The Origins of Hinduism

LEARNING SCALE
4: Along with everything in the stated learning goal, the student is able to compare/contrast the foundations and beliefs of Hinduism and Buddhism with other world religions.
LEARNING GOAL (3): THE STUDENT IS ABLE TO DESCRIBE IN DETAIL THE FOUNDATIONS
AND BELIEFS FOR BOTH HINDUISM AND BUDDHISM AS WELL AS COMPARE AND
CONTRAST THOSE FOUNDATIONS AND BELIEFS WITH EACH OTHER.
2: The student is able to describe the foundations and beliefs for Hinduism and Buddhism.
1: The student can describe the foundations and/or beliefs for either Hinduism or Buddhism.
0: The student is unable to describe either the foundations or beliefs for both Hinduism and
Buddhism.
CRASH COURSE OF WORLD HISTORY: 2000-1500 B.C
Around 2000 B.C., something drove the people of the Harappan civilization from their lands. The cause of that remains somewhat of a mystery. After, different groups of people began to into different regions of the Indian subcontinent.
These different groups of people shared those traditions and beliefs with one another, and over the course of hundreds of years, civilization throughout India had a very different and unique look.
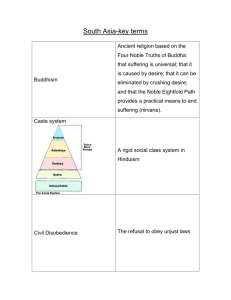
Society throughout India grew to have an identifiable social class structure called
The Caste System. This meant that individuals within each section of the social class were identified by their specific jobs.
There were thousands of different jobs, but the Indian caste system organized into 4 main groups.
After centuries, another group came into being that was considered below all other groups.
This group was called “the untouchables.”
These people were considered to have jobs that no one else wanted to do.
Early Indian religion was called Brahmanism.
Brahmins worshiped many nature gods. This belief system lasted for centuries.
As time passed, many Indians began to question how the world came into being. These questions led to changes in religious ideas. One major change was a belief that one spirit governed the universe. The religion that grew out of Brahmanism became the religion of
India.
HINDUISM
THE RELIGION OF INDIA
Hinduism is the world’s third largest religion after Christianity and Islam. An estimated 950 million people are Hindus
(14% of the world’s population).
Hinduism is the world’s oldest organized and continued religion.
Unlike other major world religions (Christianity,
Islam, Judaism, Buddhism) Hinduism has no founder. The ideas and beliefs of Hinduism developed over thousands of years. Hinduism is the combination of religious practices found from different people throughout India’s history.
This is the most important symbol of Hinduism (Aum).
MANY GODS
Hindus worship many gods (polytheists). Although they believe in many gods, Hindus also recognize one supreme God or life force (Brahman). Hindus consider the other gods to be parts of the one universal God. The three most important of the other gods are Brahma, the creator; Vishnu, the protector; and
Shiva, the destroyer. Hindus believe that there is a part of Brahman in everyone called the Atman.
Brahma Vishnu
There are an estimated 33,000,000 different Hindu gods.
http://safeshare.tv/w/mDejZRgRvj
Shiva
Many Lives
IMPORTANT VOCAB TERM: Reincarnation: A belief that each person has many lives.
Hindus believe in reincarnation. What a person does in each life determines what he or she will be in the next life, according to the doctrine called karma. Good deeds allow a person to be reborn as a higher being. Evil deeds cause a person to be reborn as a lower being, such as an insect. Hindus believe that animals, like humans, have the supreme force in them. For that reason, many Hindus are vegetarians.
Reincarnation creates a repeating cycle of birth, life, death, and rebirth. The cycle ends only when a person achieves a mystical union with God. To achieve that, a person must come to realize that his or her soul and God’s soul are one. This idea is called Moksha (the main spiritual goal of Hindus).
4 MAIN GOALS OF HINDUS
1) Moksha: The release of the soul from the cycle of rebirth.
2) Dharma: The code for leading one’s life.
3) Artha: The pursuit of material gains through lawful means.
4) Karma: Through good acts being reincarnated to a higher level. http://safeshare.tv/w/IsaAyfjGYN
Many Paths to God
Hindus believe they connect with God by following their own individual path. Part of that path concerns one’s job, which is linked to the caste system. Devout Hindus must faithfully carry out their assigned duties in life. In the mindset of a devout Hindu, no matter your place within the caste system, it was your duty to do the best you could with your role in life.
Hindus have a choice of spiritual practices to grow closer to God. Two of these are also popular in Western countries. Meditation is the practice of making the mind calm. Yoga is a complex practice that includes exercise, breathing techniques, and diet. http://safeshare.tv/w/wjtJNrwbWh