verdict - Juries decision a. Jury must deliberate – b. Must decide guilt beyond a reasonable doubt c. Acquittal – Can a person be retried for the same crime? d. What happens if the defendant is found guilty? e. What is a hung jury? 9. Appeal – If the defendant is found guilty, the defense may appeal the verdict to a higher court. Penalties for Breaking the Law What are the 4 functions of penalties? 1. 2. 3. 4. State penal code – Indeterminate Sentence – _________________________ - judge sets a specific sentence Mandatory sentence – judge sets a sentence in accordance with ________ 4