PPT: Chemical Reactions and Equations
advertisement

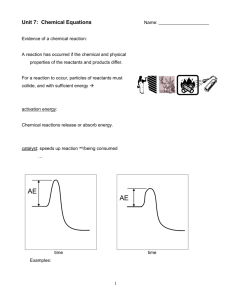
Chemistry Unit 7: Chemical Equations In a reaction: atoms are rearranged mass AND are conserved energy charge Balancing Chemical Equations law of conservation of mass = same # of atoms of each type on each side of equation CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O Reactants 1 C atom 4 H atoms 4 O atoms Products 1 C atom 4 H atoms 4 O atoms EX. solid iron reacts with oxygen gas to yield solid iron (III) oxide Fe3+ O2– ___Fe(s) + ___O2(g) ___Fe2O3(s) If all coefficients are 1… + ___O 1 2(g) 1 ___Fe(s) 1 ___Fe 2O3(s) + If we change subscripts… But we can’t!!! 1 1 3(g) 1 ___Fe ___Fe 2(s) + ___O 2O3(s) + subscript changes the substance. Changing a ___________ coefficients To balance, modify only _____________. superscripts Right now, _______________ don’t enter into our “balancing” picture. 4 3 2(g) + ___O ___Fe(s) 2 ___Fe 2O3(s) + Hint: Start with most complicated substances first and leave simplest substances for last. solid sodium reacts w/oxygen to form solid sodium oxide 4 1 2(g) ___Na(s) + ___O Na+ O2– 2 ___Na 2O(s) + Aqueous aluminum sulfate reacts w/aqueous calcium chloride to form a white precipitate of calcium sulfate. The other compound remains in solution. Al3+ SO42– Ca2+ Cl– 1_ Al2(SO4)3 (aq) + 3_ CaCl2 (aq) 3 _ AlCl3 (aq) _ CaSO4(s) + 2 Methane gas (CH4) reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide gas and water vapor. Furnaces burn primarily methane. 1 2 O2(g) _ CH4(g) + _ 1 2 H2O(g) _ CO2(g) + _ 1 CaC2(s) + _ 1 H2O(l) _ 1 _ C2H2(g) + 1 _ CaO(s) _ 3 CaSi2 + _ 2 SbI3 _ Si + 2 _ Sb + 3 _ CaI2 6 _ 2 Al + _3 6 CH3OH _1 2 Al(CH3O)3 + _3 H2 1 C2H2(g) + _ 2 5 O2(g) ** _ 1 C3H8 + _ 5 O2 ** _ 1 C5H12 + _ 8 O2 ** _ 2 CO2(g) + 1 4 2 _ _ H2O(l) Odd # Oxy 3 CO2 + _ 4 H2O _ 5 CO2 + _ 6 H2O _ ** = complete combustion (+ O2) of a hydrocarbon (CxHy) yields CO2 and H2O Write equations for the combustion of C7H16 and C8H18 1 C7H16 + 11 _ _ O2 7 CO2 + _ 8 H2O _ 1 2 C8H18 + 25 _ _ O2 8 CO2 +18 9 H2O 16 _ _ Odd # Oxy Signs of Chemical Reactions There are five main signs that indicate a chemical reaction has taken place: release input change in color change in odor production of new gases or vapor input or release of energy difficult to reverse Evidence of a chemical reaction: odor heat sound light gas emitted color change A reaction has occurred if the chemical and physical properties of the reactants and products differ. For a reaction to occur, particles of reactants must collide, and with sufficient energy collision theory activation energy: energy needed to start a reaction Chemical reactions release or absorb energy. exothermic reactions The reaction in an oxyacetylene torch is exothermic. endothermic reactions Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction. Endothermic Reaction Energy + Reactants Products Energy Activation Energy Products Reactants Reaction progress Exothermic Reaction Reactants Products + Energy 10 energy = 8 energy + 2 energy Energy of reactants Energy Energy of products Reactants Products Reaction Progress Decomposition of Nitrogen Triiodide N2 NI3 2 NI3(s) I2 N2(g) + 3 I2(g) catalyst: speeds up reaction w/o being consumed … it lowers the activation energy (Ea) Energy without catalyst AE with catalyst AE time time Examples: enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions catalytic converters convert CO into CO2 Reaction Conditions and Terminology Certain symbols give more info about a reaction (s) = solid (l) = liquid (g) = gas (aq) = aqueous (dissolved in H2O) NaCl(s) NaCl(aq) More on aqueous… “soluble” or “in solution” indicates that a substance is dissolved in water (usually) all acids are aqueous solutions Other symbols… (i.e., clues about the reaction) means...