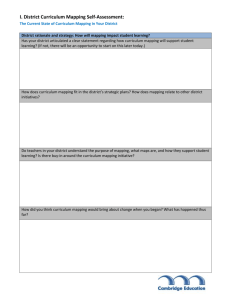
District Essential Curriculum Mapping
advertisement

District Essential Curriculum Mapping Algebra I February 2008 Written by The Albuquerque Public Schools District Essential Curriculum Mapping Task Force Lynda Idle, Instructional Manager Christina Fritz, Assessment Manager Jennifer Macdonald, Curriculum Coordinator Gina Middleton, RDA Resource Teacher Kathy Richter-Sand, TLS Resource Teacher Sue Broemmer, TLS Resource Teacher Jackie Calvert, TLS Resource Teacher Janet Malta, Sandia Cluster Staff Developer Margie Maes, Manzano Cluster Staff Developer Lynn Wilson, Valley Cluster Staff Developer Cindy Williams, Chaparral ES Instructional Coach Agenda Welcome/Sign-in/Introductions District Curriculum Mapping Initiative Connections to the A2L/High School Short-Cycle Assessment Algebra I Curriculum Map Standards Assessment Content Skills Plus/Delta Group Norms Begin and end on time Be courteous to colleagues, limit sidebar conversations Equity of voice Stay on task Turn cell phones to vibrate/step outside to take calls Take care of personal needs What is a District Essential Curriculum Map? A district planning tool used to map out standards-based instruction An alignment of instruction and assessments to state standards A communication vehicle for teachers, students, and parents to promote understanding of standards-based instruction What is a District Essential Curriculum Map? A tool that addresses Performance Standards, Essential Questions/Big Ideas, Content, Skills, and Assessments An organizer which supports professional vertical and horizontal articulation A blueprint to be used as a guide to support schools’ development of differentiated course/content planning What is the purpose of the District Essential Curriculum Maps? “DECMs” 1. 2. 3. To align with Public Education Department High School Redesign (SB561) To align with APS Redesign K-12 initiatives To align APS assessments and instruction to NM Standards DECM Goals 1. 2. 3. Every APS course/content area (K-12) will have a curriculum map Every curriculum map will be articulated horizontally and vertically Educators will have online access to District Essential Curriculum Maps through the Albuquerque Instructional Management System (AIMS) What are the key components of a Curriculum Map? Curriculum Map Template Curriculum Map Components Performance Standards Essential Questions/Big Ideas Content → with related academic vocabulary Skills → with related learning activities Assessment → Formative and Summative → Rubrics (links) Resources Performance Standards A performance standard identifies what students need to know and be able to do at a specific grade level. Linking Performance Standards to Assessments Performance Standards are aligned to district benchmark assessments High School Short Cycle Assessment is aligned to the scope and sequence of the Algebra I curricular framework The High School Short Cycle Assessment is given for: Algebra I, Geometry, & Algebra II grades 8-12 Fall, Winter, Spring administration Essential Questions Lead students to Big Ideas based upon the Performance Standards Encourage higher-level thinking Ask “Why” and “How” rather than “What” Organize key concepts Written in student-friendly language EXAMPLES In what ways can the graph of a quadratic equation help us answer questions about the height of an object? Why look for patterns? How can data be represented, organized, or interpreted? Essential Questions The “mental Velcro” that help ideas stick in students’ minds for a long time to come! Big Ideas Are student answers to Essential Questions Central themes Teachers use in planning to develop Essential Questions EXAMPLES 1. Foundations 2.Rule of Four 3.Equivalent equations/expressions 4.Linear Functions 5.Quadratic Equations 6.Data Analysis Content What students need to know Discipline- or field-based Interdisciplinary Student-centered Written in Noun form Vocabulary (academic language); words students need to know to understand concepts EXAMPLES exponents linear equations polynomials Tools and Resources Frayer Model Teaching and Learning with Text Marzano’s Building Academic Vocabulary Skills What students need to be able to do Written in Verb form Specific, not broad-based Measurable Used to develop guided learning activities Based on standards EXAMPLES Solving a story problem Analyzing graphs Applying order of operations Assessment Products or performances that demonstrate student learning Formative assessments • Guides instruction • Informs the need for differentiation EXAMPLES Student demonstration Group research project (checks along the way) Pretest KWL Quiz A2L Checking for Understanding Exit Slips Assessment Products or performances that demonstrate student learning Summative assessments • Evidence of mastery of standards at specific points-in-time • Graded assessment at the end of the unit of study Examples: Unit Tests Projects Presentations Resources to include on a map - Adopted instructional materials (math, reading, writing programs, etc.) - Technology - Supplemental materials - Links to curriculum frameworks and other websites What Does a CM Look Like? . It is a graphic organizer and planner. Standards-based units are listed. It shows a timeline of what is taught, when! The “how” is based on student data. A DECM includes Performance Standards, Essential Questions/Big Ideas, Content, Skills, Assessments, and Resources. Curriculum Map Template Next Steps to Mapping Discuss Curriculum Map template and connections to district short-cycle assessment Determine placement of assessment standards to specific months Identify and place remaining performance standards onto map Review the resources - High School Short-cycle Assessment (HSSCA) - Examine Algebra I Curricular Framework Begin mapping 8 ESSENTIAL COMPONENTS August September 1. Performance Standards 2. Essential Questions Questions that lead students to Big Ideas. 3. Big Ideas Student answers to EQs that lead them to the Big Ideas 4. Cognitive Level Webb’s/Bloom’s Taxonomy Link 5. Content What students need to know (nouns) Vocabulary List Words students need to know to understand concept 6. Skills What students need to be able to do (verbs) Learning Activities / Lesson Plan Links Essential Experiences or Guided Practice 7. Assessments: Formative Assessments How will students and teacher know what students have learned so far? Differentiated Rubric Links / Attached Summative Assessments How will students show that they have mastered the standard? Differentiated Rubric Links / Attached 8. Resources Links, Curriculum Frameworks, Other Websites A2L/HSSCA: Strand II A: 3(1), 6(1), 7(*), 8(2), 10(5), 12(3) Strand IIB: 18(1), 19(2), 20(1), 21(2) Strand IIC: 24(1), 25(*) Strand IVB: 5(1) October November December Outcomes for Today’s Work: Step 1: Review Assessments (HSSCA) & place performance standards linked to assessments on curriculum map Step 2: Place remaining performance standards on map for both semesters Step 3: Identify Assessments for each standard Step 4: Identify Content & Skills for each standard Assessments Review HSSCA on curriculum maps Look at curriculum frameworks, lesson plans, resources Plot standards on curriculum map…. Performance Standards As a whole group… Place identified HSSCA performance standards in order by month of when taught on curriculum map Place remaining performance standards on curriculum map for both semesters Content, Skills, Assessments In small groups… Complete the curriculum map for both semesters with examples of: content, skills, in-class assessments Articulation Each group share out today’s work Look for repetitions, omissions, gaps Next Steps Quickly identify next steps for February 21st Algebra I Curriculum Mapping Group Big Ideas/Essential Questions Academic Vocabulary Resources Complete Maps Look for Repetitions, Gaps, Omissions What materials do you want to bring for next time? Plus/Delta Please complete a plus/delta before you leave. Thank you!