“yields” or “produces” heat is added to the reaction means ______ MgCO3(s) MgO(s) + CO2(g) Temp. at which we perform rxn. might be given. C6H5Cl + NaOH 400oC C6H5OH + NaCl The catalyst used might be given. C2H4(g) + H2(g) Pt C2H6(g) Factors that influence the rate of a reaction To make reaction rate increase… concentration of reactants particle size temperature mechanical mixing pressure catalyst nature of reactants use one N/A Types of Chemical Reactions Synthesis (combination) reaction A + B AB AB A + B Decomposition reaction ASingle-replacement reaction BDouble-replacement reaction Combustion reaction (of a hydrocarbon) Ause A + BC AC + B element compound compound element AB + CD AD + CB All compounds… CxHy + O2 CO2 + H2O activity series to predict products/reactivity Buse solubility chart to predict products/reactivity Balance and classify the following reactions: 1 _ F2 + 1_ MgI2 _ I2 _1 MgF2 + 1 Single replacement 4 _ C3H5N3O9 1 O2 _ H2O + _ 6 _ CO2 + 10 _ N2 + 12 Decomposition 1 C5H12 + _ 8 O2 _ 5 CO2 + _ 6 H2O _ Double Replacement? Combustion Word Equations Solid iron reacts with oxygen gas to yield solid iron(III) oxide. word equation: iron + oxygen iron(III) oxide Fe3+ balanced equation: O2– 4 Fe + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3 Write a balanced equation (w/rxn conditions) from the following word equations. Solid sodium reacts w/oxygen to form solid sodium oxide. 4 Na(s) + O2(g) Na+ O2– 2 Na2O(s) + Aqueous aluminum sulfate reacts w/aqueous calcium chloride to form a white precipitate of calcium sulfate. The other compound remains in solution. Ca2+ Cl– Al3+ SO42– Al2(SO4)3 (aq) + 3 CaCl2 (aq) 3 CaSO4 (s) + 2 AlCl3 (aq) Single and Double Replacement Reactions Single-replacement reaction Mg + CuSO4 General form: A + BC MgSO4 AC + + Cu B Double-replacement reaction CaCO3 + General form: AB + 2 HCl CaCl2 + H2CO3 CD AD + CB single-replacement: one element replaces another AB + C A + CB sodium chlorine + bromide Na+ Br– 1 _ Cl2 + 2 _ NaBr copper (II) aluminum + sulfate Cu2+ SO42– 2 _ Al + 3 _ CuSO4 AB + C B + AC sodium + bromine chloride Na+ Cl– 2 _ Br2 _ NaCl + 1 aluminum ? + copper sulfate Al3+ SO42– 1_ Al2(SO4)3 + 3 _ Cu Activity Series Ca Foiled again: Aluminum is knocked out by Calcium Printable Version of Activity Series Element Reactivity Li Rb K Ba Ca Na Mg Al Mn Zn Cr Fe Ni Sn Pb H2 Cu Hg Ag Pt Au Halogen Reactivity F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 Predict if these reactions will occur 3 Mg + 2 AlCl3 2 Al + 3 MgCl2 Can magnesium replace aluminum? • Activity Series Al + YES, magnesium is more reactive than aluminum. MgCl2 NR (No Reaction) Can aluminum replace magnesium? Therefore, no reaction will occur. NO, magnesium is less reactive than aluminum. MgCl2 + Al No reaction Order of reactants DOES NOT determine how they react. We must determine if the lone element is more reactive than the bonded one… metals replace metals or non-metals replace nonmetals How do we know if a reaction will occur? For single-replacement reactions, use Activity Series. In general, elements above replace elements below. 1 1 FeSO4 _ Ba + _ 3 _ Mg + 2 _ Cr(ClO3)3 1 _ Fe + 1 _ BaSO4 2_ Cr + _ 3 Mg(ClO3)2 _ Pb + _ Al2O3 NR _ NaBr + 1 _ Cl2 2 _ _ Br2 2 NaCl + 1 _ FeCl3 + _ I2 1_ CoBr2 + 1 _ F2 NR 1 CoF2 + 1 _ _ Br2 double-replacement: AB + CD iron (III) + chloride Fe3+ Cl– 1 _ FeCl3 + AD + CB potassium hydroxide K+ OH– 3_ KOH iron (III) potassium ? + hydroxide chloride Fe3+ OH– K+ Cl– 1 _ Fe(OH)3 + 3 _ KCl lead (IV) calcium + nitrate oxide lead (IV) calcium + ? oxide nitrate Pb4+ NO3– Ca2+ O2– 1 _ Pb(NO3)4 + 2 _ CaO Pb4+ O2– Ca2+ NO3– 1_ PbO2 + 2_ Ca(NO3)2 Double Replacement Reactions Formation of a solid: AgCl AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq) KNO3 (aq) + AgCl(s) precipitate: a solid product that forms in an aqueous solution reaction When ionic substances have “(aq)” written after them, the individual ions have dissociated from the ionic crystal and are floating around separately. Na3PO4(aq) means… 3 Na+(aq) + PO43–(aq) Sodium phosphate, Na3PO4, (sometimes called “sodium phosphate, tribasic”) is a cleaning agent and food preservative. precipitate: a solid product that forms in an aqueous solution reaction Na2CO3 (aq) + Ca(NO3)2 (aq) Na+ Na+ CO32– clear Na2CO3 solution Ca2+ CaCO3(s) + 2 NaNO3(aq) NO3– NO3– clear Ca(NO3)2 solution ppt “chunks” “sinkies” “floaties” cloudy solution containing CaCO3(s) and NaNO3(aq) Predict if a reaction will occur when you combine aqueous solutions of iron (II) chloride and sodium carbonate… If the reaction does occur, write a Balanced balanced chemical equation showing it (be sure to include phase notation). iron (II) chloride + sodium carbonate Fe2+ Cl - Na+ CO32- FeCl2 Na2CO3 sodium chloride + iron (II) carbonate Na+ CO32- Fe2+ Cl- FeCO3 (s) NaCl (aq) Using the SOLUBILITY TABLE: sodium chloride is soluble iron (II) carbonate is insoluble FeCl2 (aq) + Na2CO3 (aq) 2 NaCl (aq) + FeCO3 (s) For double-replacement reactions, reaction will occur water a gas if any product is: a precipitate driving forces Check new combinations to decide. 1 Pb(NO3)2(aq) + _ 2 KI(aq) 1 PbI2(s) + 2 _ _ _ KNO3(aq) Pb2+ NO3– K+ I– _ KOH(aq) + _ 2 1 H2SO4(aq) K+ OH– H+ SO42– _ FeCl3(aq) + _ Cu(NO3)2(aq) Fe3+ Cl– Cu2+ NO3– Pb2+ I– (?) (ppt) K+ NO3– (?) (aq) _ K2SO4(aq) + 2 _ H2O(l) 1 K+ SO42– (?) H+ OH– (?) (aq) (water) NR (aq) (aq) Ions in Aqueous Solution Pb(NO3)2(aq) Pb(NO3)2(s) Pb2+(aq) + 2 NO3–(aq) Pb2+ NO3 – NO3– add water NO3– Pb2+ NO3– dissociation: “splitting into ions” NaI(aq) NaI(s) Na+(aq) + I–(aq) Na+ I– add water Na+ I– ChemThink Mix them and get the overall ionic equation… Pb2+ NO3– reactants I– Na+ NO3– Na+ – +(aq) + __I 1 2+(aq) + __NO 2 2 2 –(aq) __Pb 3 (aq) + __Na yields –(aq) + __Na +(aq) 1 2 2 + __NO __PbI (s) 3 2 Na+ Pb2+ I– NO3– I– Na+ products NO3– Cancel spectator ions to get net ionic equation… 2+(aq) + __I 1 2 –(aq) __Pb 1 __PbI 2(s) I– Pb2+ I– Pb2+ I– I– I– Polymers and Monomers polymer: a large molecule (often a chain) made of many smaller molecules called monomers Polymers can be made more rigid if the chains are linked together by way of a cross-linking agent. Monomer Polymer H H O amino acids………… proteins H–N–C–C–O–H w/Nnucleotides ( R bases A,G,C,T/U)….. nucleic acids styrene……………… polystyrene PVA…………………. “slime” polyvinyl alcohol